* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EVOLUTION-CHAPTER 1-3
Survey
Document related concepts
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
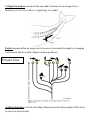
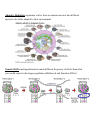
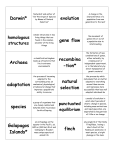
Name:______________________________________________ EVOLUTION VOCABULARY Homologous Structures- similar structures due to common ancestor. May have different function. Analogous Structures- structures that have a similar function but very different structures. ( wing of a bird and wind of a butterfly) Fossils- remains of an organism found in rock, ice or amber (tree sap) Relative Dating- younger fossils are closer to the surface and older fossils are found deeper. Absolute Dating-using Carbon 14 which gives an actual age in millions of years Vestigial Structures-structures that once had a function, but no longer have a function (eyes of a cave fish or vestigial legs of a snake) Extinct-organism that no longer exists because it was unable to adapt to a changing environment (Dodo-couldn’t adapt to human predators) Present Time Artificial Selection (selective breeding)-Humans decided what animals will be bred to select for desired traits. Natural Selection-Survival of the fittest. Nature selects out those not adapted so only the well adapted individuals survive and reproduce. Competition-More organisms are born than can possibly survive. Only those best adapted to the environment survive and reproduce. Organisms may compete for limited food, water, nesting sites and mates. Predators- Heterotrophs that feed on prey (other animals) Parasites-Feed on the host but usually do not kill it (tape worms) Genetic Variation-mutations result in some organisms in a population having genetic differences Antibiotic-medicine designed to kill specific types of bacteria Speciation-over time, mutations and changes in a population result in a new species. Morphology-branch of biology that studies physical structure of organisms Geographic Isolation populations of the same species are separated ( water, mountains, desert) and can’t breed together. Over time they may evolve into different species. Divergent Evolution-populations of organisms become more different do to different environments (see adaptive radiation below) Convergent Evolution-organism that have different ancestors may become more similar due to living in similar environments ( shape of fish, whale and penguin) Coevolution-Two species evolve together because they depend on one another (bee and flower, goldenrod and gallfly) Adaptive Radiation-organisms evolve from a common ancestor into different species to be better adapted to their environment. Genetic Drift-small population has much different frequency of alleles than what you would expect in the larger population (Bottleneck and Founders Effect)