* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide for the LS
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
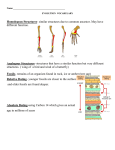
Name:_____________________________________________Test Date:___________ Study Guide Evolution Scientists estimate that the Earth is 4.6 billion years old. This gives time for evolution to occur, organisms to adapt, and species to become extinct. Fossils: The solid remains or imprints of once-living organisms. Fossils are commonly found in sedimentary rock. Fossils provide a historical sequence of life known as the fossil record. Fossils found deeper in the Earth’s crust are usually older than those found in the upper crust. Species: A group of organisms that can mate with one another to produce fertile offspring. o Example: A strawberry dart-poison frog would mate with a member of the same species – another strawberry dart-poison frog. Speciation: The evolutionary process by which two populations of the same species become so different that they can no longer interbreed. The three steps of speciation are separation, adaptation, and division. Selective Breeding: Humans select desired traits in animals to be passed from 1 generation to another. Dogs have been selectively bred to produce more than 150 different breeds. Adaptations: A characteristic that helps an organism survive in its environment & reproduce. Adaptations can include structures and behaviors for finding food, for protection, and for moving from place to place. Examples: o The smoky jungle frog’s color allows it to blend into the forest floor (camouflage) o Humans now have the opposable thumb to grasp things. Many insects can adapt very quickly to pesticides because their generation time is short. o They develop a genetic resistance to the pesticide. o Resistance means that it does not affect or hurt them. This makes some insect populations (and diseases) more difficult to control. Organisms may become extinct if their environment changes and they cannot adapt quickly enough to survive. Theory of Evolution: A theory is an explanation supported by evidence from multiple experiments. A process by which populations change over time due to mutations in DNA. Because of evolution, scientists think that all living things, from daisies to crocodiles to humans, share a common ancestor. Evidence that supports the theory of Evolution: Similar DNA structures of organisms Similar bone structures of organisms o Example: a human arm, cat front leg, dolphin front flipper Similar embryonic structures fossil record vestigial structures Vestigial Structures: Remnants of once-useful structures. Example: whales have remnants of hind-limb bones inside their bodies. NATURAL SELECTION Charles Darwin - made observations that became the foundation for his theory of evolution by natural selection. o The variations that Darwin observed among the individuals of a population of finches were caused by mutations. o The bird’s beak was the most modified. Now the finches cannot interbreed because they have evolved into different species. Natural selection is the process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at higher rates than organisms without the trait. o Natural selection happens continuously throughout time The steps in natural selection are: 1. Overproduction 2. Genetic variation 3. Struggle to survive 4. Successful reproduction The peppered moth population changed drastically due to natural selection. The white moths had an advantage for survival on the white trees until the factories made the trees dark. The dark trees gave the dark moths an advantage for survival.