* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Fossil Record
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
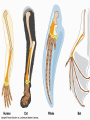
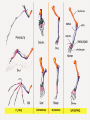
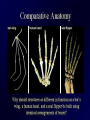
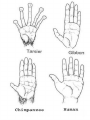
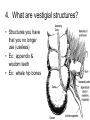
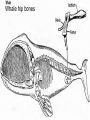
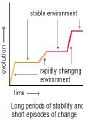
Evidence of Evolution 234-240 1. What evidence supports evolution? Page 234 1. 2. 3. 4. Similar body structures Patterns of early development Similarities in DNA Fossils 2. What is comparative anatomy? • The comparison of structures of different organisms • The more similar the anatomy, the more closely related the organisms are. 3. What are homologous structures? • Similar structures that related species have inherited from a common ancestor 4. What are vestigial structures? • Structures you have that you no longer use (useless) • Ex: appendix & wisdom teeth • Ex: whale hip bones Whale hip bones 5. What is comparative development? • Comparing how different species develop before birth. • The more similar the development; the more closely related the organisms are 6. What is comparative DNA? • Comparing genes of different species to determine how closely related they are. • The more similar the DNA sequences; the more closely related the organisms are 7. What is a fossil? • The remains or imprints of once-living organisms found in layers of rock. • They provide clues to Earth’s past 8. What do we learn from fossils? • The fossil record provides evidence about the history of life and past environments on Earth. • Use fossils to study the rate at which evolution has occurred. 9. What is gradualism? • Idea that evolution occurs slowly but steadily 10. What is punctuated equilibria? • Idea that evolution occurs quickly and is followed by long periods of little to no change. • Explains gaps in fossil record.