* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology in the United States wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Phanerozoic wikipedia , lookup
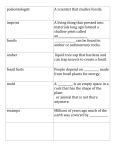
Goal 5: Evolution of Organisms and Landforms 1. Determine which time block is being described. Place a mark or symbol in the correct box. Description largest group Eon Era Period Epoch boundaries marked by mass extinctions blocks of time when a unique rock series was laid down division of the most recent periods includes the Cambrian boundary billions of years long hundreds of millions of years long tens of millions of years long several million years long 2. Determine which time blocks the following events occurred. Write the name of the specific time block in the appropriate blank. All blanks will not be filled because some events are not broken down into the same time detail. . Description Humans Eon Era Period Epoch Rise of mammals Flowering plants Birds First dinosaurs/ mammals First reptiles First amphibians First insects First fish Explosion of life forms Multi-celled organisms Single celled organisms 3. Fossils form in different ways. Identify the type of fossil being described in the list below. Place the name of the fossil type in the blank provided next to the description. ☺ Acids eat away the skeleton or shell and leave an impression in the rock → ______________________ ☺ This is formed when a mold fills with minerals → ______________________________ ☺ Minerals in plant cells crystallize; minerals enter openings or cavities in shell or bones → ____________________________ ☺ Aragonite mineral in shells turns into calcite → _____________________________ ☺ Oils leave the plant, and the remaining matter becomes a layer of carbon; in other cases, nitrogen, hydrogen, and oxygen are distilled from the plant → ____________________________ ☺ Object buried in mud has its molecules replaced by minerals → _____________________________ ☺ Whole organisms locked in tar pits, asphalt, amber, etc. → ______________________________ ☺ Mummification, frozen in ice → _____________________________ 4. Most fossils form in ________________________ rock. The ________________________ of fossils within this type of rock layers help scientists construct the geologic time scale. 5. Sequence the following events in the fossilization process: _______ Over time, the surrounding material builds up and turns to rock. _______ The rock above eventually erodes and the fossil is exposed. _______ The remains are rapidly buried by sediment in streams. _______ An animal dies and begins to decompose. 6. In the undisturbed rock strata illustrated below, indicate in which layer you will find the oldest and the youngest fossils. Write the terms “oldest” and “youngest” in the appropriate strata. ______________________________________________________ A B C D The most primitive fossils normally would be found in layer __________. 7. According to the geologic time scale, sequence the following in order of evolution. Make #1 the most primitive life form. _______ birds _______ early mammals _______ reptiles _______ amphibians _______ insects _______ single-celled life forms _______ fish _______ flowering plants _______ dinosaurs _______ (more) modern humans _______ humans _______ early multi-celled life forms 8. Which is more precise, absolute or relative dating? WHY? 9. How is radioactive dating used to tell the age of rocks and fossils? 10. In reference to item #6 above, what scientific law is begin applied to determine the answer to the question? 11. What are three possible exceptions to the Law of Superposition? Draw each of them and indicate in each drawing the youngest and oldest layers. 12. Why are fossils important tools for understanding the history of life on Earth? 13. When is an organism considered extinct? 15. What are index fossils and how are they used to determine the age of related strata? 17. If you found fossils of seashells in a rock layer near the top of a mountain, what would the fossils tell you about the history of that area? 18. When sudden, abrupt changes (or gradual changes, for that matter) occur within an organism’s habitat, one of three things must happen (the organism’s species must do one of three things). What? 19. What are two ways the extinction of an animal can affect the ecosystem in which it lives? 20. Scientists estimate that of all the species ever to exist on earth, ________ % have become extinct. 21. The average species survives _______ to ______ million years. 22. List at least 8 events that can bring about the extinction of a species. 23. Answer the following questions about mass extinctions: what is a mass extinction? are they a common occurrence in Earth’s past? how many species can face extinction? where do scientists obtain evidence for them? what is a benefit? what is the most famous example? what is believed to have caused this particular example? 24. Is the rate of extinction of species on the Earth increasing or decreasing? List some possible reasons for this. 25. ________________________________ is a process of change over time. 26. The most accepted basic theory of evolution was first proposed in writing by ________________________________________ in the 19th century. He proposed what is called the __________________________________________________________________________________. 27. Darwin based some of his theories on differences in the _______________________________ he observed while in the _____________________________________________________. 28. Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection includes four main concepts: ____________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 29. Continental drift and the evolution of landforms is partially explained by the __________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________. 30. In your own words, write a short paragraph that outlines the basic ideas behind the Theory of Plate Tectonics. (continue over to the top of the next page for more writing space) 31. Fill in the following table with information about crustal plate movement on the surface of the Earth. Boundary What Happens? Diagram Convergent Divergent Transform 33. According to Alfred Wegener’s concept of Continental Drift, pieces of Earth’s crust once were in the form of a large super-continent called ______________________________________. 34. Fill in the following table with information about crustal plate movement on the surface of the Earth. Collision/Plates Involved Oceanic/Oceanic (subduction) Oceanic/Continental (subduction) Continental/Continental 36. What is a fault? Geologic Features 37. The energy produced by earthquakes moves through the Earth in the form of ___________________ ___________________________________. 38. Compare and contrast lava and magma. 39. In the table below, indicate which type of plate movement produces earthquakes and/or volcanoes. Indicate with yes or no. Boundary Convergent Divergent Transform Intraplate Earthquake Volcano 41. What is a hot spot? Give an example. 42. Provide the following information about weathering: what is it? what are two types? ___________________________________ weathering breaks rocks apart without changing the chemical composition. ___________________________________ weathering changes the chemical composition of rocks. 43. How does water cause both chemical and mechanical weathering 59. What is topography? 64. What is ground truthing?