A Trip Through Geologic Time
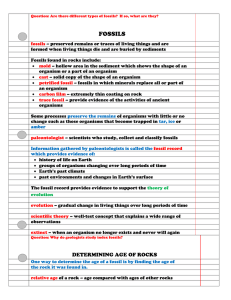
... – footprints, tracks, trails, and burrows • coprolites – tell about what an organism ate • unchanged fossils – amber, tar pits ...
... – footprints, tracks, trails, and burrows • coprolites – tell about what an organism ate • unchanged fossils – amber, tar pits ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution (Chapter 15) Evolution → change over
... " Organisms have more offspring than can survive " The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in it’s environment is called fitness • Adaptations are inherited characteristics that increase an organism’s fitness o Natural selection ! organisms that are best suited for survival in an environ ...
... " Organisms have more offspring than can survive " The ability of an organism to survive and reproduce in it’s environment is called fitness • Adaptations are inherited characteristics that increase an organism’s fitness o Natural selection ! organisms that are best suited for survival in an environ ...
Science Understandings - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over many generations as a result of heredity and environment Species ac ...
... apparent when analyzing the internal structures of organisms Although species my look very different, the similarities become apparent when analyzing their common ancestry (fossil record) Diversity of species develops gradually over many generations as a result of heredity and environment Species ac ...
Review for Evolution Test
... Provide answers to the following questions: 1. Whose work influenced Darwin’s thinking? What beliefs were held by most people at Darwin’s time? How did his journey help to change his thinking? 2. How does descent with modification explain the diversity of life? 3. What is the difference between micr ...
... Provide answers to the following questions: 1. Whose work influenced Darwin’s thinking? What beliefs were held by most people at Darwin’s time? How did his journey help to change his thinking? 2. How does descent with modification explain the diversity of life? 3. What is the difference between micr ...
Evolution starts with
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
Evolution Starts with - Parkway C-2
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
1 Name Date ______ Period ______ EVOLUTION STARTS WITH?
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
... claws, or speed, is called an _A_ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __. 13. The process whereby individuals that are better suited to their environment survive and reproduce more successfully is called N __ __ __ __ __ __ S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ , which Darwin nicknamed S __ __ __ __ __ __ __ O __ T __ __ F ...
PPT NOTES_AP Biology Chapter 25 Notes
... “_____________” – a filed of study in which evolutionary biology and developmental biology converge ...
... “_____________” – a filed of study in which evolutionary biology and developmental biology converge ...
Study Guide Pg 2 Matching
... P. A small number of plant and animal species had come to the Galapagos Islands from South America ...
... P. A small number of plant and animal species had come to the Galapagos Islands from South America ...
Evolution
... in pairs. Humans have 23 pairs. Genes located on paired chromosomes and coded for different versions of the same trait are called alleles. ...
... in pairs. Humans have 23 pairs. Genes located on paired chromosomes and coded for different versions of the same trait are called alleles. ...
fossils - Mizellis
... 1. What are fossils? Fossils are evidence of past life; they are preserved remains and traces of animals and plants. 2. Where are they found? Fossils are usually found in sedimentary rocks. 3. How do fossils form? The living thing must usually Be buried quickly (stops rapid decay) Have hard part ...
... 1. What are fossils? Fossils are evidence of past life; they are preserved remains and traces of animals and plants. 2. Where are they found? Fossils are usually found in sedimentary rocks. 3. How do fossils form? The living thing must usually Be buried quickly (stops rapid decay) Have hard part ...
Fossils
... Fossil fuels are a nonrenewable source because the organisms that create the fuels can take millions of years to form. ...
... Fossil fuels are a nonrenewable source because the organisms that create the fuels can take millions of years to form. ...
document
... Earth’s past climate past environments and changes in Earth’s surface The fossil record provides evidence to support the theory of evolution evolution – gradual change in living things over long periods of time scientific theory – well-test concept that explains a wide range of observations exti ...
... Earth’s past climate past environments and changes in Earth’s surface The fossil record provides evidence to support the theory of evolution evolution – gradual change in living things over long periods of time scientific theory – well-test concept that explains a wide range of observations exti ...
Article of the Week on Geologic Time Scale
... sedimentary rock not only provide evidence of the history of Earth itself, but also of changes in organisms whose fossil remains have been found in these layers. The collection of fossils and their placement in chronological order (e.g., through the location of the sedimentary layers in which they a ...
... sedimentary rock not only provide evidence of the history of Earth itself, but also of changes in organisms whose fossil remains have been found in these layers. The collection of fossils and their placement in chronological order (e.g., through the location of the sedimentary layers in which they a ...
Evidence for Evolution
... resemble bacterial structure genetic mitochondria & chloroplasts have their own circular DNA, like bacteria functional mitochondria & chloroplasts move freely within the cell mitochondria & chloroplasts reproduce independently from the cell ...
... resemble bacterial structure genetic mitochondria & chloroplasts have their own circular DNA, like bacteria functional mitochondria & chloroplasts move freely within the cell mitochondria & chloroplasts reproduce independently from the cell ...
Unit Test Earth Patterns, Cycles, and Changes Name
... 11. A strip of land is cleared of trees and bushes to make space for a power line. What impact might this have on birds living in the area? A. The natural enemies of birds will be ...
... 11. A strip of land is cleared of trees and bushes to make space for a power line. What impact might this have on birds living in the area? A. The natural enemies of birds will be ...
Exam_Review_3 - Bonar Law Memorial
... - Convergent evolution: unrelated species evolve similar characteristics because of the similar environments they live in. - Coevolution: specialist organisms evolve as a response to each other’s change. - Punctuated equilibrium: species evolved quickly, after long period of equilibrium - Developmen ...
... - Convergent evolution: unrelated species evolve similar characteristics because of the similar environments they live in. - Coevolution: specialist organisms evolve as a response to each other’s change. - Punctuated equilibrium: species evolved quickly, after long period of equilibrium - Developmen ...
Next .54 billion years
... ___________________________ theory = photosynthesizing prokaryotes were absorbed by other bacteria to become the first organelles - ______________________ ...
... ___________________________ theory = photosynthesizing prokaryotes were absorbed by other bacteria to become the first organelles - ______________________ ...
Evolution Review Key
... and mountains this is known as geographic isolation. 37. When two or more species reproduce at different times this is known as temporal isolation. 38. What is the difference between convergent evolution and coevolution? Convergent: unrelated organisms come to resemble each other. Coevolution: organ ...
... and mountains this is known as geographic isolation. 37. When two or more species reproduce at different times this is known as temporal isolation. 38. What is the difference between convergent evolution and coevolution? Convergent: unrelated organisms come to resemble each other. Coevolution: organ ...
Evolution
... Darwin lastly hypothesized that over long periods of time, natural selection produced organisms that have different structures resulting in today’s species looking different than their ancestors from generations past. He called this theory: – Descent with Modification: Each living species has descen ...
... Darwin lastly hypothesized that over long periods of time, natural selection produced organisms that have different structures resulting in today’s species looking different than their ancestors from generations past. He called this theory: – Descent with Modification: Each living species has descen ...
An unusual type of fossil clam is found in rock layers high in the
... the Rocky Mountains and the Swiss Alps are both volcanic in origin clams once lived in mountains, but have since evolved into sea-dwelling creatures the layers of rocks in which the fossils were found are from the same geologic age ...
... the Rocky Mountains and the Swiss Alps are both volcanic in origin clams once lived in mountains, but have since evolved into sea-dwelling creatures the layers of rocks in which the fossils were found are from the same geologic age ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.