How the Earth was Made
... 14. Plate tectonics helps to explain how continents can move. What is believed to be the primary cause of the crustal movement? ...
... 14. Plate tectonics helps to explain how continents can move. What is believed to be the primary cause of the crustal movement? ...
Evolution
... 4. Natural Selection: adapt or possibly become extinct What are Adaptations? Evolutionary process by which an animal becomes better suited for its environment. Structural: body structures that allow an animal to find and consume food, defend itself, and to reproduce its species. Behavioral: see p. 4 ...
... 4. Natural Selection: adapt or possibly become extinct What are Adaptations? Evolutionary process by which an animal becomes better suited for its environment. Structural: body structures that allow an animal to find and consume food, defend itself, and to reproduce its species. Behavioral: see p. 4 ...
Midterm Study Guide - Historical Geology
... Bias and incompleteness of the fossil record Requirements for fossilization: hard parts and quick burial Mode of fossilization: unaltered, permineralization, replacement, recrystallization, cast/mold, trace, carbonization Use of Index Fossils and fossil assemblages in age dating and correlation Use ...
... Bias and incompleteness of the fossil record Requirements for fossilization: hard parts and quick burial Mode of fossilization: unaltered, permineralization, replacement, recrystallization, cast/mold, trace, carbonization Use of Index Fossils and fossil assemblages in age dating and correlation Use ...
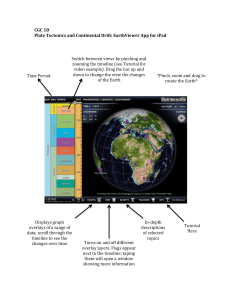
EarthViewer Questions
... a. In which period did these first land plants form? _____________________________ 11. How long ago were the first land vertebrates formed? _______________________________ 12. When did Homo Sapiens first appear? (in T ...
... a. In which period did these first land plants form? _____________________________ 11. How long ago were the first land vertebrates formed? _______________________________ 12. When did Homo Sapiens first appear? (in T ...
Questions for 3 Evolution Readings
... c. a very old organism d. trace remains of an organism that lived long ago _____ 5. The fossil record provides evidence about a. the age of rocks. b. the order in which species have existed. c. the number of layers the Earth has. d. the composition of minerals. _____ 6. All living things inherit sim ...
... c. a very old organism d. trace remains of an organism that lived long ago _____ 5. The fossil record provides evidence about a. the age of rocks. b. the order in which species have existed. c. the number of layers the Earth has. d. the composition of minerals. _____ 6. All living things inherit sim ...
Biology B CECA
... 61. Fossil evidence suggests Homo sapiens first appeared about 200,000 years ago. 62. The remnant of an organ that had a function in an early ancestor is known as a vestigial structure. 63. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of different populations can no longer mate successfully. 64. The s ...
... 61. Fossil evidence suggests Homo sapiens first appeared about 200,000 years ago. 62. The remnant of an organ that had a function in an early ancestor is known as a vestigial structure. 63. Reproductive isolation occurs when members of different populations can no longer mate successfully. 64. The s ...
vocabularyPART1
... EVOLUTION is change over time. EVOLUTIONARY THEORY is an explanation of phenomena supported by a collection of scientific facts, observation and hypothesis. FOSSILS are preserved remains of ancient organisms found in sedimentary rock (soil type). ...
... EVOLUTION is change over time. EVOLUTIONARY THEORY is an explanation of phenomena supported by a collection of scientific facts, observation and hypothesis. FOSSILS are preserved remains of ancient organisms found in sedimentary rock (soil type). ...
Ch 22 Notes
... disease, famine, homelessness and war… were a result of not enough resources. Hutton (1726-97) & Lyell (1795-1875): Geologists. Hutton was saying that things have changed slowly over time – gradualism. Geologic Time. Lyell observed, Uniformitarianism – idea that geologic processes are still goin ...
... disease, famine, homelessness and war… were a result of not enough resources. Hutton (1726-97) & Lyell (1795-1875): Geologists. Hutton was saying that things have changed slowly over time – gradualism. Geologic Time. Lyell observed, Uniformitarianism – idea that geologic processes are still goin ...
Theory of Evolution
... • ANATOMY (Body Structure) – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES • SIMILARITIES IN DNA ...
... • ANATOMY (Body Structure) – HOMOLOGOUS STRUCTURES • SIMILARITIES IN DNA ...
Unit 7 Study Guide
... disturbed causing them to be tilted, folded, eroded to form uncomformities, broken to form faults, and intrusions where magma pushes upwards and cuts through layers of rock. Evidence of these changes are provided when Fossils are found in areas they can no longer live. The composition or texture o ...
... disturbed causing them to be tilted, folded, eroded to form uncomformities, broken to form faults, and intrusions where magma pushes upwards and cuts through layers of rock. Evidence of these changes are provided when Fossils are found in areas they can no longer live. The composition or texture o ...
Chapter 25 The History of Life on Earth 25.3 Key Events in Life`s
... occurred from 750 to 580 million years ago. Glaciers covered all of the planet’s landmasses, & the seas were largely iced over. o The snowball earth hypothesis suggests that most life would have been confined to the first major diversification of multicellular eukaryotes corresponds to when Earth th ...
... occurred from 750 to 580 million years ago. Glaciers covered all of the planet’s landmasses, & the seas were largely iced over. o The snowball earth hypothesis suggests that most life would have been confined to the first major diversification of multicellular eukaryotes corresponds to when Earth th ...
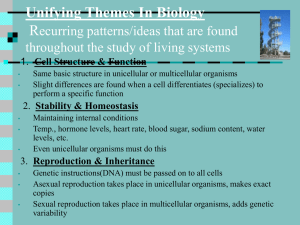
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
Evolution Round Robin Partner Questions
... How Does Evolution Really Work? 1. What are the four components of natural selection? 2. What determines an individual hummingbird’s beak length? 3. What factors in the environment might select for beak length and shape in hummingbird populations? 4. How can hummingbird DNA help scientists determine ...
... How Does Evolution Really Work? 1. What are the four components of natural selection? 2. What determines an individual hummingbird’s beak length? 3. What factors in the environment might select for beak length and shape in hummingbird populations? 4. How can hummingbird DNA help scientists determine ...
Evidence of Evolution
... 5. In science, an important part of a theory is that it is falsifiable. What observations could refute the hypothesis that an adaptation evolved by natural selection? What observations could refute the theory of evolution? 6. A scientific theory stands or falls according to how well it is supported ...
... 5. In science, an important part of a theory is that it is falsifiable. What observations could refute the hypothesis that an adaptation evolved by natural selection? What observations could refute the theory of evolution? 6. A scientific theory stands or falls according to how well it is supported ...
16.2 Applying Darwin`s Ideas
... 1. Traces of organisms that lived in the past C. Darwin predicted intermediate forms between groups of species D. Conditions that create fossils are so rare the fossil record will never be complete E. Biogeography 1. The study of the locations of organisms around the world ...
... 1. Traces of organisms that lived in the past C. Darwin predicted intermediate forms between groups of species D. Conditions that create fossils are so rare the fossil record will never be complete E. Biogeography 1. The study of the locations of organisms around the world ...
File - Mrs. LeCompte
... changes in the Earth’s crust are the result of catastrophic events rather than from gradual processes of change ...
... changes in the Earth’s crust are the result of catastrophic events rather than from gradual processes of change ...
EXAM ESSAYS 5/11/07
... evolution? Name three features that place whales with mammals and not with fish. Provide five pieces of evidence that demonstrate that whales descended from land dwelling animals. ...
... evolution? Name three features that place whales with mammals and not with fish. Provide five pieces of evidence that demonstrate that whales descended from land dwelling animals. ...
Evolution: 10.2: Darwin`s voyage provided insights into evolution. 1
... 3. The theory of endosymbiosis describes the probable evolution of what type of cell? 4. Mitochondria and chloroplasts both have their own DNA and ribosomes. How does this information support the theory of endosymbiosis? ...
... 3. The theory of endosymbiosis describes the probable evolution of what type of cell? 4. Mitochondria and chloroplasts both have their own DNA and ribosomes. How does this information support the theory of endosymbiosis? ...
File
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
... 2) ____________ mountains: When plates collide, rocks can fold if they are hot enough to act like bendable plastic. 3) ______________________ mountains: Sometimes the rocks in Earth’s crust are too brittle to fold, and they instead break, forming a fault. Fault blocks can tilt or slide down. 4) Moun ...
History of Life on Earth Practice Questions
... _____ 7. What term describes how continents have moved across Earth’s surface? (p. ______ ) a. plate tectonics b. continental drift c. continental theory d. tectonic drift _____ 8. Why is the fossil record not complete? (p. ______ ) a. There are too many fossils. c. Fossils have stopped forming. b. ...
... _____ 7. What term describes how continents have moved across Earth’s surface? (p. ______ ) a. plate tectonics b. continental drift c. continental theory d. tectonic drift _____ 8. Why is the fossil record not complete? (p. ______ ) a. There are too many fossils. c. Fossils have stopped forming. b. ...
File
... Living things evolved in early oceans – about 3 billion yrs ago First life – single celled organisms- microscopic After 100’s of millions of yrs larger, complex organisms evolved (worms, jellyfish) – soft body parts Animals with hard parts (shells, bones) appeared much later Next major group of anim ...
... Living things evolved in early oceans – about 3 billion yrs ago First life – single celled organisms- microscopic After 100’s of millions of yrs larger, complex organisms evolved (worms, jellyfish) – soft body parts Animals with hard parts (shells, bones) appeared much later Next major group of anim ...
Darwin and Natural Selection
... Darwin. These animals were distinctly their own species but were similar to species found elsewhere, which led Darwin to believe that organisms could change over time. He spent the next 22 years studying how animals could change over time. Darwin used an idea proposed by Thomas Malthus about hum ...
... Darwin. These animals were distinctly their own species but were similar to species found elsewhere, which led Darwin to believe that organisms could change over time. He spent the next 22 years studying how animals could change over time. Darwin used an idea proposed by Thomas Malthus about hum ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.