Vocabulary Chapter 14
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
... Plants, animals and bacteria can form fossils, but only organisms that are buried rapidly in sediment are readily preserved. Most organisms decompose before they have a chance to become fossilized. ...
homologous structures
... How can comparative anatomy and physiology can be used to show relatedness, and therefore be used as evidence of evolution? ...
... How can comparative anatomy and physiology can be used to show relatedness, and therefore be used as evidence of evolution? ...
Name: Date: Chapter 5 Vocabulary — The Evolution of Living
... 13. Essay on the Principle of Population stated- Humans have the potential to reproduce rapidly and food supplies coult not support unlimited population growth. However, human populations are limited by choices that humans make or by problems such as starvation and disease. Darwin learned that any s ...
... 13. Essay on the Principle of Population stated- Humans have the potential to reproduce rapidly and food supplies coult not support unlimited population growth. However, human populations are limited by choices that humans make or by problems such as starvation and disease. Darwin learned that any s ...
Natural Selection and the Evidence of Evolution
... • As record becomes more complete, the sequence of evolution is clearer ...
... • As record becomes more complete, the sequence of evolution is clearer ...
review_answers_ch._7__8
... equilibrium. The loss of life that stems from evolution is not a form of evolution, but it allows others patterns to emerge instead. 7. Homologous body structures are used as evidence to support evolution and to prove that organisms are descendant from common ancestors. Convergent evolution is not t ...
... equilibrium. The loss of life that stems from evolution is not a form of evolution, but it allows others patterns to emerge instead. 7. Homologous body structures are used as evidence to support evolution and to prove that organisms are descendant from common ancestors. Convergent evolution is not t ...
chapters_7__8_review_answers_0
... equilibrium. The loss of life that stems from evolution is not a form of evolution, but it allows others patterns to emerge instead. 7. Homologous body structures are used as evidence to support evolution and to prove that organisms are descendant from common ancestors. Convergent evolution is not t ...
... equilibrium. The loss of life that stems from evolution is not a form of evolution, but it allows others patterns to emerge instead. 7. Homologous body structures are used as evidence to support evolution and to prove that organisms are descendant from common ancestors. Convergent evolution is not t ...
Evolution chapters 16-17 test review sheet 1. Biologists in Darwin`s
... 4. What did the work of Hutton Lyell suggest about the earth? The earth was millions of years old 5. Describe Lamarck’s evolutionary hypothesis. Body structures can change according to the action of the animal. 6. Describe artificial selection and give example that humans may have used. Choosing ind ...
... 4. What did the work of Hutton Lyell suggest about the earth? The earth was millions of years old 5. Describe Lamarck’s evolutionary hypothesis. Body structures can change according to the action of the animal. 6. Describe artificial selection and give example that humans may have used. Choosing ind ...
Landforms Study Guide
... Landforms Study Guide (SOL 5.7) Test Thursday November 17th Students will need to be able to: apply basic terminology to explain how Earth’s surface is constantly changing. (weathering, erosion, deposition) draw and label the rock cycle and describe the major processes and rock types involved. ...
... Landforms Study Guide (SOL 5.7) Test Thursday November 17th Students will need to be able to: apply basic terminology to explain how Earth’s surface is constantly changing. (weathering, erosion, deposition) draw and label the rock cycle and describe the major processes and rock types involved. ...
Evolution Unit Vocabulary Vocabulary word Definition Mutation A
... The largest population that a given environment can support over a long period of time. ...
... The largest population that a given environment can support over a long period of time. ...
Notes: Evolutionary Theory
... anatomy or structure of organisms used to help determine their ancestry. 1. Homologous structures: Characteristics that are similar because they were inherited from a common ancestor. Examples: Bones in the forelimbs of humans, bat, bird, and whale. 2. Vestigial structures: Inherited but unused ...
... anatomy or structure of organisms used to help determine their ancestry. 1. Homologous structures: Characteristics that are similar because they were inherited from a common ancestor. Examples: Bones in the forelimbs of humans, bat, bird, and whale. 2. Vestigial structures: Inherited but unused ...
Earth`s History in Fossils - PAMS
... History of the Earth: Scientists use various methods to determine the age of rocks and the Earth. Following are the various dating techniques scientists use. 1. Law of Superposition •Fossils are almost always found in sedimentary rock which are made of layers •Law of Superposition states that in a s ...
... History of the Earth: Scientists use various methods to determine the age of rocks and the Earth. Following are the various dating techniques scientists use. 1. Law of Superposition •Fossils are almost always found in sedimentary rock which are made of layers •Law of Superposition states that in a s ...
Evidence of the Past
... Species can produce too many offspring but starvation, disease, war, and predators limit the population size. So there must be something special about the survivors— they must inherit traits that help them survive in their environment. ...
... Species can produce too many offspring but starvation, disease, war, and predators limit the population size. So there must be something special about the survivors— they must inherit traits that help them survive in their environment. ...
Ch.15 Notes - Green Local Schools
... Distribution of Fossils • Law of superposition: lowest layers of rock are oldest • Fossil-bearing strata show when organisms became extinct • Mass extinction: brief period in which large #’s of species disappeared ...
... Distribution of Fossils • Law of superposition: lowest layers of rock are oldest • Fossil-bearing strata show when organisms became extinct • Mass extinction: brief period in which large #’s of species disappeared ...
The History of Life
... Theory of continental drift - the world was made up of a single continent through most of geologic and eventually separated and drifted apart, forming into the seven continents we ...
... Theory of continental drift - the world was made up of a single continent through most of geologic and eventually separated and drifted apart, forming into the seven continents we ...
16.1 Darwin`s Voyage of Discovery - OG
... During Darwin’s time, new field called geology, study of rocks Provided evidence about Earth’s history – Earth probably not just 4,000 years old – much older! Famous geologists – James Hutton and Charles Lyell Wrote that Earth is extremely old and processes that changed Earth in the past are the sam ...
... During Darwin’s time, new field called geology, study of rocks Provided evidence about Earth’s history – Earth probably not just 4,000 years old – much older! Famous geologists – James Hutton and Charles Lyell Wrote that Earth is extremely old and processes that changed Earth in the past are the sam ...
Ecology: Interactions of Life
... 3. They both deal with life and where organisms live. 4. Population is organisms of a certain species and community includes all the organisms. 5. Yes it does because different organisms require different amounts of rain to survive. ...
... 3. They both deal with life and where organisms live. 4. Population is organisms of a certain species and community includes all the organisms. 5. Yes it does because different organisms require different amounts of rain to survive. ...
Unit 8 Test Review
... 7. Describe the 1st cells (autotroph or heterotroph; prokaryote or eukaryote; aerobic or anaerobic)? 8. Describe the early Earth. Why wouldn’t there be liquid oceans at first? What was in the atmosphere? What wasn’t? 9. What is the Endosymbiotic Hypothesis? What does it have to do with chloroplasts ...
... 7. Describe the 1st cells (autotroph or heterotroph; prokaryote or eukaryote; aerobic or anaerobic)? 8. Describe the early Earth. Why wouldn’t there be liquid oceans at first? What was in the atmosphere? What wasn’t? 9. What is the Endosymbiotic Hypothesis? What does it have to do with chloroplasts ...
Discussion Questions: Introduction to Darwin
... Analyze multiple sources of evidence for evolution. Explain how a great diversity of species increase the chance that at least some organisms will survive major changes in the environment Analyze fossil evidence with regard to biological diversity, episodic speciation, and mass extinction. ...
... Analyze multiple sources of evidence for evolution. Explain how a great diversity of species increase the chance that at least some organisms will survive major changes in the environment Analyze fossil evidence with regard to biological diversity, episodic speciation, and mass extinction. ...
Earths History - Mrs. Meadows Science
... missing one area of rock bed. The missing layer is called an unconformity. Makes it more difficult to understand how earth changed at a specific time. ...
... missing one area of rock bed. The missing layer is called an unconformity. Makes it more difficult to understand how earth changed at a specific time. ...
Evolution
... levels of rock older than ones above. (relative age) • Extinction! • Very hard for an organism to become a fossil. (see HHMI evolution, lecture ...
... levels of rock older than ones above. (relative age) • Extinction! • Very hard for an organism to become a fossil. (see HHMI evolution, lecture ...
Table of Contents - Milan Area Schools
... • Periods of geological history are marked by mass extinctions or by dramatic increases in diversity called evolutionary radiations. • Although the fossil record is fragmentary before 550 mya, it is still good enough to show that the total number of species and individuals increased dramatically in ...
... • Periods of geological history are marked by mass extinctions or by dramatic increases in diversity called evolutionary radiations. • Although the fossil record is fragmentary before 550 mya, it is still good enough to show that the total number of species and individuals increased dramatically in ...
Document
... correct answer in the actual column. In your notebook please note the page number where you found your information. You may Use pages in your book, powerpoint lessons, and interactive computer activities to guide you. Statement ...
... correct answer in the actual column. In your notebook please note the page number where you found your information. You may Use pages in your book, powerpoint lessons, and interactive computer activities to guide you. Statement ...
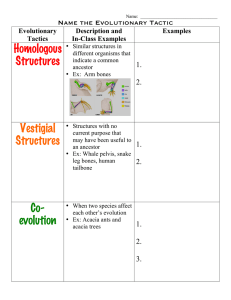
Homologous Structures Vestigial Structures Co
... • Structures with no current purpose that may have been useful to an ancestor • Ex: Whale pelvis, snake leg bones, human tailbone ...
... • Structures with no current purpose that may have been useful to an ancestor • Ex: Whale pelvis, snake leg bones, human tailbone ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.