bio 1_13_15 natural selection
... species geographically and historically, and why (or why not) they are found in a geographical area. • Look at page 383 in your text. • What land is shared by two rodent species? • Why do you think rodent species in the Americas are divided into different ranges? or 832 ...
... species geographically and historically, and why (or why not) they are found in a geographical area. • Look at page 383 in your text. • What land is shared by two rodent species? • Why do you think rodent species in the Americas are divided into different ranges? or 832 ...
Document
... A. Evolution – any change in a population over time. 1. Micro – small changes within a species. 2. Macro – change into a new species. ...
... A. Evolution – any change in a population over time. 1. Micro – small changes within a species. 2. Macro – change into a new species. ...
Evolution - Science with Ms. Peralez
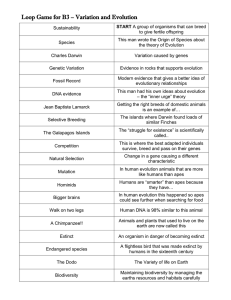
... began in 1831, Charles Darwin made three important observations: The world includes tremendous diversity of living things throughout a wide range of habitats Animal species, like those in the Galapagos Islands, that are related, can have different characteristics or occupy different habitats in ...
... began in 1831, Charles Darwin made three important observations: The world includes tremendous diversity of living things throughout a wide range of habitats Animal species, like those in the Galapagos Islands, that are related, can have different characteristics or occupy different habitats in ...
Bio1100Ch22W
... The Origin of Species challenged a worldview that had been accepted for centuries • The Old Testament account suggests rapid creation, not evolution • The Darwinian view of life has two main features. (1) The diverse forms of life have arisen by descent ...
... The Origin of Species challenged a worldview that had been accepted for centuries • The Old Testament account suggests rapid creation, not evolution • The Darwinian view of life has two main features. (1) The diverse forms of life have arisen by descent ...
Tracing Phylogeny
... – Becomes recognizable stratum in stratigraphic sequence of rocks – Strata of the same age tend to contain the similar fossil assemblages – Helps geologists determine relative dates of embedded fossils despite upheavals ...
... – Becomes recognizable stratum in stratigraphic sequence of rocks – Strata of the same age tend to contain the similar fossil assemblages – Helps geologists determine relative dates of embedded fossils despite upheavals ...
Evolution powerpoint
... For humans, it is not a change we will observe in our lifetime but studies are done on organisms with a short life span and done by farmers in something called selective breeding The mechanism of evolution is called NATURAL SELECTION – Charles Darwin and the Galapagos Islands In nature plants and ma ...
... For humans, it is not a change we will observe in our lifetime but studies are done on organisms with a short life span and done by farmers in something called selective breeding The mechanism of evolution is called NATURAL SELECTION – Charles Darwin and the Galapagos Islands In nature plants and ma ...
A Trip Through Earths History
... Some processes preserve the remains of organisms with little or no change such as those organisms that become trapped in tar, ice or amber ...
... Some processes preserve the remains of organisms with little or no change such as those organisms that become trapped in tar, ice or amber ...
Title: Sum of the Parts
... MS-ESS1-4. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6-billion-year-old history. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how analyses of rock formations and the fossils they contain are used to establish relat ...
... MS-ESS1-4. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6-billion-year-old history. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how analyses of rock formations and the fossils they contain are used to establish relat ...
Evolution Notes - Spring Branch ISD
... Natural Selection: the survival of a species based on its ability to adapt and survive. The struggle to survive in nature. Survival of Competition: the Fittest: The organisms with the greatest “fitness” will survive long enough to reproduce and pass of their traits. Artificial Selection: When the tr ...
... Natural Selection: the survival of a species based on its ability to adapt and survive. The struggle to survive in nature. Survival of Competition: the Fittest: The organisms with the greatest “fitness” will survive long enough to reproduce and pass of their traits. Artificial Selection: When the tr ...
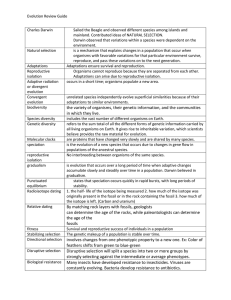
Evolution Review Guide Charles Darwin Sailed the Beagle and
... No interbreeding between organisms of the same species. is evolution that occurs over a long period of time when adaptive changes accumulate slowly and steadily over time in a population. Darwin believed in gradualism. states that speciation occurs quickly in rapid bursts, with long periods of stabi ...
... No interbreeding between organisms of the same species. is evolution that occurs over a long period of time when adaptive changes accumulate slowly and steadily over time in a population. Darwin believed in gradualism. states that speciation occurs quickly in rapid bursts, with long periods of stabi ...
Name
... curves. Scientists determine which reflectance curves show plants, water, soil, and other materials on earth. Together, satellite images and spectral analysis allow scientists to gather information on the Earth from a distance. Ground truthing is when scientists directly observe the areas they are a ...
... curves. Scientists determine which reflectance curves show plants, water, soil, and other materials on earth. Together, satellite images and spectral analysis allow scientists to gather information on the Earth from a distance. Ground truthing is when scientists directly observe the areas they are a ...
Evolution in biology
... organisms that lived on Earth in the past. Fossils show change in species diversity over geologic time. Fossils are dated using carbon radiometric dating up to 50,000-80,000 years. Other isotopes are used for dating older fossils. ...
... organisms that lived on Earth in the past. Fossils show change in species diversity over geologic time. Fossils are dated using carbon radiometric dating up to 50,000-80,000 years. Other isotopes are used for dating older fossils. ...
Slide 1
... Several mass extinctions shown in fossil record Effect is to leave many habitats open for surviving species Often a burst of evolution follows mass extinctions ...
... Several mass extinctions shown in fossil record Effect is to leave many habitats open for surviving species Often a burst of evolution follows mass extinctions ...
Geologic Change Over Time Study Guide 1. Describe what
... a tropical past climate. Other materials, such as tree rings, can tell about past growing conditions. Sea-floor sediments and ice cores can tell us the past chemical compositions of the ocean and atmosphere. Ages of these can be found by radiometric dating techniques. For organic materials, radiocar ...
... a tropical past climate. Other materials, such as tree rings, can tell about past growing conditions. Sea-floor sediments and ice cores can tell us the past chemical compositions of the ocean and atmosphere. Ages of these can be found by radiometric dating techniques. For organic materials, radiocar ...
Evolution of Organisms and Landforms EOG review
... can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of species that have used rocks as habitats. D. They ...
... can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth. B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms. C. They compare the life histories of species that have used rocks as habitats. D. They ...
Evolution
... 6. A trait that makes an individual different from others in its species ______variation__________________. 7. A change in the DNA of an organism _______mutation – can be helpful if makes the living thing better adapted ...
... 6. A trait that makes an individual different from others in its species ______variation__________________. 7. A change in the DNA of an organism _______mutation – can be helpful if makes the living thing better adapted ...
Evolution - Gander biology
... • One of the first scientist to publish his ideas about evolution in The Origin of Species • He developed his theory of evolution from observations he had made during his world ...
... • One of the first scientist to publish his ideas about evolution in The Origin of Species • He developed his theory of evolution from observations he had made during his world ...
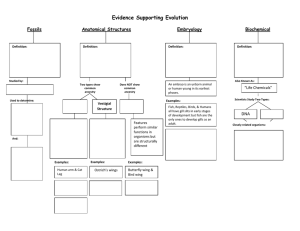
Lesson 1/Explore – Page 193 “Fossil Evidence of
... The fossil record is made up of all the fossils ever discovered on Earth. It contains millions of fossils that represent many thousands of species. Most of the species are no longer alive on Earth. The fossil record provides evidence that species have changed over time. The fossil record is ...
... The fossil record is made up of all the fossils ever discovered on Earth. It contains millions of fossils that represent many thousands of species. Most of the species are no longer alive on Earth. The fossil record provides evidence that species have changed over time. The fossil record is ...
Paleontology

Paleontology or palaeontology (/ˌpeɪlɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpeɪlɪənˈtɒlədʒi/ or /ˌpælɪɒnˈtɒlədʒi/, /ˌpælɪənˈtɒlədʒi/) is the scientific study of life existent prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene Epoch roughly 11,700 years before present. It includes the study of fossils to determine organisms' evolution and interactions with each other and their environments (their paleoecology). Paleontological observations have been documented as far back as the 5th century BC. The science became established in the 18th century as a result of Georges Cuvier's work on comparative anatomy, and developed rapidly in the 19th century. The term itself originates from Greek παλαιός, palaios, i.e. ""old, ancient"", ὄν, on (gen. ontos), i.e. ""being, creature"" and λόγος, logos, i.e. ""speech, thought, study"".Paleontology lies on the border between biology and geology, but differs from archaeology in that it excludes the study of morphologically modern humans. It now uses techniques drawn from a wide range of sciences, including biochemistry, mathematics and engineering. Use of all these techniques has enabled paleontologists to discover much of the evolutionary history of life, almost all the way back to when Earth became capable of supporting life, about 3,800 million years ago. As knowledge has increased, paleontology has developed specialised sub-divisions, some of which focus on different types of fossil organisms while others study ecology and environmental history, such as ancient climates.Body fossils and trace fossils are the principal types of evidence about ancient life, and geochemical evidence has helped to decipher the evolution of life before there were organisms large enough to leave body fossils. Estimating the dates of these remains is essential but difficult: sometimes adjacent rock layers allow radiometric dating, which provides absolute dates that are accurate to within 0.5%, but more often paleontologists have to rely on relative dating by solving the ""jigsaw puzzles"" of biostratigraphy. Classifying ancient organisms is also difficult, as many do not fit well into the Linnean taxonomy that is commonly used for classifying living organisms, and paleontologists more often use cladistics to draw up evolutionary ""family trees"". The final quarter of the 20th century saw the development of molecular phylogenetics, which investigates how closely organisms are related by measuring how similar the DNA is in their genomes. Molecular phylogenetics has also been used to estimate the dates when species diverged, but there is controversy about the reliability of the molecular clock on which such estimates depend.