* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title: Sum of the Parts
Survey
Document related concepts
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Boring Billion wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
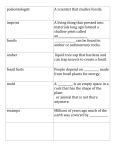
5E Inquiry Lesson Plan Title: FOSSILS ROCK Grade level: 6 National Standards: MS-ESS1-4. Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6-billion-year-old history. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how analyses of rock formations and the fossils they contain are used to establish relative ages of major events in Earth’s history. Examples of Earth’s major events could range from being very recent (such as the last Ice Age or the earliest fossils of homo sapiens) to very old (such as the formation of Earth or the earliest evidence of life). Examples can include the formation of mountain chains and ocean basins, the evolution or extinction of particular living organisms, or significant volcanic eruptions.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include recalling the names of specific periods or epochs and events within them.] MS-ESS2-2. Construct an explanation based on evidence for how geoscience processes have changed Earth’s surface at varying time and spatial scales. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on how processes change Earth’s surface at time and spatial scales that can be large (such as slow plate motions or the uplift of large mountain ranges) or small (such as rapid landslides or microscopic geochemical reactions), and how many geoscience processes (such as earthquakes, volcanoes, and meteor impacts) usually behave gradually but are punctuated by catastrophic events. Examples of geoscience processes include surface weathering and deposition by the movements of water, ice, and wind. Emphasis is on geoscience processes that shape local geographic features, where appropriate.] MS-ESS2-3. Analyze and interpret data on the distribution of fossils and rocks, continental shapes, and seafloor structures to provide evidence of the past plate motions. [Clarification Statement: Examples of data include similarities of rock and fossil types on different continents, the shapes of the continents (including continental shelves), and the locations of ocean structures (such as ridges, fracture zones, and trenches).] [Assessment Boundary: Paleo magnetic anomalies in oceanic and continental crust are not assessed.] ACOS: SC2005 (6) SC20152015 (6) Describe factors that cause changes to Earth's surface over time. Construct explanations from geologic evidence (e.g., change or extinction of particular living organisms; field evidence or representations, including models of geologic cross-sections; sedimentary layering) to identify patterns of Earth's major historical events (e.g., formation of mountain chains and ocean basins, significant volcanic eruptions, fossilization, folding, faulting, igneous intrusion, erosion). SC20152015 (6) Provide evidence from data of the distribution of fossils and rocks, continental shapes, and seafloor structures to explain past plate motions. Objectives: Determine how fossils are formed Identify how fossils are important in scientific research Determine the geographic range of fossils over the earth Identify various fossils and their basic anatomy Explain how fossils can be used to determine changes in the earth’s surface, in the life forms and in the environments through time Interpret fossil evidence to help determine the history of an era Reconstruct a skeleton from a “pile of bones” and identify the mystery animal Make a model of an amber-like fossil Procedures Materials: Activity 1 Fossil Kit GEO 5342 from Carolina Biological Student Background information for Activity 1 (6) fossil replicas: allosaurus claw fragment, ammonite, cave bear tooth, crinoid, saber tooth tiger tooth fragment and trilobite Activity 2 Student Lab Guide Paleontologist Mystery Puzzle Student Worksheet Mystery Animal Skeleton and Bones Mystery Puzzle Follow-up Questions Making a Model of an Amber-like Fossil Clear glue or clear fingernail polish Dead/plastic bug Waxed paper Engage FOSSIL ROCK ANTHEM: http://www.schooltube.com/video/b2edc79780134e1b9bce/FossilRockAnthem Pre Test IS IT A FOSSIL OR NOT? Power Point Presentation Explore Activity 1: FOSSIL IDENTIFICATON Activity 2: INTERPRETING EVENTS from FOSSIL EVIDENCE Explain PALEONTOLOGIST MYSTERY PUZZLE Making a Model of an Amber-like Fossil FOSSILS ROCK - Power Point Presentation Elaborate More advanced students can create their own fossil video to present to their classmates and/or design an activity to make their own fossil cast using various objects. Fossil Bingo Evaluate Post Test