View - Mid Wales Geology Club
... 1820s.9 Fossils were common in younger rocks but during his work in the mid 1820s he thought the older rocks ‘below the region of animal life’ and did not even look for fossils.10 When the two men entered Wales there was no concept of the movement and collision of continents, and no understanding of ...
... 1820s.9 Fossils were common in younger rocks but during his work in the mid 1820s he thought the older rocks ‘below the region of animal life’ and did not even look for fossils.10 When the two men entered Wales there was no concept of the movement and collision of continents, and no understanding of ...
Department of Geology
... GEOL 198, 298, 398, 498, 598 – Tutorial (1-3) GEOL 101 – Environmental Geology (3) A study of geology and the human environment. Topics begin with the basics of geology: minerals and rocks, the earth’s internal structure, earthquakes, volcanoes and plate tectonics. Surface processes affecting the en ...
... GEOL 198, 298, 398, 498, 598 – Tutorial (1-3) GEOL 101 – Environmental Geology (3) A study of geology and the human environment. Topics begin with the basics of geology: minerals and rocks, the earth’s internal structure, earthquakes, volcanoes and plate tectonics. Surface processes affecting the en ...
Learning Outcome mapping of old spec to new
... core, and current theories of its origin and age ...
... core, and current theories of its origin and age ...
geologic time, concepts, and principles
... Gould argued that Hutton's interpretation of uniformitarianism actually included a cyclical series of events in which all of Earth history was repeated with "repair" of the earlier age, much as many primal societies view time as a cyclical, rather than linear, phenomenon. Furthermore, the rates of g ...
... Gould argued that Hutton's interpretation of uniformitarianism actually included a cyclical series of events in which all of Earth history was repeated with "repair" of the earlier age, much as many primal societies view time as a cyclical, rather than linear, phenomenon. Furthermore, the rates of g ...
AS/A level
... geological fieldwork on at least two occasions and in respect of each of those opportunities: the date on which it was provided the number of learners who participated the location at which it was provided a brief description of the fieldwork undertaken confirm that each learner has been p ...
... geological fieldwork on at least two occasions and in respect of each of those opportunities: the date on which it was provided the number of learners who participated the location at which it was provided a brief description of the fieldwork undertaken confirm that each learner has been p ...
Cenozoic paleobotany of the John Day Basin, central Oregon
... The John Day Basin of central Oregon preserves an astonishingly rich fossil record of Cenozoic vertebrates, plants (macrofossils, pollen and spores, and, more recently discovered, phytoliths), and fossil soils. The basin contains an almost uninterrupted 2200-m-thick sequence of richly fossiliferous ...
... The John Day Basin of central Oregon preserves an astonishingly rich fossil record of Cenozoic vertebrates, plants (macrofossils, pollen and spores, and, more recently discovered, phytoliths), and fossil soils. The basin contains an almost uninterrupted 2200-m-thick sequence of richly fossiliferous ...
Wegener Reading [Biography]
... have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." Alfred Wegener. The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) Some truly revolutionary scientific theories may take years or decades to win general a ...
... have to be prepared always for the possibility that each new discovery, no matter what science furnishes it, may modify the conclusions we draw." Alfred Wegener. The Origins of Continents and Oceans (4th edition) Some truly revolutionary scientific theories may take years or decades to win general a ...
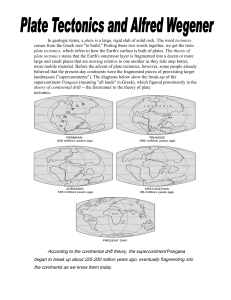
In geologic terms, a plate is a large, rigid slab of solid rock. The word
... heights? Scientists, philosophers, and theologians have wrestled with questions such as these for centuries. Until the 1700s, most Europeans thought that a Biblical Flood played a major role in shaping the Earth's surface. This way of thinking was known as "catastrophism," and geology (the study of ...
... heights? Scientists, philosophers, and theologians have wrestled with questions such as these for centuries. Until the 1700s, most Europeans thought that a Biblical Flood played a major role in shaping the Earth's surface. This way of thinking was known as "catastrophism," and geology (the study of ...
Lab: Dance of the Continents
... information, Wegener began to look for, and to find, more cases of similar organisms separated by great oceans. At the time, science explained such cases by hypothesizing that land bridges had once connected far-flung continents. But, Wegener also noticed the close fit between the coastlines of Afri ...
... information, Wegener began to look for, and to find, more cases of similar organisms separated by great oceans. At the time, science explained such cases by hypothesizing that land bridges had once connected far-flung continents. But, Wegener also noticed the close fit between the coastlines of Afri ...
31. From Continental Drift to Plate Tectonics
... are typically found in association with one another, and the genus Glossopteris is the characteristic fossil for which the flora is named (Fig. 31.4). During Wegener’s lifetime this flora was known from rocks of the Permian Period in South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Madagascar; it has si ...
... are typically found in association with one another, and the genus Glossopteris is the characteristic fossil for which the flora is named (Fig. 31.4). During Wegener’s lifetime this flora was known from rocks of the Permian Period in South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Madagascar; it has si ...
25_Lecture_Presentation
... • Continental drift has many effects on living organisms – A continent’s climate can change as it moves north or south – Separation of land masses can lead to allopatric speciation ...
... • Continental drift has many effects on living organisms – A continent’s climate can change as it moves north or south – Separation of land masses can lead to allopatric speciation ...
A View of Life
... – Multicellularity arose approximately 1 billion years later (1.4 bya). Mader: Biology 8th Ed. ...
... – Multicellularity arose approximately 1 billion years later (1.4 bya). Mader: Biology 8th Ed. ...
Research Pack
... together into one big mass, which he called Pangaea. He thought Pangaea had split up to form Earth’s continents. These continents then drifted apart. He first suggested his ‘Continental Drift’ theory in 1912, and published a book about it in 1915. Wegener had no idea exactly how the continents could ...
... together into one big mass, which he called Pangaea. He thought Pangaea had split up to form Earth’s continents. These continents then drifted apart. He first suggested his ‘Continental Drift’ theory in 1912, and published a book about it in 1915. Wegener had no idea exactly how the continents could ...
Mesozoic Era - edsc127summer2012
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
O-25 David Rudkin
... • the horseshoe crab fossil record is now traceable back to the Early Ordovician, but may eventually be extended into the Cambrian Period • the earliest known horseshoe crabs were established in open marine habitats during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event • environmental parameters duri ...
... • the horseshoe crab fossil record is now traceable back to the Early Ordovician, but may eventually be extended into the Cambrian Period • the earliest known horseshoe crabs were established in open marine habitats during the Great Ordovician Biodiversification Event • environmental parameters duri ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
PHESCh13Earth`s History
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
... • Later, primary plants evolved that used photosynthesis and released oxygen. • Oxygen began to accumulate in the atmosphere about 2.5 billion years ago. ...
Lesson 2 - Continental Drift Alfred Wegener.key
... 2. Land bridges could explain a lot of Wegener's evidence Lots of Wegener's evidence for continental drift was based on things like similar fossils being found on the opposite sides of oceans and matching layers of rock on different continents. Other people had noticed this too and in 1920, scientis ...
... 2. Land bridges could explain a lot of Wegener's evidence Lots of Wegener's evidence for continental drift was based on things like similar fossils being found on the opposite sides of oceans and matching layers of rock on different continents. Other people had noticed this too and in 1920, scientis ...
Earth`s History
... •North American plate began to override the Pacific plate •Mountains of western North America began forming Mesozoic life •Survivors of the great Paleozoic extinction •Gymnosperms become the dominant trees ...
... •North American plate began to override the Pacific plate •Mountains of western North America began forming Mesozoic life •Survivors of the great Paleozoic extinction •Gymnosperms become the dominant trees ...
Grade 4 Earth Science Unit (4.E.2.)
... evidence can help in matching rock layers. The Law of Superposition, which states that in an undisturbed horizontal sequence of rocks the oldest rock layers will be on the bottom, with successively younger rocks on top of these, helps geologists correlate rock layers around the world. This also mean ...
... evidence can help in matching rock layers. The Law of Superposition, which states that in an undisturbed horizontal sequence of rocks the oldest rock layers will be on the bottom, with successively younger rocks on top of these, helps geologists correlate rock layers around the world. This also mean ...
ch10
... More than 80% of all marine species became extinct in the waning stages of the Permian Period. The causes of the Permian biotic crisis were a combination of changes that dealt the lethal blow to so many species. The fusing of the continents into the supercontinent Pangea, reduced the area of shallow ...
... More than 80% of all marine species became extinct in the waning stages of the Permian Period. The causes of the Permian biotic crisis were a combination of changes that dealt the lethal blow to so many species. The fusing of the continents into the supercontinent Pangea, reduced the area of shallow ...
Activity 5
... According to Wegener, about 200 millions years ago, a huge supercontinent called Pangea (Greek for all land) broke into separate continents that moved apart.Wegener claimed that compression at the leading edge of the moving continent led to the formation of mountains.Wegener’s hypothesis allowed him ...
... According to Wegener, about 200 millions years ago, a huge supercontinent called Pangea (Greek for all land) broke into separate continents that moved apart.Wegener claimed that compression at the leading edge of the moving continent led to the formation of mountains.Wegener’s hypothesis allowed him ...
EASTERN ARIZONA COLLEGE Historical Geology
... consideration of the historical aspects of plate tectonics, the geologic development of North America, and important events in biological evolution and the resulting assembly of fossils. It provides an appreciation for the vast extent of geologic time, the natural processes affecting change on the e ...
... consideration of the historical aspects of plate tectonics, the geologic development of North America, and important events in biological evolution and the resulting assembly of fossils. It provides an appreciation for the vast extent of geologic time, the natural processes affecting change on the e ...
History of paleontology

The history of paleontology traces the history of the effort to understand the history of life on Earth by studying the fossil record left behind by living organisms. Since it is concerned with understanding living organisms of the past paleontology can be considered to be a field of biology, but its historical development has been closely tied to geology and the effort to understand the history of the Earth itself.In ancient times Xenophanes (570-480 BC), Herodotus (484-425 BC), Eratosthenes (276-194 BC), and Strabo (64 BC-24 AD), wrote about fossils of marine organisms indicating that land was once under water. During the Middle Ages, fossils were discussed by the Persian naturalist, Ibn Sina (known as Avicenna in Europe), in The Book of Healing (1027), which proposed a theory of petrifying fluids that Albert of Saxony would elaborate on in the 14th century. The Chinese naturalist Shen Kuo (1031–1095) would propose a theory of climate change based on evidence from petrified bamboo.In early modern Europe, the systematic study of fossils emerged as an integral part of the changes in natural philosophy that occurred during the Age of Reason. The nature of fossils and their relationship to life in the past became better understood during the 17th and 18th centuries, and at the end of the 18th century the work of Georges Cuvier ended a long running debate about the reality of extinction and led to the emergence of paleontology, in association with comparative anatomy, as a scientific discipline. The expanding knowledge of the fossil record also played an increasing role in the development of geology, particularly stratigraphy.In 1822 the word ""paleontology"" was invented by the editor of a French scientific journal to refer to the study of ancient living organisms through fossils, and the first half of the 19th century saw geological and paleontological activity become increasingly well organized with the growth of geologic societies and museums and an increasing number of professional geologists and fossil specialists. This contributed to a rapid increase in knowledge about the history of life on Earth, and progress towards definition of the geologic time scale largely based on fossil evidence. As knowledge of life's history continued to improve, it became increasingly obvious that there had been some kind of successive order to the development of life. This would encourage early evolutionary theories on the transmutation of species. After Charles Darwin published Origin of Species in 1859, much of the focus of paleontology shifted to understanding evolutionary paths, including human evolution, and evolutionary theory.The last half of the 19th century saw a tremendous expansion in paleontological activity, especially in North America. The trend continued in the 20th century with additional regions of the Earth being opened to systematic fossil collection, as demonstrated by a series of important discoveries in China near the end of the 20th century. Many transitional fossils have been discovered, and there is now considered to be abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. The last few decades of the 20th century saw a renewed interest in mass extinctions and their role in the evolution of life on Earth. There was also a renewed interest in the Cambrian explosion that saw the development of the body plans of most animal phyla. The discovery of fossils of the Ediacaran biota and developments in paleobiology extended knowledge about the history of life back far before the Cambrian.




![Wegener Reading [Biography]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/004189784_1-5fd15e1925a2c907481f1ec648102120-300x300.png)