* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Vestigial structures
Cambrian explosion wikipedia , lookup
Dawkins vs. Gould wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness in humans wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
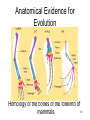
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary mismatch wikipedia , lookup
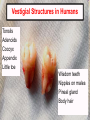
Anatomical terminology wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
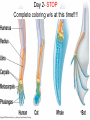
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
The eclipse of Darwinism wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Day 1-Start Chapter 12 1 Let’s make some fossils!!!!- Lab Day 1- STOP 2 Fossils-video Amber preserves insects and other organisms from mineralization. Petrified wood. Footprints Day 2- Start 3 4 A baby mammoth has been uncovered in the permafrost of north-west Siberia (9,000 years old). 5 How does a fossil form? 1. Death 2. Sedimentation • Dirt covers it up 3. Permineralization • Lower layers are compressed by upper layers and turned into rock. 4. Uplift • Former sea floors are lifted up and become dry land. 5. Erosion • Rain, wind, earthquakes, freeze and thaw all work toward erosion. 6 Fossils in lower layers of sedimentary rock are older. Can be dated on TYPE of fossils. 7 Fossil Evidence of Evolution Fossil records document the course of life through time 8 Fossil Evidence of Evolution Fossil of Archaeopteryx 9 Fossil Evidence of Evolution Evolutionary change in body size and toe 10 reduction of horses Anatomical Evidence for Evolution • Homologous structures: structures with different appearances and functions that all derived from the same body part in a common ancestor • The bones in the forelimb of mammals are homologous structures • Different functions, same ancestor structure 11 Anatomical Evidence for Evolution Homology of the bones of the forelimb of 12 mammals Day 2- STOP Complete coloring w/s at this time!!!! 13 Day 3- Start Anatomical Evidence for Evolution • Vestigial structures: have no apparent function, but resemble structures their ancestors possessed Vestigial structures of a whale 14 Vestigial Structures in Humans Tonsils Adenoids Coccyx Appendix Little toe Wisdom teeth Nipples on males Pineal gland Body hair 15 Embryological Evidence- developmental similarities 16 Some definitions Embryos= early stages of developing plants or animals Comparative embryology= shows relationships not obvious in the fully grown organism. pig and human Comparative biochemistry= studies of organisms on a biochemical level blood and amino acids 17 Anatomical Evidence for Evolution • Strongest anatomical evidence supporting evolution comes from comparisons of how organisms develop. • Early vertebrate embryos possess pharyngeal pouches that develop into: – In humans: glands and ducts – In fish: gill slits Complete embryonic development w/s at this time!!!! Day 3- STOP 18 Day 4- Start Charles Darwin I’m a NATURALIST! 19 What did he do? Formed the Theory of Evolution which states that: – Species change over time and space – All organisms share common ancestors with other organisms • Populations divide into different species – Evolutionary change is gradual and slow Click here for video! 20 A struggle for existence!!!1st clue Natural selection= one of the basic mechanisms of evolution, along with mutation, migration, and genetic drift. There are 4 parts!!!! 21 1. There is variation in traits. For example, some beetles are green and some are brown. 22 2. There is differential reproduction. Since the environment can't support unlimited population growth, not all individuals get to reproduce to their full potential. In this example, green beetles tend to get eaten by birds and survive to reproduce less often than brown beetles do. 23 3. There is heredity. The surviving brown beetles have brown baby beetles because this trait has a genetic basis. 24 4. End result: The more advantageous trait, brown coloration, which allows the beetle to have more offspring, becomes more common in the population. If this process continues, eventually, all individuals in the population will be brown. Remember the horses???? 25 nd 2 clue- Artificial Selection =intentional reproduction of individuals in a population that have desirable traits. 26 Click here for video 27 Artificial Selection Agriculture Corn looks very different from its ancestor 28 Artificial Selection Over time, we have selectively bred hogs to be leaner. 29 Artificial Selection Can selection produce major evolutionary changes? video Breeds of dogs: The differences among dog breeds are greater than the differences displayed among wild species of canids. 30 Day 4- STOP Day 6 31 Day 7 Population Genetics =an entire population evolves, not just an individual and 32 Some definitions Gene pool= total of all genes, or genetic information, in any population Allele Frequencies= the number of copies of a particular allele divided by the number of copies of all alleles at the genetic place (locus) in a population 33