* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Phanerozoic wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of paleontology wikipedia , lookup
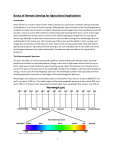
Name ________________________________________________________ Date ___________ Period _____ EOG Review- Evolution Goal 5 5.01 Interpret ways in which rocks, fossils, and ice cores record earth’s geologic history and the evolution of life including: Geologic Time Scale Index Fossils Law of Superposition Unconformity Evidence for climate change Extinction of species Catastrophic events 1. The Earth is __________________ year old. 2. List the divisions of the Geologic Time scale from largest to smallest: 3. _________________ can be taken from Antarctica to show climate data from thousands of year ago. 4. A ____________________ is a fossil of an organism that was common in one time period in multiple areas. These can be used to find the relative age of ___________ layers and other fossils. 5. Original remains are the actual __________ _____________ of once living things. These can be preserved in ___________, ____________, or ____________. 6. Rock fossils form in _____________________ rock. The four types of rock fossils are __________________, ____________________, _____________________, and ______________________. 7. According to the Law of Superposition, in a layer of rocks, the bottom layer is the ________________ and the top layer is the __________________. 8. Igneous rock forms from cooled molten rock. Igneous rock that cuts through layers of rock is always the _______________ layer. 9. A period of time when a large number of organisms become extinct is know as a _____________________. 10. The dinosaurs died in the ____________________ extinction and more than 90% of ocean life died in the __________________ extinction. 11. The earliest evidence of life comes from the ______________ and these organisms were __________________. 12. ___________________________ can be used to find the absolute age of a fossil. 13. What is unconformity? 5.02 Correlate evolutionary theories and processes: Biological Geological Technological 1. What did Alfred Wegner propose and why was this important? 2. What are Darwin’s two theories? 3. What evidence did Darwin use to support his theories? 5.03 Examine evidence that the geologic evolution has had significant global impact including: Distribution of living things Major geological events Mechanical and chemical weathering 1. What is the difference between mechanical and chemical weathering? 2. What are some major geological events? How do these affect living organisms? 3. How do the geological features of the Earth affect the ability of organisms to live in different places? 5.04 Analyze satellite imagery as a method to monitor Earth from space: Spectral analysis Reflectance curves 5.05 Use maps, ground truthing, and remote sensing to make predictions regarding: Changes over time Land use Urban sprawl Resource management In order to study how the Earth has changed, scientists need to observe large areas. Remote sensing uses satellite images to look at these large areas. Satellite images are like any other pictures: they are made of pixels and may have poor resolution. To improve these images, scientists also use spectral analysis. Spectral analysis looks at how light reflects (reflectance curves) to determine “signature” reflectance curves. Scientists determine which reflectance curves show plants, water, soil, and other materials on earth. Together, satellite images and spectral analysis allow scientists to gather information on the Earth from a distance. Ground truthing is when scientists directly observe the areas they are analyzing with satellite images. 1. What is remote sensing? 2. What is spectral analysis? 3. What can reflectance curves tell us? 4. Why might a scientist need to directly observe (ground truthing) an area they are studying through remote sensing? 5. What changes on the Earth’s surface might a scientist find by using satellite images? 6. What do you think urban sprawl is? How does it affect the Earth? 7. Why is it important to study land use and resource management? 8. What is the difference between a renewable resource and a nonrenewable resource?