* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Patterns of evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
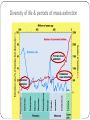
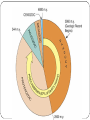
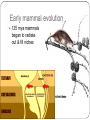
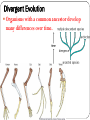
Patterns of Evolution Biology Unit 6 Powerpoint #2 1) Mass Extinction When many different species of organisms go extinct at the same time. End of Paleozoic: 95% of complex life (both plants and animals on the land and in the sea) went extinct. Diversity of life & periods of mass extinction Cambrian explosion Fossil Evidence of Mass Extinction Fossilization does not happen very often. Mass Extinctions also do not occur very often. Scientist believe that there are more fossils to be found around the time of mass extinctions than any other time. Geologic Time Based Upon major changes in the fossil record in the rock strata ERAS are longer time divisions than PERIODS There are four eras: Precambrian (4.6 billion – 544 million years ago) Paleozoic (544 - 245 million years ago) Mesozoic (245 – 65 million years ago) Cenozoic (65 million – Present) Cretaceous extinction The Chicxulub impact crater in the Caribbean Sea near the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico indicates an asteroid or comet struck the earth and changed conditions 65 million years ago Early mammal evolution 125 mya mammals began to radiate out & fill niches From sea to land Causes of Mass Extinction Climate Change: rapid changes in yearly weather patterns. Example: Ice Age Volcanism: the sudden oozing of millions of cubic meters of lava from the earth that release gasses poisoning the atmosphere Impact Events: Meteors or asteroids impacting the earth 2) Adaptive Radiation (Divergent evolution) A single species, or small group, evolves, through natural selection into diverse forms. Example: Darwin’s Galapagos Finches Divergent Evolution Organisms with a common ancestor develop many differences over time. 3) Convergent Evolution When unrelated organisms come to resemble each other due to environmental demands. Example: Placental v. Marsupials 4) Coevolution When two species evolve in response to changes to each other over time Example: Insects and flowers 5) Punctuated Equilibrium Long stable periods interrupted by periods of rapid change. Example: Darwin’s Galapagos Finches 6) Gradualism Small genetic changes occurring slowly within a population