* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CH 2.3-Carbon Compounds
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
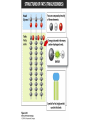
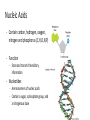
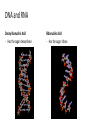
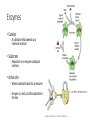
CH 2.3-Carbon Compounds Chemistry and Properties of Carbon - Carbon can bond with itself to make chains - It can bond with many other elements to make complex structures - It is a component of the four types of molecules all living things use: - Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Macromolecules - “Giant Molecule” - Monomer - Smaller unit or building block that can be used to build bigger molecules - Polymer - Molecule made up of many monomers - Polymerization - Joining monomers together to make polymers or macromolecules Carbohydrates - Contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) - Functions - Energy! - Structure - Monosaccharides - Also called simple sugars Are carbohydrate monomers Can be used to build larger carbs Used by living things for quick energy - Disaccharides - Are two linked monosaccharides More Carbohydrates - Polysaccharides - Also called complex carbohydrates - Made of many linked monosaccharides - Can be broken down to release energy - Can be used for structure - Animals store carbs as glycogen - Plants store carbs as starch - Plants use cellulose for structure Lipids - Contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (C,H,O) - Functions - Energy storage - Cell membranes - Waterproofing - Lipids are not soluble in water - Lipids are made from fatty acid chains and glycerol - These are lipid monomers Saturated and Unsaturated Fats - Saturated fats - Have the maximum number of hydrogen atoms in their fatty acids - Solid at room temperature - Polyunsaturated fats - Have some double bonds in their fatty acids - Liquid at room temperature Proteins - Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur (C,H,O,N,S) - Functions - Control rate of chemical reactions Regulate cell processes Form cellular structures Transport substances Fight disease More Proteins - Amino Acids - Are monomers of proteins - Have an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other - Have 20 different types - Peptide Bonds - Link amino acids together to form chains - Chains are called polypeptides - Polypeptide chains fold to make proteins Nucleic Acids - Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and phosphorus (C,H,O,N,P) - Function - Store and transmit hereditary information - Nucleotides - Are monomers of nucleic acids - Contain a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base DNA and RNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid - Has the sugar deoxyribose Ribonucleic Acid - Has the sugar ribose CH 2.4-Enzymes Chemical Reactions • Processes that change one set of chemicals into another • Involve changes in the chemical bonds that join atoms or compounds • Reactants - The elements or compounds that enter a reaction • Products - The elements or compounds produced by a reaction AB + CD AC + BD Enzymes • Catalyst - A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction • Substrate - Reactants in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction • Active site - Where substrates bind to an enzyme - Enzyme is a lock, and the substrate is the key Enzyme Activity • Enzymes are proteins - Activity can be impacted by anything that damages a protein • Heat and pH - Can “denature” or destroy proteins • Low temperature - Lower temperatures prevent molecules from interacting as quickly • Regulatory molecules - Molecules exist to turn enzymes on or off