* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Boundless Study Slides
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
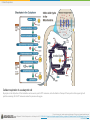
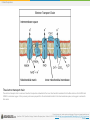
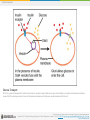
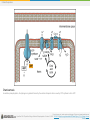
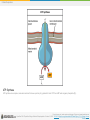
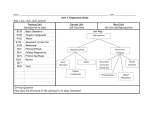
Boundless Lecture Slides Available on the Boundless Teaching Platform Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Boundless Teaching Platform Boundless empowers educators to engage their students with affordable, customizable textbooks and intuitive teaching tools. The free Boundless Teaching Platform gives educators the ability to customize textbooks in more than 20 subjects that align to hundreds of popular titles. Get started by using high quality Boundless books, or make switching to our platform easier by building from Boundless content pre-organized to match the assigned textbook. This platform gives educators the tools they need to assign readings and assessments, monitor student activity, and lead their classes with pre-made teaching resources. Using Boundless Presentations The Appendix The appendix is for you to use to add depth and breadth to your lectures. You can simply drag and drop slides from the appendix into the main presentation to make for a richer lecture experience. Get started now at: http://boundless.com/teaching-platform Free to edit, share, and copy Feel free to edit, share, and make as many copies of the Boundless presentations as you like. We encourage you to take these presentations and make them your own. If you have any questions or problems please email: [email protected] Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com About Boundless Boundless is an innovative technology company making education more affordable and accessible for students everywhere. The company creates the world’s best open educational content in 20+ subjects that align to more than 1,000 popular college textbooks. Boundless integrates learning technology into all its premium books to help students study more efficiently at a fraction of the cost of traditional textbooks. The company also empowers educators to engage their students more effectively through customizable books and intuitive teaching tools as part of the Boundless Teaching Platform. More than 2 million learners access Boundless free and premium content each month across the company’s wide distribution platforms, including its website, iOS apps, Kindle books, and iBooks. To get started learning or teaching with Boundless, visit boundless.com. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration Energy in Living Systems Glycolysis Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle Oxidative Phosphorylation Metabolism without Oxygen Cellular Respiration Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration (continued) Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways Regulation of Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration > Energy in Living Systems Energy in Living Systems • Transforming Chemical Energy • Electrons and Energy • ATP in Metabolism Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/energy-in-living-systems-73/ Cellular Respiration > Glycolysis Glycolysis • Importance of Glycolysis • The Energy-Requiring Steps of Glycolysis • The Energy-Releasing Steps of Glycolysis • Outcomes of Glycolysis Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/glycolysis-74/ Cellular Respiration > Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle • Breakdown of Pyruvate • Acetyl CoA to CO2 • Citric Acid Cycle Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/oxidation-of-pyruvate-and-the-citric-acid-cycle-75/ Cellular Respiration > Oxidative Phosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation • Electron Transport Chain • Chemiosmosis and Oxidative Phosphorylation • ATP Yield Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/oxidative-phosphorylation-76/ Cellular Respiration > Metabolism without Oxygen Metabolism without Oxygen • Anaerobic Cellular Respiration Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/metabolism-without-oxygen-77/ Cellular Respiration > Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid... Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways • Connecting Other Sugars to Glucose Metabolism • Connecting Proteins to Glucose Metabolism • Connecting Lipids to Glucose Metabolism Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/connections-of-carbohydrate-protein-and-lipid-metabolicpathways-78/ Cellular Respiration > Regulation of Cellular Respiration Regulation of Cellular Respiration • Regulatory Mechanisms for Cellular Respiration • Control of Catabolic Pathways Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com www.boundless.com/biology/textbooks/boundless-biology-textbook/cellular-respiration-7/regulation-of-cellular-respiration-79/ Appendix Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration Key terms • acetyl CoA a molecule that conveys the carbon atoms from glycolysis (pyruvate) to the citric acid cycle to be oxidized for energy production • adenosine triphosphate a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme, often called the "molecular unit of energy currency" in intracellular energy transfer • adenosine triphosphate a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme, often called the "molecular unit of energy currency" in intracellular energy transfer • adenosine triphosphate a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme, often called the "molecular unit of energy currency" in intracellular energy transfer • aerobic respiration the process of converting the biochemical energy in nutrients to ATP in the presence of oxygen • allosteric a compound that binds to an inactive site, affecting the activity of an enzyme by changing the conformation of the protein (can activate or deactivate) • anaerobic respiration A form of respiration using electron acceptors other than oxygen. • archaea A group of single-celled microorganisms. They have no cell nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelles within their cells. • ATP synthase An important enzyme that provides energy for the cell to use through the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). • beta-oxidation A process that takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and catabolizes fatty acids by converting them to acetyl groups while producing NADH and FADH2. • catabolism Destructive metabolism, usually including the release of energy and breakdown of materials. • catabolism Destructive metabolism, usually including the release of energy and breakdown of materials. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration • catabolism the breakdown of large molecules into smaller ones usually accompanied by the release of energy • cellular respiration the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP) • chemiosmosis The movement of ions across a selectively permeable membrane, down their electrochemical gradient. • citric acid cycle a series of chemical reactions used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidization of acetate derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into carbon dioxide • complex A structure consisting of a central atom, molecule, or protein weakly connected to surrounding atoms, molecules, or proteins. • deamination The removal of an amino group from a compound. • disaccharide A sugar, such as sucrose, maltose, or lactose, consisting of two monosaccharides combined together. • electron shuttle molecules that bind and carry high-energy electrons between compounds in cellular pathways • enzyme a globular protein that catalyses a biological chemical reaction • fermentation An anaerobic biochemical reaction. When this reaction occurs in yeast, enzymes catalyze the conversion of sugars to alcohol or acetic acid with the evolution of carbon dioxide. • glucose a simple monosaccharide (sugar) with a molecular formula of C6H12O6; it is a principal source of energy for cellular metabolism • glycogen A polysaccharide that is the main form of carbohydrate storage in animals; converted to glucose as needed. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • glycolysis the cellular metabolic pathway of the simple sugar glucose to yield pyruvic acid and ATP as an energy source • heterotroph an organism that requires an external supply of energy in the form of food, as it cannot synthesize its own • keto acid Any carboxylic acid that also contains a ketone group. • kinase any of a group of enzymes that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP, to specific target molecules (substrates); the process is termed phosphorylation • Krebs cycle a series of enzymatic reactions that occurs in all aerobic organisms; it involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy • Krebs cycle a series of enzymatic reactions that occurs in all aerobic organisms; it involves the oxidative metabolism of acetyl units and serves as the main source of cellular energy • lipid A group of organic compounds including fats, oils, waxes, sterols, and triglycerides; characterized by being insoluble in water; account for most of the fat present in the human body. • metabolism the complete set of chemical reactions that occur in living cells • mitochondria in cell biology, a mitochondrion (plural mitochondria) is a membrane-enclosed organelle, often described as "cellular power plants" because they generate most of the ATP • monosaccharide A simple sugar such as glucose, fructose, or deoxyribose that has a single ring. • NADH nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) carrying two electrons and bonded with a hydrogen (H) ion; the reduced form of NAD Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration • nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) An organic coenzyme involved in biological oxidation and reduction reactions. • oxaloacetate a four carbon molecule that receives an acetyl group from acetyl CoA to form citrate, which enters the citric acid cycle • oxidation A reaction in which the atoms of an element lose electrons and the valence of the element increases. • oxidative phosphorylation A metabolic pathway that uses energy released by the oxidation of nutrients to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). • phosphate Any salt or ester of phosphoric acid • phosphofructokinase any of a group of kinase enzymes that convert fructose phosphates to biphosphate • phosphorylation the addition of a phosphate group to a compound; often catalyzed by enzymes • prosthetic group The non-protein component of a conjugated protein. • pyruvate any salt or ester of pyruvic acid; the end product of glycolysis before entering the TCA cycle • reduction A reaction in which electrons are gained and valence is reduced; often by the removal of oxygen or the addition of hydrogen. • TCA cycle an alternative name for the Krebs cycle or citric acid cycle • ubiquinone A lipid soluble substance that is a component of the electron transport chain and accepts electrons from complexes I and II. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration Energy Plant This geothermal energy plant transforms thermal energy from deep in the ground into electrical energy, which can be easily used. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Introduction. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44430/latest/Figure_07_00_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Protein phosphorylation In phosphorylation reactions, the gamma phosphate of ATP is attached to a protein. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Energy in Living Systems. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44431/latest/Figure_07_01_03.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration The first half of glycolysis: investment The first half of glycolysis uses two ATP molecules in the phosphorylation of glucose, which is then split into two three-carbon molecules. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Glycolysis. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/Figure_07_02_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Anaerobic bacteria The green color seen in these coastal waters is from an eruption of hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria. These anaerobic, sulfate-reducing bacteria release hydrogen sulfide gas as they decompose algae in the water. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Metabolism Without Oxygen. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44444/latest/Figure_07_05_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Glycolysis The glycolysis pathway is primarily regulated at the three key enzymatic steps (1, 2, and 7) as indicated. Note that the first two steps that are regulated occur early in the pathway and involve hydrolysis of ATP. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Regulation of Cellular Respiration. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44442/latest/Figure_07_07_02.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Connection of Amino Acids to Glucose Metabolism Pathways The carbon skeletons of certain amino acids (indicated in boxes) are derived from proteins and can feed into pyruvate, acetyl CoA, and the citric acid cycle. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid Metabolic Pathways. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44441/latest/Figure_07_06_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Breakdown of Pyruvate Each pyruvate molecule loses a carboxylic group in the form of carbon dioxide. The remaining two carbons are then transferred to the enzyme CoA to produce Acetyl CoA. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikimedia. "09 10PyruvateToAcetylCoA-L." CC BY http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:09_10PyruvateToAcetylCoA-L.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Acetyl CoA and the Citric Acid Cycle For each molecule of acetyl CoA that enters the citric acid cycle, two carbon dioxide molecules are released, removing the carbons from the acetyl group. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle. November 10, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44433/latest/ View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Citric Acid Cycle Enzymes, isocitrate dehydrogenase and α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, catalyze the reactions that make the first two molecules of NADH in the citric acid cycle. Rates of the reaction decrease when sufficient ATP and NADH levels are reached. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikimedia. "Citric acid cycle." CC BY-SA http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Citric_acid_cycle.svg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Electron Chain Transport Levels of ADP and ATP affect the rate of electron transport through this type of chain transport. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikimedia. "Electron transport chain simple." CC BY-SA http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Electron_transport_chain_simple.png View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Adenosine triphosphate ATP is the main source of energy in many living organisms. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "ATP-3D-vdW." Public domain http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:ATP-3D-vdW.png View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Cellular respiration in a eukaryotic cell Glycolysis on the left portion of this illustration can be seen to yield 2 ATP molecules, while the Electron Transport Chain portion at the upper right will yield the remaining 30-32 ATP molecules under the presence of oxygen. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Cellular Respiration in a Eukaryotic Cell." CC BY-SA 3.0 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_respiration%23mediaviewer/File:CellRespiration.svg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Glycolysis produces 2 ATP, 2 NADH, and 2 pyruvate molecules Glycolysis, or the aerobic catabolic breakdown of glucose, produces energy in the form of ATP, NADH, and pyruvate, which itself enters the citric acid cycle to produce more energy. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Glycolysis." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Glycolysis.svg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Lactic acid fermentation Lactic acid fermentation is common in muscle cells that have run out of oxygen. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Metabolism Without Oxygen. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44444/latest/Figure_07_05_02.png View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration The second half of glycolysis: return on investment The second half of glycolysis involves phosphorylation without ATP investment (step 6) and produces two NADH and four ATP molecules per glucose. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Glycolysis. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/Figure_07_02_02.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Fructose Metabolism Although the metabolism of fructose and glucose share many of the same intermediate structures, they have very different metabolic fates in human metabolism. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikibooks. "Medical Physiology/Basic Biochemistry/Sugars." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Medical_Physiology/Basic_Biochemistry/Sugars%23Galactose_Metabolism View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration The structure of NADH and NAD+ The oxidized form of the electron carrier (NAD+) is shown on the left and the reduced form (NADH) is shown on the right. The nitrogenous base in NADH has one more hydrogen ion and two more electrons than in NAD+. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Energy in Living Systems. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44431/latest/Figure_07_01_01ab.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration Glycolysis is the first pathway of cellular respiration that oxidizes glucose molecules. It is followed by the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Carbohydrate Metabolism. November 10, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m46451/latest/ View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Adenosine triphosphate. ATP (adenosine triphosphate) has three phosphate groups that can be removed by hydrolysis to form ADP (adenosine diphosphate) or AMP (adenosine monophosphate).The negative charges on the phosphate group naturally repel each other, requiring energy to bond them together and releasing energy when these bonds are broken. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Energy in Living Systems. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44431/latest/Figure_07_01_02.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration The citric acid cycle In the citric acid cycle, the acetyl group from acetyl CoA is attached to a four-carbon oxaloacetate molecule to form a six-carbon citrate molecule. Through a series of steps, citrate is oxidized, releasing two carbon dioxide molecules for each acetyl group fed into the cycle. In the process, three NAD+ molecules are reduced to NADH, one FAD molecule is reduced to FADH2, and one ATP or GTP (depending on the cell type) is produced (by substratelevel phosphorylation). Because the final product of the citric acid cycle is also the first reactant, the cycle runs continuously in the presence of sufficient reactants. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Oxidation of Pyruvate and the Citric Acid Cycle. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44433/latest/Figure_07_03_02.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Alcohol Fermentation Fermentation of grape juice into wine produces CO2 as a byproduct. Fermentation tanks have valves so that the pressure inside the tanks created by the carbon dioxide produced can be released. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Metabolism Without Oxygen. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44444/latest/Figure_07_05_03.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration The electron transport chain The electron transport chain is a series of electron transporters embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane that shuttles electrons from NADH and FADH2 to molecular oxygen. In the process, protons are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix to the intermembrane space, and oxygen is reduced to form water. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Oxidative Phosphorylation. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/Figure_07_04_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Glucose Transport GLUT4 is a glucose transporter that is stored in vesicles. A cascade of events that occurs upon insulin binding to a receptor in the plasma membrane causes GLUT4-containing vesicles to fuse with the plasma membrane so that glucose may be transported into the cell. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Regulation of Cellular Respiration. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44442/latest/Figure_07_07_01.jpg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Glycogen Structure Schematic two-dimensional cross-sectional view of glycogen: A core protein of glycogenin is surrounded by branches of glucose units. The entire globular granule may contain around 30,000 glucose units. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Wikipedia. "Glycogen Structure." Public domain https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glycogen%23mediaviewer/File:Glycogen_structure.svg View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Glycogen Pathway Glycogen from the liver and muscles, hydrolyzed into glucose-1-phosphate, together with fats and proteins, can feed into the catabolic pathways for carbohydrates. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "Glycogen pathway.jpg." CC BY-SA 3.0 https://cnx.org/contents/ZP457F64@7/Connections-of-Carbohydrate-Pr View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Chemiosmosis In oxidative phosphorylation, the hydrogen ion gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP. Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Oxidative Phosphorylation. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/Figure_07_04_03.png View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration ATP Synthase ATP synthase is a complex, molecular machine that uses a proton (H+) gradient to form ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate (Pi). Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Oxidative Phosphorylation. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/Figure_07_04_02.png View on Boundless.com Cellular Respiration Attribution • Wikipedia. "adenosine triphosphate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/adenosine%20triphosphate • Wikipedia. "cellular respiration." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/cellular%20respiration • Wiktionary. "photosynthesis." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/photosynthesis • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44430/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/nicotinamide_adenine_dinucleotide • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/electron-shuttle • Wiktionary. "reduction." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/reduction • Wiktionary. "oxidation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/oxidation • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44431/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "phosphorylation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/phosphorylation • Wikipedia. "adenosine triphosphate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/adenosine%20triphosphate • Wiktionary. "phosphate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/phosphate • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44431/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "heterotroph." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/heterotroph • Wiktionary. "glycolysis." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/glycolysis • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wikipedia. "adenosine triphosphate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/adenosine%20triphosphate Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration • Wiktionary. "glucose." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/glucose • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "NADH." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/NADH • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "pyruvate." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/pyruvate • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44432/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wikipedia. "acetyl CoA." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/acetyl%20CoA • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44433/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "Krebs cycle." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Krebs_cycle • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/tca-cycle • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/oxaloacetate • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 29, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44433/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "Krebs cycle." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/Krebs_cycle • Wikipedia. "mitochondria." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/mitochondria • Wikipedia. "citric acid cycle." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/citric%20acid%20cycle • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44433/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "prosthetic group." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/prosthetic_group • Wikipedia. "Oxidative phosphorylation." CC BY-SA 3.0 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oxidative_phosphorylation Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com Cellular Respiration • Wiktionary. "complex." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/complex • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wikipedia. "ATP synthase." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATP%20synthase • Wikipedia. "oxidative phosphorylation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/oxidative%20phosphorylation • Wikipedia. "chemiosmosis." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/chemiosmosis • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "catabolism." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/catabolism • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44437/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "fermentation." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/fermentation • Wikipedia. "anaerobic respiration." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/anaerobic%20respiration • Wikipedia. "archaea." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/archaea • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 28, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44444/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44444/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "monosaccharide." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/monosaccharide • Wiktionary. "disaccharide." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/disaccharide • Wiktionary. "glycogen." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/glycogen • Wikibooks. "Medical Physiology/Basic Biochemistry/Sugars." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Medical_Physiology/Basic_Biochemistry/Sugars%23Galactose_Metabolism • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com http://cnx.org/content/m44441/latest/?collection=col11448/latest Cellular Respiration • Wiktionary. "deamination." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/deamination • Wiktionary. "catabolism." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/catabolism • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44441/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Boundless Learning. "Boundless." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://www.boundless.com//biology/definition/beta-oxidation • Wiktionary. "lipid." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/lipid • Wikibooks. "Metabolomics/Metabolites/Lipids/Energy Storage." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Metabolomics/Metabolites/Lipids/Energy_Storage • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44441/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "allosteric." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/allosteric • Wiktionary. "enzyme." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/enzyme • Wiktionary. "metabolism." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/metabolism • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44442/latest/?collection=col11448/latest • Wiktionary. "phosphofructokinase." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/phosphofructokinase • Wiktionary. "kinase." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/kinase • Wiktionary. "glycolysis." CC BY-SA 3.0 http://en.wiktionary.org/wiki/glycolysis • OpenStax CNX. "OpenStax College, Biology. October 16, 2013." CC BY 3.0 http://cnx.org/content/m44442/latest/?collection=col11448/latest Free to share, print, make copies and changes. Get yours at www.boundless.com