* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Proteins*
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
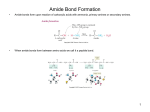
Proteins… Let’s Review…… then….. Let’s discover proteins…. PollEv.com/tinalambiase209 Functions of Proteins … Enzymes – reduces activation energy Ex: amylase – helps to digest amylose ATP synthase – helps to make ATP Structural Proteins – provide support ex: elastin, horn, silk (web), keratin (hair & nails) Movement – actin and myosin muscles Defense – antibodies in bloodstream Storage – albumin in egg whites Signaling – growth hormones in bloodstream What do you think is happening to the proteins within these eggs???? Proteins C, H, O, N and sometimes S Made in ribosomes Cell membranes Hormones (insulin) Hemoglobin Enzymes (control the rate of reactions) Proteins Proteins are made of Amino Acids There are 20 different amino acids. Each having a similar general structure - Differ only in their “R” groups Peptide Bonds Amino acids form proteins via dehydration synthesis forming peptide bonds Two amino acids linked together are called dipeptides More than 2 linked together are called polypeptides polypeptides can be thousands of amino acids long Can you draw a peptide bond? Which two functional groups join to make the peptide bond??? Dehydration synthesis of a protein Hydrolysis of a Protein Protein Structure Protein types include globular proteins which are usually enzymes and Fiberous proteins which usually serve for structure (eg. Hair) Proteins Exhibit 4 “levels of structure. Primary Structure Primary Structure of a protein is it’s sequence of amino acids Primary Structure dictates all further levels of protein structure Secondary Structure The Sequence (primary structure) causes parts of a protein molecule to fold into sheets or bend into helix shapes - this is a protein’s Secondary Structure. Tertiary Structure The protein then can compact and twist on itself to form a mass called it’s Tertiary Structure Quaternary Structure Several Proteins then can can combine and form a protein’s Quaternary Structure Various conformations are usually caused by the formation of hydrogen or disulfide bonds. PH, changes or heat can disrupt these bonds, permanently denaturing the protein.