* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download organization of the immune system
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
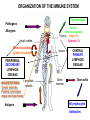
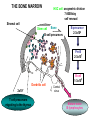
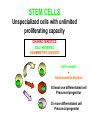
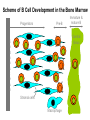
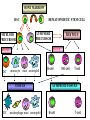
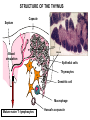
ORGANIZATION AND STRUCTURE OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM ORGANS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM LYMPHOID ORGANS GENERATION AND MIGRATION OF CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM LYMPHOCYTE HOEMOSTASIS, RECIRCULATION THE ROLE OF LYMPHATICS IN THE TRANSPORTATION OF ANTIGENS INITIATION OF IMMUNE RESPONSE IN PERIPHERAL LYMPHOID ORGANS ORGANIZATION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM LYMPHOCYTES CONGREGATE IN SPECIALIZED TISSUES • CENTRAL (PRIMARY) LYMPHOID ORGANS – Bone marrow – Thymus DEVELOPMENT TO THE STAGE OF ANTIGEN RECOGNITION • PERIPHERAL (SECONDARY) LYMPHOID ORGANS – Spleen – Lymph nodes – Skin-associated lymphoid tissue (SALT) – Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) – Gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) – Bronchial tract-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) ACTIVATION AND DIFFERENTIATION TO EFFECTOR CELLS • BLOOD AND LYMPH CIRCULATION – Lymphatics – collect leaking plasma (interstitial fluid) in connective tissues – Lymph – cells and fluid – No pump – one way valves ensure direction – edema – Several liters (3 – 5) of lymph gets back to the blood daily – vena cava superior GENERATION OF BLOOD CELLS BEFORE BIRTH AFTER BIRTH Cell number (%) Yolk sac 80 Flat bones Liver 60 40 Spleen 20 Tubular bones 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 years months BIRTH BONE MARROW TRANSPLANTATION ORGANIZATION OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM T-lymphocytes Pathogens Allergens Lymph nodes Blood circulation Lymph circulation Cellular immune response Thymus Helper Th Cytotoxic Tc Spleen PERIPHERAL SECONDARY LYMPHOID ORGANS WALDEYER RING Tonsils, adenoids Palatinal, pharyngeal lingual and tubar tonsils Antigens Nyirokerek Lymphatic vessels Bone marrow CENTRAL PRIMARY LYMPHOID ORGANS Stem cells B-lymphocytes Antibodies THE BONE MARROW HSC cell: assymetric division 7-8000/day self renewal Stromal cell Stem cell Bone csont B-cell precursors B-precursor 2-3x108 Pre-B 2-3x107 B-cell 1-3x106 Dendritic cell 2x107 T cell precursors migrating to the thymus Central centrális sinus sinus Mature naive B-lymphocytes STEM CELLS Unspecialized cells with unlimited proliferating capacity CHARACTERISTICS SELF RENEWAL ASSIMMETRIC DIVISION Self renewal + Assimmmetric division At least one differentiated cell Precursor/progenitor Or more differentiated cell Precursor/progenitor Scheme of B Cell Development in the Bone Marrow Progenitors E n d o o s t e u m Stromal cells Pre-B X X X Macrophage Immature & mature B Central Sinus BONE MARROW HSC MYELOID PRECURSOR HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL LYMPHOID PRECURSOR BLOOD BLOOD DC monocyte mast neutrophil TISSUES DC THYMUS mackrophage mast neutrophil B-cell NK-cell T-cell LYMPHOID TISSUES B-cell T-cell STRUCTURE OF THE THYMUS Capsule Septum Blood circulation Epithelial cells Thymocytes Dendritic cell Macrophage Mature naive T- lymphocytes Hassal’s corpuscle THYMUS INVOLUTION •Up to puberty/adolescence the size of the thymus is increasing and naive T lymphocytes are produced in waves to ensure protective immune responses •A sustained loss of tissue mass, cellularity and functionality of the thymus starts after puberty and lasts to middle age followed by a slower rate of involution extending to old age •DN cells do not proliferate and differentiate •Diversity of the TCR repertoire progressively becomes more limited •The thymic tissue is replaced by fat deposits •In old people naive peripheral T cells proliferate more extensively than those in younger individuals to compensate low cell numbers and reach their replicative limits earlier than in young people REDUCED RESISTANCE TO INFECTION AND TUMORIGENESIS Similar number of T cell progenitors to young individuals Limited IL-7 production, Bcl-2 expression and TCRβ rearrangement Replicative potential of thymic stromal cells is decreased The levels of nerve growth factor (NGF) secreted by medullary thymic epitelial cells (TEC) and IGF-1 produced by thymic macrophages decline