* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tissues of the immune system
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
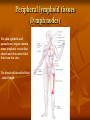
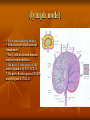
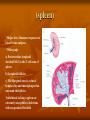
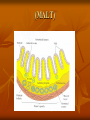
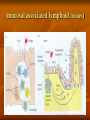
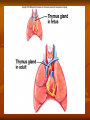
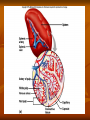
Types of lymphoid tissues A- Generative organs or primary lymphoid organs The sites for cell proliferation and maturation Such as Bone marrow and thymus B- peripheral lymphoid organs or secondary organs Where lymphocytes responses to foreign Ags Such as :spleen ,lymph nodes,cutaneous and mucosal immune system . Bone marrow Stem cells in bone marrow express CD34 and stem cell antigen -1(sca-1) Proliferation and maturation of precursor cells are stimulated by cytokines(CSFs)produced by stromal cells and macrophages Plasma cells,stem cells and their progeny Thymus The site of T cell maturation Bilobed organ divided into multiple lobules and each lobule consists of an cortex and an medula Thymus contain thymocytes and non lymphoid cells Why peripheral lymphoid tissues? 1)To optimise the cellular interaction , lymphocyts and APCs are localised and concentrated in anatomically defined tissues.(immune response) 2)The sites where foreign Ags are transported and concentrated. (Ag trapping) Peripheral lymphoid tissues (lymph nodes) The skin ,epithelia and parenchymal organs contain many lymphatic vessels that absorb and drain interstitial fluis from this sites. The absorbed interstitial fluid , called lymph. (lymph node) * The Cortex consist of follicles * Follicles are the B cell zones of lymph nodes * The T cells are located beneath and between the follicles * The naïve T cells express CCR7 and its ligand is CCL19 ,CCL21 * The naïve B cells express CXCR5 and its ligand is CXCL13 (spleen) * Major site of immune responses to blood borne antigens. * White pulp: a) Periarteriolar lymphoid sheaths(PALS) is the T cell zone of spleen b) Lymphoid follicles c) The Marginal zone is a rim of lymphocytes and macrophages that surround the follicles *individuals lacking a spleen are extremely susceptible to infections with encapsulated bacteria White pulp (MALT) (mucosal associated lymphoid tissues) Mucosal associated lymphoid tissues(MALT) * In the mucosa of the gastrointestinal tract lymphocytes are found in : a)Within the epithelial layer :T cells and 10% b)Scattered throughout the lamina propria:T cells ,B cells ,MØ,plasma cells,DC ,EO,Mast cells c)In Peyers patches • M cells