* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 14 The Peripheral Nervous System
Neurocomputational speech processing wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
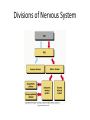
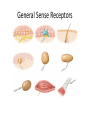
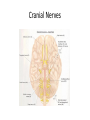
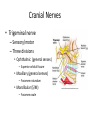
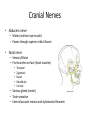
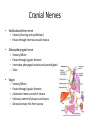
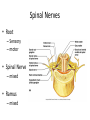
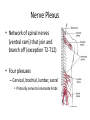
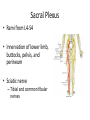
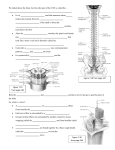
Ch. 14 The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives • Know the divisions of the PNS • Know the various types of general sense receptors • Be able to describe the cranial nerves • Be able to define a nerve plexus • Be able to describe the nerve plexus Divisions of Nervous System legacy.owensboro.kctcs.edu Structures of PNS • Sensory receptors – Detect sensor information from the environment • Nerves and ganglia – Bundles of axons • Mixed nerves • Motor endings – Innervate the effector Sensory Receptors • Modality (stimulus detected) – Thermoreceptors, photoreceptors, nociceptors • Origin (location) – Exteroceptors – Interoceptors – Proprioceptors • Structure – General • Free nerve endings • Encapsulated nerve endings – Special General Sense Receptors Unencapsulated Receptors • Free nerve endings – Pain, warmth, cold Encapsulated Receptors • Tactile (Meissners) corpuscles – Phasic, light touch, texture • Krause end bulbs • Tactile discs – Tonic, light touch, texture – Merkel cells • Hair receptors – Monitor movement – tactile, mucus membranes • Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles – Phasic, deep pressure, stretch, tickle, vibration • Bulbous (Ruffini) corpuscles – Tonic, heavy touch, pressure, joint movment, skin stretching General Sense Receptors Cranial Nerves Cranial Nerves • Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vagus, Accessory, Hypoglossal • On Occasion Our Trusty Truck Acts Funny --- Very Good Vehicle AnyHow • Functions (sensory, motor, both) – Some Say Marry Money, But My Brother Says Bad Business Marry Money Cranial Nerves • Olfactory nerve – Sensory (smell) – Passes through cribriform plate • Optic nerve – Sensory (vision) – Passes through optic canal • Oculomotor nerve – Motor (extrinsic eye muscles, iris and ciliary bodies) – Passes through superior orbital fissure • Trochlear nerve – Motor (extrinsic eye muscle) – Passes through superior orbital fissure Cranial Nerves • Trigeminal nerve – Sensory/motor – Three divisions • Ophthalmic (general senses) – Superior orbital fissure • Maxillary (general senses) – Foramen rotundum • Mandibular (S/M) – Foramen ovale medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com Cranial Nerves • Abducens nerve – Motor (extrinsic eye muscle) – Passes through superior orbital fissure • Facial nerve – Sensory/Motor – Five branches on face (facial muscles) • • • • • Temporal Zygomatic Buccal Mandibular Cervical – Various glands (motor) – Taste sensation – Internal acoustic meatus and stylomastoid foramen daviddarling.info Cranial Nerves • Vestibulocochlear nerve – Sensory (hearing and equilibrium) – Passes through internal acoustic meatus • Glossopharyngeal nerve – – – – Sensory/Motor Passes through jugular foramen Innervates pharyngeal muscles and parotid gland Taste • Vagus – – – – – Sensory/Motor Passes through jugular foramen Autonomic motor control of viscera Voluntary control of pharynx and larynx General sensory info from viscera medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com Cranial Nerves • Accessory nerve – Motor (sternocleidomastoid and trapezius) – Rootlets enter via foramen magnum, exits through jugular foramen • Hypoglossal nerve – Motor (tongue) – Passes though the hypoglossal canal Spinal Nerves • Root – Sensory – motor • Spinal Nerve – mixed • Ramus – mixed Nerve Plexus • Network of spinal nerves (ventral rami) that join and branch off (exception T2-T12) • Four plexuses – Cervical, brachial, lumbar, sacral • Primarily serve to innervate limbs medicalook.com Cervical Plexus • Innervation of the neck (C1-C4) • Cutaneous innervation, some motor • Phrenic nerves – Somatic motor and sensory innervation of diaphragm – Necessary for respiration Brachial Plexus • Innervation of upper limb • Rami from C5-T1 – Converge to form 3 trunks • Upper, middle, lower – Trunks split into divisions • Anterior and posterior – Divisions converge to form 3 cords • Lateral, posterior, medial – Cords split into 5 nerves • Musculocutaneous, Median, Ulnar, Radial, Axillary pitt.edu Lumbar Plexus • Rami of L1-L4 • Innervation of lower limb – Anterior and medial thigh • Femoral nerve Sacral Plexus • Rami from L4-S4 • Innervation of lower limb, buttocks, pelvis, and perineum • Sciatic nerve – Tibial and common fibular nerves doyoutri.net