* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Serotonin (5-HT) - Addiction Science Network
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of antiandrogens wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic agonist wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
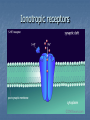
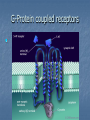
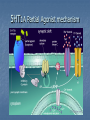
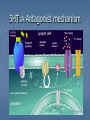
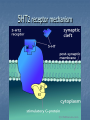
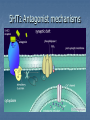
Indoleamines Lisham Ashrafioun Michele San George Melatonin vivo.colostate.edu Melatonin Receptors (ML1A) CNS locations SCN (biological clock) Anterior pituitary (seasonal breeding) PNS locations Retina - circadian and reproductive responses Cardiovascular system - caudal artery that potentiates NEinduced contraction Reproductive system – ovaries Immune system – T cells Kidneys – Na retention GI Tract – relaxes smooth muscles (melatonin-5-HT feedback) Serotonin 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Synthesis Tryptophan Tryptophan Hydroxylase 5-Hydroxytrophan (5-HTP) 5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) Amino Acid Decarboxylase Metabolism 5-HT Monoamine Oxidase 5-HIAA 5-HIAA: 5-Hydroxy indole amine acid Inactivation- 5HT reuptake Distribution(PNS) Majority released from gut Cardiovascular system – vasoconstrictor/vasodilator of vessels Responsible for smooth muscle contractions Release stimulated by food intake Inhibits release of gastric acid Softens stool Bonchioconstriction Uterine contractions Distribution: rodent (Cooper, Bloom, Roth, 2003) 5HT Receptors receptor 5HT1 subtype 5HT1 5HT2A, A, 5HT2B, 5HT1 5HT2C B, 5HT1 D, 5ht1E, 5HT1 F major cAMP signaling ↓ pathway 5HT2 IP3 5HT3 5HT4 5HT3A, 5HT3B ion channel 5ht5 5ht6 5HT7 5ht1A, 5ht1B cAMP cAMP? cAMP cAMP A few words about signal transduction mechanisms… 4 Families of Receptors Channel linked (Ionotropic) G-protein coupled (Metabotropic) Kinase- linked (enzymatic) Intracellular (gene transcription) Ionotropic receptors G-Protein coupled receptors The Major G Proteins Gs Stimulatory- Activates Ca channels, activates adenylyl cyclase Gi Inhibitory- Activates K channels, inhibits adenylyl cyclase Gq – Activates phospholipase C Go - Inhibits Ca channels G12/13 – Diverse ion transporter interactions Second MessengersAdenylyl Cyclase http://www.endocrinesurgeon.co.uk Second MessengerPhospholipase C http://www.endocrinesurgeon.co.uk 5HT1A receptor CNSforum.com 5HT1A Partial Agonist mechanism 5HT1A Antagonist mechanism 5HT2 receptor mechanism 5HT2 Antagonist mechanisms The Swiss army knife of Neurotransmitters Depression Anxiety Social phobia Schizophrenia Obsessive-compulsive Panic disorder Migraine Hypertension Pulmonary hypertension Eating disorders Vomiting Irritable bowel syndrome Serotenergic Drugs 5HT1A Buspirone, ipsapirone treat anxiety, depression (partial agonist) 5HT1D Sumatriptan, treat migraine (partial agonist) 5HT2A/2C methysergide, trazodone, risperidone, ketanserin treat migraine, depression, schizophrenia (antagonist) Drugs continued… 5HT3 Ondansetron treat chemotherapyinduced emesis (antagonist) 5HT4 Cisapride treat GI disorders (agonist) 5HT transporter SSRIs (Fluoxetine, sertraline) treat depression, OCD, panic disorder, social phobia, post traumatic stress disorder (inhibitor) Antidepressants Decreased amounts and impaired function of 5-HT associated with aggression, depression and other forms of antisocial behavior Antidepressants attempt to increase 5-HT levels Serotonin Syndrome Toxic, potentially fatal effects require a combination of serotonergic agents, such as an SSRI with an MAOI. Symptoms: euphoria, drowsiness, sustained rapid eye movement, overreaction of reflexes, rapid muscle contraction,abnormal movements of the foot, drunk, dizzy feeling,high body temperature, shivering , diarrhea ,loss of consciousness, death Treatment suspected agents should be discontinued OTC drugs containing ingredients known to increase serotonin levels, such as dextromethorphan, pseudoephedrine or phenylpropanolamine, also should be discontinued. Benzodiazepines for mild to moderate cases Cyproheptadine, Methysergide, and Propranolol for severe cases Oh man I just saw God and he was playing a mandolin and he told me to watch Fear and Loathing in Las Vegas while listening to The Doors self-titled album and dude they totally go together LSD Non-selective 5HT agonist/partial agonist Ergot derivative Mimics 5HT at 5HT1A autoreceptors on raphe cell bodies, slows firing rate of serotonergic neurons Current theories focus on glutamate release in thalamocortical terminals, causing dissociation between sensory relay and cortical output Hallucinogens and drug discrimination trials Animal model thought to reflect subjective effects Mediated by activation of 5HT2A receptors Acts as partial or full agonist at 5HT2A and 5HT2C receptors Phenethylamine derivatives (psilocybin) are selective 5HT2A/2C agonists Human Studies Psilocybin and PET imaging studiespattern resembles brain activation in schizophrenic patients Action of psilocybin is blocked by pretreatment with 5HT2A/2C antagonists Yeah rub Vaseline on my eyelids – 5-HT & MDMA MDMA causes an increased release of 5HT and blocks reuptake High affinity for SERT Effects fine axons Responsible for temperature increases Receptor Overview 5HT2 subtypes