* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hypothalamus
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Perivascular space wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
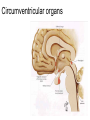
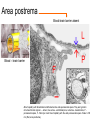
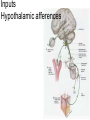
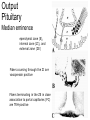
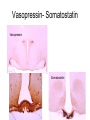
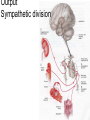
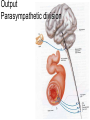
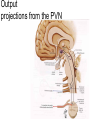
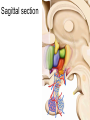
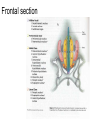
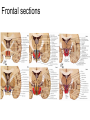
Hypothalamus Marco Celio Mai 2010 Historical Plates from the seventh book of the first edition (1543) of the Fabrica by Andreas Vesalius, showing what is believed to be the oldest anatomical images in Western literature of the hypothalamic-pituitary unit.1) Enlarged view of the pituitary gland (A), hypothalamic infundibulum (B) and ducts comprising the foramen lacerum and superior orbital fissure (C, D, E, F) believed to drain the brain mucus or phlegm (in Latin pituita) from the pituitary gland to the nasopharynx; 2) anatomical relationships between the infundibulum (D), the dural diaphragma sellae (F), the internal carotid arteries (C, D) and the oculomotor nerve. Drawings by Leonardo da Vinci (1508-1509) taken from the Codici di Anatomia of the Windsor’s Collection (A) Inferior surface of the brain, showing the rete mirabilis (arrow) that surrounds the pituitary gland; (B) three-dimensional representation of the cerebral ventricles. The third ventricle (3v) was believed to be the site of afference and elaboration of the "sensus communis” (Latin for peripheral physical sensations) Historical • John Newport Langley (1852-1925) – Introduced • the term autonomic nervous system • the concept of antagonism between sympathicus and vagus • and discovered preganglionic and postganglionic cells Historical • Walter Bradford Cannon (1871-1945) • • • • • • • Circuits in the central nervous system are responsible for the integrative action of the autonomic nervous system Cannon was influenced by the Harvard philosopher William James according to whom the emotional state of an organism is associated with afferent feedbacks from the body, notably from vascular and visceral structures Cannon proposed that the different emotional states are represented in the brain rather being peripheral in origin and are expressed by changes of activity in the sympathetic and parysympathetic nervous system Cannon view of the autonomic nervous system was that of a system designed to preserve life during grave physical crisis requiring extreme efforts (« fight or flight ») Writes the book: « The wisdom of the body » Introduces the concept of « homeostasis » Parasympathetic system conserve body energy Claude Bernard: « le milieu intérieur » Historical • Walter Rudolf Hess (1881-1973) • Observed the behavior elicited in conscious cats by local electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus • Transferred the idea of a dichotomy of the functional organization of the autonomic nervous system to the hypothalamus • Rostral part: integrate somatic, autonomic and endocrine reactions • • Promote revovery and conservation of energy, digestion, excretion and evacuation of waste as well as reproductive function – parasympathetic nervous system -- trophotrophc reaction Caudal part: general activation of the sympathetic nervous system • Mobilization of body energy and enhancement of performance capacity (ergotropic reaction) Whereas earlier studies found that electrical stimulation or lesions in the hypothalamus profoundly affect autonomic function, more recent investigation have demonstrated that many of these effects are due to the involvement of descending and ascending pathways of the cerebral cortex or the basal forebrain passing through the hypothalamus. Axonal tracing Hypothalamus • 1% of brain volume (4 gr) • connected to all part of the nervous system (2’000 projections) • 50 to 100 different group of neurons (nuclei) • Masterplan similar in all mammalian Characterized by the projection of their axons, their synaptic inputs and their histochemistry Immunohistohemistry (in-situ hybridisation) The hypothalamus integrates autonomic and endocrine functions with behavior The hypothalamus serves this integrative function be regulating six basic principal needs: Drinking and salt appetite, maintenance of blood osmolality and vasomotor tone – blood pressure and electrolyte concentration Control of metabolic thermogenesis and behaviors such as seeking a warmer or – body temperature cooler environment By feeding, digestion and – energy metabolism metabolic rate Through hormonal control – reproduction of mating, pregnancy and lactation flow to muscle – emergency responses (stress) Blood and other tissues and secretion of adrenal stress hormones – emotional response The hypothalamus regulates these basic life processes by recourse to 3 main mechanisms • Receiving sensory information from virtually the entire body. Direct inputs from the retina, olfactory system and visceral sensory system. Inputs from the circumventricular organs. Internal sensory neurons responsive to changes in temperature, osmolality, glucose and Na+. • Comparing sensory information with biological set points (temperature, osmolality, Na+, etc.) • Adjusting deviations from a set point by an array of autonomic, endocrine and behavioral responses. If the body is too warm the hypothalamus intervene by: • shifting blood flow from deep to cutaneous vascular beds • increasing sweating and heat loss through the skin • increasing vasopressin secretion to conserve water for sweating • activating coordinated behaviors (seeking a cooler environment) Homeostasis / • Stability of systems that maintain life – pH – concentration of different ions in the extracellular fluid (Na+, Ca2+) – osmolality of extracellular fluid – glucose levels – arterial oxygen tension Constantly present Allostasis • Adaptation to changing external and internal environment – – – – arterial blood pressure heart rate body core temperature concentration of circulating hormones – sleep-wake cycle – energy metabolism Temporary process, e.g. under stress Circumventricular organs Area postrema Blood-brain barrier absent Blood – brain barrier Blood capillary with fenestrated endothelium and a wide perivascular space. They are typical in circumventricular organs. L - lumen, blue arrow - endothelial pore, red arrow - basal lamina, P perivascular space, F - fibrocyte. Inset: blood capillary with the wide perivascular space. Scale = 200 nm. (Rat, area postrema.) Inputs Hypothalamic afferences Output Pituitary Median eminence ependymal zone (E), internal zone (ZI), and external zone (ZE) Fibers coursing through the ZI are vasopressin positive Fibers terminating in the ZE in close association to portal capillaries (PC) are TRH-positive Vasopressin- Somatostatin Vasopressin Somatostatin Output Sympathetic division Output Parasympathetic division Output projections from the PVN Hypothalamus • Subdivided in three longitudinal zones – Periventricular, medial and lateral • Rostrocaudally divided in • anterior, tuberal and posterior (mammillary) part • Based on patterns of connectivities subdivided in – – – – Neuroendocrine motor zone: contains the endocrine motor neurons relted to posterior and anterior pituitary Circadian timing generator: organizes the temporal structure of hypothalamis functions Pattern generating network: coordinates endocrine and autonomic patterns Behavior control column: regulation of defensive, ingestive (nutrition and fluid balance), reproductive and thermoregulatory behavior. Sagittal section Frontal section Frontal sections Intermingling of nerve cells A pair of photomicrographs illustrating the distribution of oxytocin and vasopressin neurons in the human paraventricular nucleus.. Scale = 250 μm.