* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
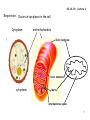
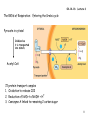
Download Respiration: Occurs in two places in the cell Cytoplasm and
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
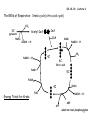
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
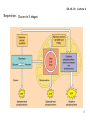
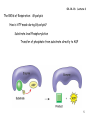
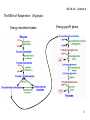
04-14-16: Lecture 6 Respiration: Occurs in two places in the cell Cytoplasm and mitochondria Outer membrane Inner membrane cytoplasm Matrix Intermembrane space 1 04-14-16: Lecture 6 Respiration: Occurs in 3 stages Glycolysis “split sugars” 6C sugar 2 ● 3C sugars (glucose) (pyruvate) Kreb’s cycle redox 3C sugar (pyruvate) CO2 + NADH + FADH2 Oxidative Phosphorylation NADH + FADH2 ADP + Pi oxidized NAD+ & FAD ATP made O2 is used (AEROBIC) 2 04-14-16: Lecture 6 Respiration: Occurs in 3 stages 3 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Glycolysis Glycolysis “split sugars” 6C sugar 2 ● 3C sugars (glucose) (pyruvate) in cytoplasm G3P Glceraldehye-3-phosphate High energy phosphate from ATP 2 Phases Energy investment phase: Energy payoff phase: NET: 4 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Glycolysis How is ATP made during Glycolysis? Substrate level Phosphorylation Transfer of phosphate from substrate directly to ADP 5 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Glycolysis Energy investment phase Energy payoff phase 6 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Glycolysis What do I need to know about glycolysis? Take place in cytoplasm 6C sugar (glucose) 2 ● 3C sugars (pyruvate) (will go to Kreb’s cycle in matrix of mitoch.) 2 Phases Energy investment phase Energy payoff phase Key step: G3P (intermediate) is oxidized to reduce NAD+ to NADH ATP made by substrate level phosphorylation Using kinases 7 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Entering the Krebs cycle Pyruvate in cytosol Oxidized as it is transported into mitoch. Acetyl CoA 72 protein transport complex 1. Oxidation to release CO2 2. Reduction of NAD+ to NADH + H+ 3. Coenzyme A linked to remaining 2 carbon sugar 8 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) CO2 3C pyruvate NAD+ NADH + CoA Acetyl-CoA CoA H+ NADH + H+ CO2 4C NADH + H+ NAD+ 6C Citric acid NAD+ 5C FADH2 4C Energy Totals for Krebs NAD+ FAD NADH + H+ ATP ADP substrate level phosphorylation 9 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Glycolysis and Krebs Energy totals Key products of Glycolysis 2 ATP 2 NADH + H+ 2 pyruvates (3C sugar) Key products of Krebs 2 ATP 8 NADH + H+ 2 FADH2 Need to do to make ATP? Need to regenerate NAD+ and FAD Oxidative Phosphorylation 1. Electron transport: oxidation of NADH and FADH2 to NAD + and FAD 2. Chemiosmosis will generate ATP 10 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain NADH + H+ + ½ 02 NAD+ + H20 ΔG << 0 Separate etransport them thru several proteins Multiple small rxns 02 is ultimate acceptor of emultiple electron transport proteins involved redox reactions – passed from 1 to the next NADH enters at the beginning to donate its eFADH2 enters later (therefore FADH2 = 2/3 energy of NADH) 3 protein complexes pump e- from matrix into the intermembrane space 11 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain NADH + H+ + ½ 02 NAD+ + H20 ΔG = -53 kcal 12 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis and the proton (H+) motive force Linking e- transport and H+ shuttling to ATP synthesis NADH + H+ FADH2 NAD+ + 2e- + 2 H+ FAD + 2e- + 2 H+ As e- enters the electron transport chain H+ are pumped across the membrane (from matrix to intermembrane space) NADH FADH2 3 H+ complexes which generates – 3 ATPs made 2 H+ complexes which generates – 2 ATPs made H+ now in high concentration in the intermembrane space (2/3 energy of NADH – because enters ETC later!) H+ repel back into the matrix Through the ATP synthase: channel which uses H+ gradient to make ATP ADP + Pi ATP 13 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain 14 Show movie:http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/etc/movie.htm 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: ATP synthase Linking e- transport and H+ shuttling to ATP synthesis H+ gradient + ADP + Pi ATP Energy is generated from ion gradient H+ ions: higher in the intermembrane space than in the matrix Key is diffusion: spontaneous movement of a molecule from high conc. to low conc. H+ repel back into the matrix But membrane is impermeable to H+ ions – so can’t get across ___________ is the one channel H+ ions can get back across captures the energy of H+ movement down its conc. gradient to make ATP 15 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: ATP synthase 16 Show movie:http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/atpgradient/movie.htm 04-14-16: Lecture 6 The RXNs of Respiration: Energy totals Krebs: matrix of mitochondria 2ATP + 8 NADH + 2FADH2 30 ATP total substrate level phosphorylation 24 ATP 4 ATP Grand Total 36-38 ATPs (3 per NADH) (2 per FADH2) Glycolysis: cytosol 2ATP + 2 NADH substrate level phosphorylation 4 ATP 6 ATP NADH made by glycolysis in the cytoplasm is impermeable to membranes. Its e- are passed to either NAD+ or FAD in the Mitoch. via electron shuttling systems Why 4 or 6 ATP? Pay a toll of 2 ATPs if passed to FAD FADH2 NAD+ NADH + H+ cytosol e- FAD NAD+ 50:50 chance NADH +H+ Mitoch. matrix 17 04-14-16: Lecture 6 Aerobic vs. Anaerobic Respiration Aerobic requires O2: Oxidative Phosphorylation Need O2 to oxidize NADH and FADH2 (REDOX) Normally: Anaerobic does not requires O2: Fermentation: In anaerobic conditions – 18 04-14-16: Lecture 6 Fermentation: In anaerobic conditions – make NAD+ creak along on 2 ATPs per glucose 1Glucose (6C) 2 NAD+ 2 NADH + H+ 2ATP 2 Pyruvate (3C) Anaerobic no O2 O2 36-38 ATPs Muscle Yeast, bacteria Lactic Acid Ethanol Recovery NAD+ Recovery NAD+ Get by on 2 ATPs per glucose! 19 04-14-16: Lecture 6 Regulation of Respiration Positive allosteric regulator No O2 turn on fermentation Feedback control Negative allosteric regulators 20