* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download spinal cord
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
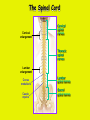
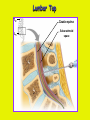
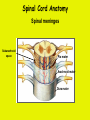
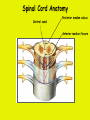
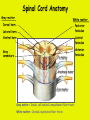
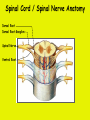
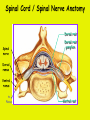
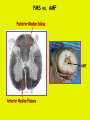
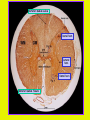
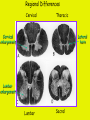
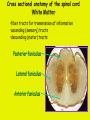
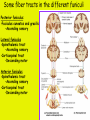
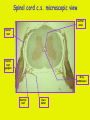
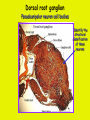
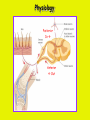
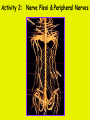
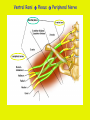
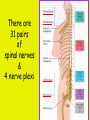
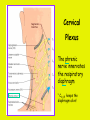
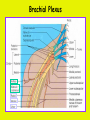
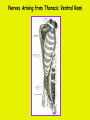
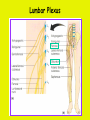
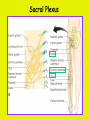
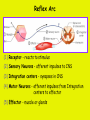
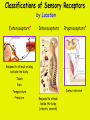
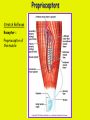
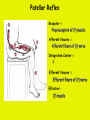
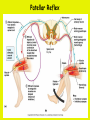
Week 11 The Spinal Cord & PNS What’s ahead • Identify structures of the spinal cord • Identify peripheral nerves • Identify components of the reflex arc Activity 1: The Spinal Cord The Spinal Cord Cervical enlargement Cervical spinal nerves Thoracic spinal nerves Lumbar enlargement Conus medullaris Cauda equina Lumbar spinal nerves Sacral spinal nerves L2 L3 Conus Medullaris L4 L5 Cauda Equina (horse’s tail) Lumbar Tap T12 Cauda equina Subarachnoid space L5 L4 L5 Spinal Cord Anatomy Spinal meninges Subarachnoid space Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Spinal Cord Anatomy Central canal Posterior median sulcus Anterior median fissure Spinal Cord Anatomy Gray matter White matter Dorsal horn Posterior funiculus Lateral horn Ventral horn Lateral funiculus Gray commisure Anterior funiculus Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater Gray matter = Inside, cell bodies & unmyelinated fiber tracts White matter = Outside, myelinated fiber tracts Spinal Cord / Spinal Nerve Anatomy Dorsal Root Dorsal Root Ganglion Spinal Nerve Ventral Root Spinal Cord / Spinal Nerve Anatomy Dorsal root Spinal nerve Dorsal root ganglion Dorsal ramus Ventral ramus to Plexus Ventral root Posterior Spinal Cord What do Posterior you median suppose sulcus this is? Denticulate ligament Dorsal root Arachnoid mater Dorsal root ganglion Dura mater What do Ventral youroot suppose this is? How can you tell the Ventral side from the Dorsal side? PMS vs. AMF Posterior Median Sulcus AMF Anterior Median Fissure Cross sectional anatomy of the spinal cord Gray Matter A visual analogy Dorsal horns Sensory/inter neurons Dorsal horn Ventral horn Ventral horns motor neurons ? Posterior 1amedian sulcus Dorsal 2a ? horn Lateral 2b ? horn Vental 2c ? horn 1b ? fissure Anterior median Regional Differences Cervical Thoracic Cervical enlargement Lateral horn Lumbar enlargement Lumbar Sacral Cross sectional anatomy of the spinal cord White Matter •fiber tracts for transmission of information •ascending (sensory) tracts •descending (motor) tracts Posterior funiculus Lateral funiculus Anterior funiculus Some fiber tracts in the different funiculi Posterior funiculus: •Faciculus cuneatus and gracilis •Ascending sensory Lateral funiculus •Spinothalamic tract •Ascending sensory •Corticospinal tract •Descending motor Anterior funiculus •Spinothalamic tract •Ascending sensory •Corticospinal tract •Descending motor Spinal cord c.s. microscopic view Central canal Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion Gray commissure Ventral root Dura mater Dorsal root ganglion Pseudounipolar neuron cell bodies Identify the structural classification of these neurons Physiology Posterior In Anterior Out Dorsal root: afferent, sensory Ventral root: efferent, motor Dorsal ramus: mixed, motor and sensory to trunk Ventral ramus: mixed motor and sensory form nerve plexi Activity 2: Nerve Plexi & Peripheral Nerves Ventral Rami Plexus Peripheral Nerve There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves & 4 nerve plexi Cervical Plexus The phrenic nerve innervates the respiratory diaphragm “ C3,4,5 keeps the diaphragm alive! Brachial Plexus Nerves Arising from Thoracic Ventral Rami Lumbar Plexus Sacral Plexus Activity 3: Human Reflex Physiology Reflex Terminologies Reflex: A rapid, predictable, involuntary motor response to a stimulus that acts to return the body to homeostasis Mediated by the spinal cord Reflex Arc: The neural pathway a nerve impulse follows that mediates a reflex (from sensory receptor effector organ) Autonomic (Visceral) Reflex: Mediated through the ANS Not subject to conscious control Vasoconstriction/dilation, sweating, salivation, digestion, heart rate, pupil dilation/constriction Somatic Reflex: Involve stimulation of skeletal muscles by the somatic division of the nervous system Subject to conscious interference Reflex Arc (1) Receptor - reacts to stimulus (2) Sensory Neurons - afferent impulses to CNS (3) Integration centers - synapses in CNS (4) Motor Neurons - efferent impulses from Integration centers to effector (5) Effector - muscle or glands Classifications of Sensory Receptors by Location Exteroceptors* Interoceptors Proprioceptors* Respond to stimuli arising outside the body: Touch Pain Detect stretch Temperature Pressure Respond to stimuli inside the body (viscera, vessels) Proprioceptors Stretch Reflexes Receptor = Proprioceptor of the muscle Patellar Reflex Receptor = Proprioceptors of (?) muscle Afferent Neuron = Afferent fibers of (?) nerve Integration Center = ? Efferent Neuron = Efferent fibers of (?) nerve Effector= (?) muscle Patellar Reflex Patellar Reflex 3 Tests 1. Simultaneous muscle activity 2. Mental distraction 3. Fatigue Is the response greater or less than baseline? Pupillary Reflex Contralateral? – or - Ipsilateral? Lab Activity: • Study Spinal Cord & Peripheral Nerves • Perform Reflex experiments & analyze On the Practical: • Identify the structures of the Spinal Cord from models and slides • Identify the Peripheral Nerves and Nerve Plexi from models • Identify the components of the Reflex Arc