* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6-8 Lesson Plan 5 - Delaware Access Project
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
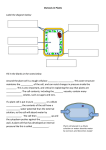
Lesson Plan: 5 Teacher(s): Subject: Science Unit: 6-8 Plant & Animal Cells Grade band(s): 6-8 Number of students: Setting: Lesson Objective(s): Objective 1: Students will be able to identify the features and functions of a plant cell. Objective 2: Students will identify similarities and differences between animal and plant cells. Objective 3: Students will conduct a simple experiment that demonstrates the passage of material through the cell membrane (osmosis). Connections to the GBEs: Standard(s): Nature and Application of Science and Technology 8.2 Design and conduct investigations with controlled variables to test hypotheses. Essence: Conduct an investigation on a hypothesis E1: Create a multi-step investigation to explore a hypothesis. E2: Follow a multi-step investigation to explore a hypothesis. E3: Given a multi-step investigation, identify materials that are needed. Nature and Application of Science and Technology 8.3 Accurately collect data through the selection and use tools and techniques appropriate to the investigation. Construct tables, diagrams, and graphs, showing relationships between two variables, to display and facilitate analysis of data. Compare and question results with and from other students. Essence: Collect, record, and compare data E1: Collect, display, and compare data related to an investigation. E2: Collect, display, and compare data related to an investigation. E3: Record data in a given chart or table. Life Processes 7.3 (1) Explain that individual cells are able to carry out basic life functions that are similar in organisms; however, explain that multi-cellular organisms, cells become specialized, interdependent upon one another, and unable to survive dependently. Essence: Cells and organisms E1: Explain what happens to cells in multi-cellular organisms. E2: Identify the function of individual cells. E3: Identify if given examples are multi-cellular organisms. Life Processes 7.5 Observe and sketch cells using microscopes and other appropriate tools. Compare and contrast plant, animal, protest, and bacterial cells by noting the presence or absence of major organelles) i.e., cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, chloroplasts, mitochondria and vacuoles) using the sketches and other resources. Essence: Cell types E1: Compare and contrast different cell types. E2: Label the parts of a given cell. E3: Identify given cells as plant or animal. ACCESS Project, Center for Disabilities Studies, UD Delaware Department of Education Least support Moderate support Most support Create a multi-step investigation to explore a hypothesis. Follow a multi-step investigation to explore a hypothesis. Given a multi-step investigation, identify materials that are needed. Collect, display, and compare data related to an investigation. Collect, display, and compare data related to an investigation. Record data in a given chart or table. Compare and contrast different cell types. Label the parts of a given cell. Identify given cells as plant or animal. Explain what happens to cells in multi-cellular organisms. Identify the function of individual cells. Identify if given examples are multi-cellular organisms. Materials: Science Journal Plant/animal cell models and diagram Cell wonder story Plant cell video (optional) “Eggcellent” Experiment materials KWHL chart Activities: 1. Plant cell Introduction: Use a wonder story to introduce the plant cell to students and talk about the basic structure. Use plant cell model to highlight similarities (refer back to digital pictures taken with the Zoomy in Lesson 3 of plant samples). 2. Plant cell structure and vocabulary introduction: Highlight important vocabulary that students will need to know about the structure and function of a plant cell. 3. Plant cell anatomy video: Check out YouTube, teacher tube or other online video source that has educational videos to supplement/enhance this lesson if needed. 4. Interactive structure of plant cell: This diagram can be used for whole group or independent practice with cell structures. Students do not have to work on identifying all the structures in this diagram, just those determined by the teacher. This can be done at the smart board and also serves as a formative assessment. http://www.neok12.com/diagram/Cell-Structures01.htm Teacher should prompt students to identify similarities and differences between animal and plant cells. Be sure to highlight major differences in shape (cell wall and chloroplasts can only be ACCESS Project, Center for Disabilities Studies, UD Delaware Department of Education 5. “Eggcellent” experiment preview: See instruction sheet. Talk about the cell membrane and how this experiment will demonstrate its’ function. Introduce the term “osmosis.” Osmosis: the distribution of liquid with a low concentration flowing through a membrane into an area with a higher concentration. 7. Students complete the “W” on the KWHL chart: Direct students to complete the “W” for what they would like to know about the topic. At this time you can pose several questions to students to get them thinking about how water moves in and out of cells. found in plant cells). Emphasize the fact that both cell types have a cell membrane and explain the function (passage of liquid in and out of cells from low to high concentration). 6. Introduce to students to the KWHL chart: Have students complete the “K” for what they already know about the materials being used in the experiment. Feel free to use picsyms or object prompts when they are describing the different materials they will be working with. 8. Hypothesis (prediction) statement: Prior to beginning the experiment have students form a hypothesis/prediction about what they think will happen during the experiment. Students can record this on the KWHL chart. 9. Exploration of materials: At this time allow 10. Conduct the “EggCELLent” Experiment: students to manipulate materials. See if they can This can be done in pairs, small groups or whole figure out he best method or mode to begin group (detailed instructions are included). conducting the experiment. Guide them to the preferred mode to conduct the experiment and have them complete the “H” for How can we find out? on the KWHL chart. Are they going to stir, mix or shake materials? What tools will you need to use? 11. Read Concept Statement: Teacher develops a concept statement “big idea” for students. It’s the “take-away” from the lesson. Example: Water travels in and out of cells through osmosis. After students read this statement have them complete the “L” for what they learned on the KWHL chart (concept statement). 12. Review Results of the Experiment: Make sure you go back and talk about the students’ predictions. Example: Did the egg placed in water get smaller of larger? (low to high concentration) 13. Concept summarization: this is your concept statement in a question format. This is your formative assessment and a way for students to communicate or show you what they have learned (format can be set up similar DCAS-Alt test providing 3 answer choices). Example: During osmosis water moves from a _____ to high concentration. Warm-up: Show students plant cell model and have them describe it features. Talk about how it is different from the animal cell model. ACCESS Project, Center for Disabilities Studies, UD Delaware Department of Education Key Vocabulary: Animal Cell Science Journal Concentration Plant Cell Observation Cell membrane Characteristics Osmosis Passage Barriers: Print Non-verbal communication Universal Design for Learning (UDL) brainstorm: Representation How will instructional content and materials be presented to the students (the “what” of learning)? Actions/ Expression How are the students able to interact with the materials and demonstrate knowledge (the “how” of learning)? Engagement What interests and engages students in the learning process (the “why” of learning)? Teaching Strategies: Modeling Brainstorming Graduated guidance Scaffolding ACCESS Project, Center for Disabilities Studies, UD Delaware Department of Education Think aloud Assessments: Response mode: Answering questions Teacher observations/checklists Lab activity Possible accommodations to use with this lesson: Picsyms Multimedia Closing Activity: Completion of “Concept Summarization.” ACCESS Project, Center for Disabilities Studies, UD Delaware Department of Education