* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download to get the file
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
Michael E. Mann wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
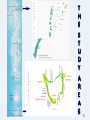
Climatic Research Unit email controversy wikipedia , lookup
Soon and Baliunas controversy wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
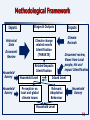
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
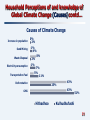
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
IPCC Fourth Assessment Report wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Vulnerability of Maldives Islands to Climate Change and Extreme Weather Events: A Study on Perceptions, Impacts & Adaptations by Miruza Mohamed Examination Committee: • Dr. Ranjith Perera (Chairperson) • Dr. Vilas Vitivattananon • Prof. Sivanappan Kumar 1 CLIMATE CHANGE & ITS IMPACTS Why Small Islands & in Particular Maldives? Small Islands - Amongst the most vulnerable to climate change and its consequences Maldives - Amongst the four countries (worldwide) comprised entirely of low lying atolls Geophysical nature- small (235sqkm of land area, 96% less than 1 sqkm), low lying (80% land area less than 1 meter above MSL, 42% of the population & all housing structures within 100m of the coastline) unconsolidated islands Import-dependent and a LDC 2 Rationale of the Study Many studies on SLR, less on Climate on extreme weather , its Change, Why impacts & Adaptation. Extreme Weather Already experiencing the Events impacts Why concentrate Why specifically on RUC & why HOUSEHOLD LEVEL Solution to unconsolidated nature = RUC/Safer Islands with high population and developed infrastructure high density settlements exposure of more people in a single location 3 Research Questions & Objectives What are the climatic Threats to urban settlements in the selected Regional Urban Centres (RUC) and in what ways have these threats affected RUCs? How have households of these regional centres responded to the impacts of climate induced events? How are climate change and its effects perceived by the households of these urban centres? To Understand and describe the climatic threats and its impacts to the urban settlements of the Selected RUCs To identify climate change impacts on households and to analyze the adaptation actions taken in addressing the climate variability and extreme weather events To determine the public perceptions of and knowledge of climate change to determine the consciousness of the general public 4 Observed evidence and projections for climate change Observed SLR in Maldives – long term trend 1.7mm/yr – towards the upper end of estimated range of global SLR over the past century & above the central estimate rate- 1.5mm/yr Increasing the frequency and intensify of extreme weather events in Maldives: flooding in more than 90 inhabited islands over the last 6 years at least one 37 islands flooded regularly In 2004, one event alone caused flooding in 71 inhabited islands, in 2007, one event alone affected 60 islands in 16 atolls 5 Adaptation to Climate Change Adaptation - an important option for reducing vulnerability to long term climate change impacts Adaptive Capacity - the ability of a system to adjust to climate change (including climate variability and extremes) to moderate potential damages, to take advantage of opportunities, or to cope with the consequences (IPCC, 2001). Knowledge – a pre-requisite for adaptation. “Formulation of adaptation measures requires how to utilize and enhance local and indigenous resilience practices and knowledge possessed by local communities.”(Japan, 2007) 6 Conceptual Framework Global Climate Change Slow on set changes Sudden, Extreme Events Impacts on Coastal Areas/Small Islands Perception/Knowledge Adaptation to What? Adaptation How does Adaptation occur? Who & What Adapts? What Type of Adaptation? 7 8 Selection of the study areas Urban regional cenres- impacts more if an event strikes. Selected for Population Consolidation Programme/Safer Island Most urbanized and high population concentration Importance in the context or urbanization- growth centres Importance at the national scale Have 2 sea ports out of the total 3 in Maldives, 2 airports out of the four airports, Highest health & facilities (except for Male’) 9 T H E S T U D Y A R E A S 10 S. Hithadhoo 11 HDH. KULHUDHUFFUSHI Hdh. Kulhudhuffushi 12 Methodological Framework Inputs Historical Data Document Review Household Survey Household Survey Stages & Outputs Climate change related events Identification (THREATS) Related Impacts Identification Household Level Perception on local and global climate issues Inputs Climate Records Document review, Views from Local people, His oral impact Identification Island Level Relevant Adaptation Behaviour Household Survey Household Level 13 14 Vulnerability of Two Islands to Climatic Variability Hdh. Kulhudhuffushi Exposed to NE monsoon generated winds & storm activities originating from the cyclone belt of Indian Ocean –storm surges and windstorm S. Hithadhoo Most southern- so exposed to wave actions from both E & W directions in Indian ocean – exposed to southwest monsoon related surges and long distance swells 15 Climatic Trends of two study areas Annual Rainfall (mm) 3200 250 200 150 100 50 0 2700 2200 1700 1200 1978 1981 1984 1987 1990 1993 1996 1999 for Hithadhoo from 1978-2006 for Kulhudhufushi from 1992-2006 Linear (for Hithadhoo from 1978-2006) 2002 2005 January February March April May June July August Septem… October Novemb… Decemb… Mean monthly rainfall Hdh. Hanimaadhoo S. Gan Linear (for Kulhudhufushi from 1992-2006) 16 Climatic Trends of two study areas contd… Maximum Temperature (°C) 31.4 31.2 31 30.8 30.6 30.4 30.2 30 1986 1991 1996 2001 Hdh. Kulhudhufushi S. Hithadhoo Linear (Hdh. Kulhudhufushi) Linear (S. Hithadhoo) 2006 Max- 31.3 °C +0.9 °C/year N, and +0.04 °C/year S 17 Climatic Trends of two study areas contd… North Meterological Station, Hanimaadhoo Sea level (mm) 2250 2200 2150 2100 2050 2000 1950 1900 Jun-90 Nov-91 Mar-93 Aug-94 Dec-95 Apr-97 Sep-98 Jan-00 Jun-01 South Meterological Station, Gan Sea level (mm) 1750 1700 1650 1600 1550 1500 1450 Aug-87 May-90 Jan-93 Oct-95 Jul-98 Apr-01 18 Most Common Events & Impacts at Island Level Heavy rainfall Wind storm Swell surges Flooding, damage to plants and household appliances Blowing off roofs and damage to plants Flooding & damage to plants 19 Determinants of Adaptive capacity and Social Vulnerability Gender of the respondents- Females were more vulnerable than males (Dwyer et al. 2004). Household Size- large households more vulnerable than small householdsHousehold Income &Types of Employment -important for determining the vulnerability, coping capacity and recovery after an impact Educational Level – educated populations are important in reducing the vulnerability 20 Household Perceptions of Local weather patterns HDH. Kulhudhuffushi S. Hithadhoo 91.2% believed that local weather pattern is changing 65.5% believed that temperature has increased -None believed that temperature has decreased 86.6% believed that local weather pattern is changing 55.0% from S. Hithadhoo Other observations include that rain & wind episodes are more stormy, Rain in unexpected times, Increase in storm surges, flooding and disasters, etc 21 Household Perceptions of and knowledge of Global Climate Change (Causes) HDH. Kulhudhuffushi S. Hithadhoo 91.0% have heard about climate change 42% knowledgeable on causes 51% identified GHGs emission 95% believed that local climate is changing 44% knowledgeable on causes 43% identified GHGs emission Respondents education attainment with their knowledge of causes of climate change showed a relationship so does with their types of occupation 22 Household Perceptions of and knowledge of Global Climate Change (Causes) contd… Causes of Climate Change Increase in population Sand Mining 0% 2% 1% 4% Waste Disposal 2% Electricity consumption 1% Transportation Fuel 8% 7% 5% 11% Deforestation 25% 43% 43% GHG Hithadhoo 51% Kulhudhufushi 23 Household Perceptions of and knowledge of Global Climate Change (Impacts) HDH. Kulhudhuffushi S. Hithadhoo Comparatively respondents were more aware on impacts of climate change 77% knowledgeable on impacts 64% knowledgeable on impacts Respondents education attainment with their knowledge on impacts of climate change showed no relationship however, with types of occupation there appeared a relationship Housewives and unemployed people are more knowledgeable on impacts than causes of climate change 24 Household Perceptions of and knowledge of Global Climate Change (Impacts) contd… Impacts of Climate Change Sea Level rise 21% 7% Degree of Icemelting 24% 13% 19% 17% Ozone Layer depletion Magnitude and Extent of… 0% 3% Impacts on weather patterns 22% 25% 2% Species extinction and/or… 1% Impacts on Ssmall Islands… Impacts on natural… Impacts on human health S. Hithadhoo 9% 11% 9% 8% 6% 5% HDH. Kulhudhufushi 25 Household Perceptions of and knowledge of Global Climate Change (gender) An important indicator for assessing the vulnerability Poverty – both a cause of vulnerability and a consequence of hazard impacts linked with female Respondents gender North (N= 113) South (N= 149) Cause Impact Cause Impact Female 29 38.7% 57 76.0% 41 39.0% 63 60.0% Male 17 50.0% 27 79.4% 21 56.8% 28 75.7% 26 Household Impacts & Adaptive Behaviour HDH. Kulhudhuffushi S. Hithadhoo 20.4% households affected (heavy rainfall, high temperature, Windstorm, Swell Surges & thunderstorm 31.5% household (heavy rainfall, high temperature, Windstorm & thunderstorm Adaptation actions North South Affected Not Affected Not affected affected Taken Adaptation actions 69.6% 12.2% 38.3% 13.7% 27 Individually Perceived ability Most on ‘stopping cutting down trees (57.5% Kulhudhuffushi & 48.3% in S. Hithadhoo) Most importantly respondent’s responses on ‘what they can do as an individual to alleviate the problem of climate change’ was somehow related to the environmental problems existing in their islands As, more responses from Hdh as ‘use proper ways to dispose waste’ and ‘stop sand mining’ in Hithadhoo shows this. 28 Conclusions Change in climate patterns, exposed to swell surges, windstorm, etc Global Climate Change Sudden, Extreme Events Impacts Perception/Knowledge • Local Weather Patterns • Causes & Impacts of Climate Change Adaptation Who & What Adapts? Due to, heavy rainfall, swell surges, high temperature and thunderstorm, windstorm How does Adaptation occur? Adaptation to What? 29 Contributions Findings of this research is expected to provide information to MEEW, contributing climate change related events in the islands Overall, this research could be extended to other regional urban centres MOE- knowledge on climate change issues MPND, Safer island Programme, Pop. Cos. Programe To others researches based on these islands, as this research explored various year’s information on events 30 Policy Implications While these centres are developed as safer islands and regional hubs, the impacts on households should be integrated when developing further infrastructure + building codes NAPA should include adaptation actions by households based on their impacts Different determinants of adaptive capacity should be included in NAPA Policies towards strengthening awareness, should include specific climate change issues, their views. 31 Recommendations for further studies Should extend to other regional urban centres Should research on how people acquire climate change knowledge. Flooding was one of the many impacts, thus, Ministry of Health should consider conducting a survey on health impacts of climate change on households Socio-economic impacts and costs involved in impacts as well adaptation actions would be useful to determine the economic effects 32 33