* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Knowledge for development under climate change Habiba Gitay
Climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
German Climate Action Plan 2050 wikipedia , lookup
Global warming controversy wikipedia , lookup
2009 United Nations Climate Change Conference wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Heaven and Earth (book) wikipedia , lookup
ExxonMobil climate change controversy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of climate change mitigation wikipedia , lookup
Climate change denial wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate resilience wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Mitigation of global warming in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Climate engineering wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Climate governance wikipedia , lookup
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Saskatchewan wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Citizens' Climate Lobby wikipedia , lookup
Economics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Solar radiation management wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Climate change adaptation wikipedia , lookup
Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Business action on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
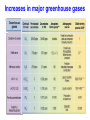
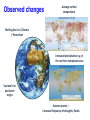
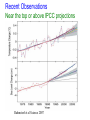
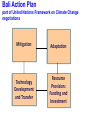
Knowledge for development under climate change Habiba Gitay World Bank Institute • A brief overview of climate change and risks to development • knowledge and capacity For publications and news on the latest climate change initiatives Look for “climate change” on www.worldbank.org includes Development Outreach and Environment Matters Earth systems • Interacting components between land, ocean and atmosphere Importance of greenhouse gases • Greenhouse gases keep the earth “habitable” Increases in major greenhouse gases Past atmospheric concentrations of CO2 700 Projected (2100) 650 600 Vostok Record IPCC IS92a Scenario Law Dome Record Mauna Loa Record 500 Concentration of carbon dioxide(CO2) in the atmosphere Current has remained within tight bounds 450 400 350 300 250 200 150 400,000 300,000 200,000 Years Before Present (B.P. -- 1950) 100,000 0 CO2 Concentration (ppmv) 550 Observed changes Average surface temperature Melting Sea Ice / Glaciers / Permafrost Increased precipitation e.g. in the northern temperate areas Sea level rise and storm surges Extreme events – increased frequency of droughts, floods Observed impacts Marine and coastal systems mangroves, coral reefs, coastal fisheries, erosion of coastlines Human societies– floods, droughts, sea level rise/storm surges affected infrastructure and livelihoods; increased water scarcity, malnutrition, vector and water borne diseases (e.g. dengue fever, cholera, diarrhoea) Observed impacts Terrestrial systems –poleward and upward migration of species/ecosystems; increase in frequency and intensity of pest and disease outbreaks (e.g. in forests), wildfires. Changes in growing seasons, increased in crops in northern temperate areas, decrease in many parts of Africa Impacts lends urgency … risk losing developmental gains Inertia and lifetime of GHGs Recent Observations Near the top or above IPCC projections Rahmstorf et al Science 2007 Managing climate risk • Impacts and ability to manage them depends on – Geographical location and exposure • Present and historical climate • Condition of natural resources (e.g. fresh water supplies, fishery, forests, agricultural production) – Sensitivity • Are the areas and populations near their “climatic limit” – Socioeconomic, institutional factors • Education • Technical and financial capacity • Political will Impacts likely to get worse A Global Deal for action • Climate Change “fundamental failure of markets” • Atmosphere suffers from “tragedy of the commons” • Action has to be effective, economically efficient and equitable and be “global” • Includes technology development and rapid sharing of technology and knowledge • Finances for both adaptation and for low carbon economies Modified from Stern & Noble 2007 Bali Action Plan part of United Nations Framework on Climate Change negotiations Mitigation Adaptation Technology Development and Transfer Resource Provision: Funding and Investment Knowledge, capacity and resources • Climate Change and how it affects development • Develop human capacity – Share knowledge rapidly – Make the needed change, learn for implementation and share that knowledge • Research and development - Knowledge generation for local context – – – – – policy changes regulatory changes technological changes Innovations (Development Market Place as an idea) Scaling-up Knowledge – Mitigation Option Include introduction and/or scaling up of: –Improved energy efficiency and conservation –cleaner oil and coal technologies; –renewable energy, including solar, wind and hydropower; –market mechanisms for carbon trading –the role of forestry and agriculture, including reduced emissions from deforestation and degradation (REDD), –policy instruments, including regulatory frameworks, as well as carbon taxes, incentives, subsidies and education to help change behavior patterns. Economically efficient technologies Sweeney 2007 Adaptation Reduce other impacts, adapt to changed conditions • Use natural resources efficiently • Change some input-intensive production systems to less intensive (e.g. agriculture) • Fix what doesn’t work now – better prepared for the future. Reality….. – Better cope with present climatic extremes – Deal with present climatic extremes in the context of all other pressures – part of development. Action from communities, government and private sector Urgency means – knowledge and capacity paramount • Improve knowledge sharing on – Early phase technologies and Approaches to adaptation – Scaling up - policies and strategies to do so national action • Enhance and maintain capacity – Understanding of climate change in university curricula – Active participation of stakeholders affected – Implement learning by doing and sharing knowledge on early action – Working across “silos” • Better risk management of present climatic conditions and preparedness for future climate • Large challenges for future generations • Work towards Low carbon economies and resilient societies Thank you More information at www.worldbank.org/ and click on climate change