* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download powerpoint
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
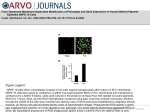
Mechanisms governing the secondary burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and basic pathways of cell death from hyperoxia. 1: Loss of plasma membrane integrity from lipid peroxidation by ROS. 2: ROS damage to the mitochondria membranes and deactivation of enzyme systems and cytochrome chain. 3: This results in the release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm. 4: ROS damage to the nuclear membrane and fragmentation of DNA. 5: Evolving cell trauma from steps 1, 2, and 4 trigger the production and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines into the extracellular space and circulation. 6: This attracts and activates platelets, neutrophils, and macrophages, resulting in a secondary burst of ROS from these inflammatory cells. Richard H Kallet, and Michael A Matthay Respir Care 2013;58:123-141 (c) 2012 by Daedalus Enterprises, Inc.