* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Framework for Teachable Unit
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
RNA silencing wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Secreted frizzled-related protein 1 wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
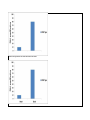
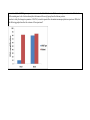
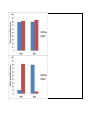
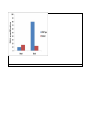
Framework for Teachable Unit Topic: EPIGENETICS Group Members’ Names: Alex, Ann, Michael, Rhishi, Tish, Yaldez, Vangelis, Jim Learning Goal: The aim of this unit is to help students understand the mechanisms of epigenetics and the role of epigenetics in organism health and development Learning Objectives: The students will be able to: 1. Model histone – DNA interactions 2. Compare and contrast the impact of acetylation and methylation on gene expression 3. Evaluate an experiment that demonstrates epigenetic silencing 4. Discuss consequences of epigenetics on human health Summative Assessments (describe how you would assess your objectives and paste in any summative assessments you have created): Drugs aimed at histone modifications are called histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors. HDACs are enzymes that remove the acetyl groups from DNA, which condenses chromatin and stops transcription. Blocking this process with HDAC inhibitors turns on gene expression. The most common HDAC inhibitors include phenylbutyric acid, SAHA, depsipeptide, and valproic acid (Egger et al., 2004). A sick patient is found to have unusual patterns of histone acetylation on a gene X that causes the transformation of haematopoietic cells into leukaemia stem cells. Treating with HDAC inhibitors targeted at gene X would have which effect(s)? Mark all that are true. _ increase in the gene expression of gene X _ no change in gene expression of gene X _ increase in the number of haematopoietic cells _ decrease in the number of growing leukaemia stem cells _ decrease in the affinity of histone tails for other nucleosomes _ increase in the recruitment of gene silencing proteins to the histone tail If a patient with cancer is found to have unusual patterns of methylation, then treating with HDAC inhibitors would have which effect(s)? Mark all that are true. _ decrease in the gene expression of gene X _ no change in gene expression of gene X _ increase in the number of haematopoietic cells _ decrease in the number of growing leukaemia stem cells _ decrease in the affinity of histone tails for other nucleosomes _ increase in the recruitment of gene silencing proteins to the histone tail This is the knowledge that the above question is testing: Acetylation increases transcription by loosening the tail by: 1) adding (+) charge to the histone tail which reduces affinity for DNA (DNA loosens) 2) reduces affinity for other nucleosomes, reducing tightness of the second order structure Methylation 1) No change in charge but methylation recruits silencing or repressive proteins to the site Formative Assessments (activities/instruction you designed to teach the learner; please describe your instructional methods referring your PowerPoint presentation so that others could give this presentation at their own institution.) An experimental technique called chromatin immunoprecipitation is used to assess DNA protein interactions. The protein complex bound DNA (Example: DNA and histones in nucleosomes) can be detected by amplifying the target DNA by PCR. Researchers used this technique to study the promoter of an organ specific gene - GATA4 which is exclusively expressed in heart and no other cell type. The amplification product from the experiment is measured and is proportional to the strength of DNAhistone interaction (Figure 1). Which bar represents the heart and which the brain? In mutant cells, the GATA4 gene expression was seen to be abolished in heart cells. Successive experiments annotated the function of the mutant genes to be a histone deacetylase that removed the acetyl group from the histone proteins. In order to study the changes in promoter of GATA4, scientists repeated the chromatin immunoprecipitation experiment. Which of the following graphs describes the outcome of the experiment?