* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fast and simple purification of GST fusion proteins using prepacked
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
G protein–coupled receptor wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Intrinsically disordered proteins wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
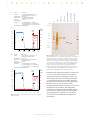
I N N O V A T I O N S F O R U Fast and simple purification of GST fusion proteins using prepacked GSTrap affinity columns L. Haneskog, H. J. Johansson, and A. Heijbel Amersham Biosciences, Uppsala, Sweden P R O T E I N P U R I F I C A T I O N ready-to-use 1 ml and 5 ml HiTrap columns containing Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow (Fig 1). The columns are designed for one-step purification of GST fusion proteins, other glutathione S-transferases, and glutathione binding proteins. Sample application, washing, and elution can be performed using a syringe, pump, or liquid chromatography system such as ÄKTA™design, GradiFrac™, or FPLC™. GSTrap™ affinity columns are prepacked, ready-to-use 1 ml and 5 ml HiTrap™ columns containing Glutathione Sepharose™ 4 Fast Flow. They are designed for one-step purification of glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion proteins, other glutathione S-transferases, and glutathione binding proteins. Sample application, washing, and elution can be performed using a syringe, pump, or liquid chromatography system. Here, we demonstrate the performance of the columns by purifying a GST fusion protein from 8 ml and 40 ml of a cell lysate using GSTrap 1 ml and 5 ml columns, respectively. On-column cleavage with thrombin is also demonstrated. Introduction The Glutathione S-transferase (GST) Gene Fusion System is a versatile expression system that has been cited in thousands of published studies involving protein-protein interactions, nucleic acid-protein interactions, antibody production, and many other applications. The system is based on inducible, highlevel, bacterial expression of genes or gene fragments as fusions with Schistosoma japonicum GST (1). GST fusion proteins are constructed by inserting a gene or gene fragment into the multiple cloning site of one of the 13 pGEX vectors. Expression in E. coli yields fusion proteins with the 26 kDa GST moiety at the amino terminus and the protein of interest at the carboxyl terminus. Fig 1. GSTrap and Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow are designed for the isolation and purification of GST fusion proteins, other glutathione S-transferases and glutathione binding proteins. Column design HiTrap columns are convenient, reliable, and affordable multi-use columns designed for fast and easy preparative separations. The columns can be used separately or connected together in series. Columns are made of medical-grade polypropylene, a biocompatible material that does not interact with biomolecules. Top and bottom frits are manufactured from porous polyethylene. The frits allow high flow rates but prevent columns from running dry. GSTrap columns are delivered with a stopper on the inlet and a twist-off end on the outlet. Both ends have M6 connections (6 mm metric threads). GST fusion proteins are easily purified from bacterial lysates by affinity chromatography using immobilized glutathione. GST fusion proteins are captured by the affinity medium and impurities are simply removed by washing. Fusion proteins are eluted under mild, nondenaturing conditions using reduced glutathione. The purification process preserves protein antigenicity and function. Three GST purification modules are available that use Glutathione Sepharose 4B in gravity flow-, centrifugation-, or vacuum-based methods. GSTrap affinity columns present a fourth option for fast and easy purification of GST fusion proteins in a convenient format. GSTrap columns are prepacked, Life Science News 4, 2000 Amersham Biosciences 1 M I N N O V A T I O N S F O R U Glutathione Sepharose Fast Flow Easy operation Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow, a high-capacity affinity media with excellent flow properties, is the base matrix for GSTrap 1 ml and 5 ml columns. The glutathione ligand is coupled via a 10-carbon linker to highly cross-linked 4% agarose. The coupling is optimized to give a high binding capacity for GST fusion proteins and other glutathione binding proteins. The total binding capacity is approximately 10 mg recombinant GST/ml gel. The dynamic binding capacity will vary depending on flow rate and sample properties. Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow is available in lab packs for scale-up. Table 1 lists the main characteristics of GSTrap and Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow. GSTrap columns are quick and easy to use. Instructions and connectors (M6 and luerlock) are included. The columns can be used simply with a syringe for loading, washing, and elution. Alternatively, columns can be used with a pump or liquid chromatography system. The use of GSTrap columns with ÄKTAexplorer 10 is highlighted below. Purification of a GST fusion protein An E. coli culture expressing a GST fusion protein was harvested, washed and resuspended (1 g/10 ml) in phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.3) supplemented with 1 mM PMSF, 10 mM DTT, 100 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mg/ml lysozyme, and 1.7 U/ml DNase. The cell suspension was incubated for 1 h at +4 ˚C with slow magnetic stirring. The suspension was then frozen and thawed to lyse the cells. The lysate was incubated at + 4 ˚C for an additional 30 min to cleave chromosomal DNA and reduce viscosity. Cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 47 000 × g, + 4 ˚C for 20 min. The supernatant was filtered (0.2 µm filter) before applying to GSTrap. Table 1. Main characteristics of GSTrap and Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow. Column dimensions i.d. × h GSTrap 1 ml 0.7 × 2.5 cm GSTrap 5 ml 1.6 × 2.5 cm Column volumes 1 ml and 5 ml Ligand glutathione and 10-carbon linker arm Ligand concentration 120–320 µmol glutathione/ml gel Binding capacity 10 mg recombinant glutathione S-transferase/ml gel (GST, Mw: 26 kDa) GSTrap columns were equilibrated with 4 column volumes (CV) PBS (pH 7.3) and the lysates were applied (8 ml on GSTrap 1 ml and 40 ml on GSTrap 5 ml). The columns were washed with 10 CV PBS and eluted using 5 CV 50 mM TrisCl (pH 8.0), 10 mM reduced glutathione (Fig 2). The runs were completed in 25 min using ÄKTAexplorer 10. Analysis by SDSPAGE indicated the isolation of highly pure GST fusion protein (Fig 3). Fusion protein yields were 2.7 mg from GSTrap 1 ml and 13.4 mg from GSTrap 5 ml. 11 mg GST fusion protein/ml gel Mw: 43 kDa (GSTrap 1 ml at 1 ml/min) Mean particle size 90 µm Bead structure highly cross-linked 4% agarose Maximum back pressure GSTrap 0.3 MPa, 3 bar Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow 0.1 MPa, 1 bar (packed in XK column. May vary if used in other columns) Maximum flow rates GSTrap 1 ml 4 ml/min GSTrap 5 ml 15 ml/min On-column proteolytic cleavage Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow 450 cm/h, (15 ml/min using XK 16/20 column, run at room temp. with aqueous buffer) Although many applications do not require the removal of the GST moiety, it may be necessary when the presence of an affinity tag raises concerns about the physical or structural properties of the protein of interest (e.g. crystallographic studies). To address this need, all pGEX vectors include sequences between the GST gene and the multiple cloning site that encode protease recognition sites (thrombin, factor Xa, or PreScission™ Protease). Treatment with the appropriate protease cleaves the GST moiety from the protein of interest. Recommended flow rates Sample loading: GSTrap 1 ml 0.2–1 ml/min GSTrap 5 ml 1–5 ml/min Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow < 100 cm/h (< 3 ml/min using XK 16/20 column) Wash and elution: GSTrap 1 ml 1–2 ml/min GSTrap 5 ml 5–10 ml/min (5 ml) Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow 100–300 cm/h (3–10 ml/min using XK 16/20 column) Chemical stability All commonly used aqueous buffers, e.g. 1 M acetate pH 4.0 and 6 M guanidine hydrochloride for 1 hour at room temperature pH stability pH 6–9 Storage temperature + 4–8 ˚C Storage buffer 20% ethanol Proteolytic cleavage can be performed in solution after elution or while the fusion protein is bound to an affinity medium (2), such as GSTrap. Cleaving while bound to GSTrap eliminates the extra step of separating the released protein from GST because the GST moiety remains bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow. Life Science News 4, 2000 Amersham Biosciences 2 M O S GSTrap 1 ml 8 ml cytoplasmic extract from E. coli expressing a GST fusion protein PBS, pH 7.3 50 mM TrisCl (pH 8.0) with 10 mM reduced glutathione 1 ml/min Flow rate: Chromatographic procedure: 4 CV binding buffer, 8 ml sample, 10 CV binding buffer, 5 CV elution buffer, 5 CV binding buffer (CV = column volume) Instrumentation: ÄKTAexplorer 10 A280 F O R U Mr (× 103) % elution buffer elution buffer 3.5 94 – 3.0 100 2.5 67 – 2.7 mg pure GST fusion protein wash 2.0 80 43 – 60 1.5 30 – 40 1.0 20.1 – 20 0.5 14.4 – 0 0 5.0 5.0 B. N M I thrombin solution T GST after thrombin Binding buffer: Elution buffer: A target after thrombin Column: Sample: V GSTrap 5 ml O GSTrap 1 ml A. N lysate N M I Column: Sample: Binding buffer: Elution buffer: 10.0 10.0 15.0 15.0 ml min 20.0 20.0 GSTrap 5 ml 40 ml cytoplasmic extract from E. coli expressing a GST fusion protein PBS, pH 7.3 50 mM TriHCl (pH 8.0) with 10 mM reduced glutathione 5 ml/min Fig 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of a GST fusion protein purified with GSTrap affinity columns. A cytoplasmic extract from an E. coli culture expressing a GST fusion protein was loaded onto GSTrap 1 ml and GSTrap 5 ml columns (8 ml and 40 ml of lysate, respectively). Fusion protein was eluted using 10 mM reduced glutathione (lanes marked “GSTrap 1 ml” and “GSTrap 5 ml”). On-column cleavage with thrombin (20 U/ml) was performed with GSTrap 1 ml loaded with fusion protein. The GST-free target protein was eluted with phosphatebuffered saline (lane marked “target after thrombin”) and the GST moiety was eluted with 10 mM glutathione (lane marked “GST after thrombin”). M = LMW Marker Kit (17-0446-01), reduced. Flow rate: Chromatographic procedure: 4 CV binding buffer, 40 ml sample, 10 CV binding buffer, 5 CV elution buffer, 5 CV binding buffer (CV = column volume) Instrumentation: ÄKTAexplorer 10 % elution buffer A280 elution buffer 3.5 3.0 Results from this technique are shown in Figures 3 and 4. A GST fusion protein containing the recognition sequence for thrombin was applied to GSTrap 1 ml. After washing, the column was filled by syringe with 1 ml thrombin solution (20 U/ml in PBS), prepared according to the manufacturer’s protocol (Amersham Biosciences, Fig 4A). The column was sealed using the supplied connectors and left for 16 h at room temperature. After incubation, the target protein minus the GST moiety was eluted using PBS, and the bound GST was eluted using elution buffer (Fig 4B). The cleavage reaction yield was 100%. Intact GST fusion protein was not detected in the glutathione eluate (Fig 3). 100 wash 2.5 13.4 mg pure GST fusion protein 2.0 80 60 1.5 40 1.0 20 0.5 0 0 20 4 40 8 60 12 80 16 100 20 ml min Fig 2. Purification of a GST fusion protein on GSTrap 1 ml (A) and GSTrap 5 ml (B). Life Science News 4, 2000 Amersham Biosciences 3 M I N A. N O Column: Sample: Binding buffer: Elution buffer: Flow rate: Chromatographic procedure: Instrumentation: V A T I O S F O R U Summary GSTrap 1 ml 10 ml cytoplasmic extract from E. coli expressing a GST fusion protein PBS, pH 7.3 50 mM TrisCl (pH 8.0) with 10 mM reduced glutathione 1 ml/min GSTrap combines the versatility of HiTrap columns with the high capacity and excellent flow properties of Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow to provide a fast and convenient method for purification of GST fusion proteins. GSTrap columns are directly compatible with existing purification protocols for GST fusion proteins, including on-column proteolytic cleavage methods. Purifications can be scaled-up easily by connecting multiple columns in series, or larger columns can be prepared using Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow, which is available in a lab pack size. 4 CV binding buffer, 10 ml sample, 10 CV binding buffer, filling column with 1 ml thrombin solution using a syringe (CV = column volume) ÄKTAexplorer 10 A280 3.5 3.0 N wash 2.5 References 1. Smith, D.B. and Johnson, K.S., Gene 67, 31–40 (1988). 2. Gearing, D.P. et al., Bio/Technology 7, 1157–1161 (1989). incubation 16 h room temp. 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 0 5.0 B. Column: Sample: Binding buffer: Elution buffer: Flow rate: Chromatographic procedure: Instrumentation: 10.0 15.0 GSTrap 1 ml column after 16 h incubation with thrombin PBS, pH 7.3 50 mM TrisCl (pH 8.0) with 10 mM reduced glutathione 1 ml/min 8 CV binding buffer (elution of cleaved target protein), 5 CV elution buffer (elution of free GST and non-cleaved GST-fusion protein), 5 CV binding buffer (CV = column volume) ÄKTAexplorer 10 A280 3.5 3.0 100 2.5 GSTrap 2 × 1 ml 17-5130-02 GSTrap 5 × 1 ml 17-5130-01 GSTrap 1 × 5 ml 17-5131-01 Glutathione Sepharose 4 Fast Flow 25 ml* 17-5132-01 * Larger quantities are available. Please contact Amersham Biosciences for more information. % elution buffer 80 2.0 free GST 1.5 1.0 ORDERING INFORMATION min 60 target protein 40 20 0.5 0 0 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 min Fig 4. On-column thrombin cleavage of a GST fusion protein. A. Equilibration, sample application, and washing of a GST fusion protein on GSTrap 1 ml was performed using ÄKTAexplorer 10. After washing, the column was filled by syringe with 1 ml thrombin solution (20 U/ml PBS) and incubated for 16 h at room temperature. B. GST-free target protein was eluted using PBS. GST was eluted using 10 mM reduced glutathione. The GST-free target protein fraction also contains a small amount of thrombin (not detectable on SDS-PAGE, see Fig 3). © Amersham Biosciences Ltd. 2000—All rights reserved. Life Science News 4, 2000 Amersham Biosciences 4 M









![[Type text] Calculating GST at 15% As the new GST rate of 15% is](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015582132_1-3c99bf1d61a64dd4330838d96e160e5b-150x150.png)