* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes- Nerve Impulses and Junctions
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
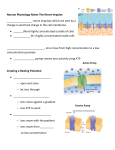
Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ Notes- Nerve Impulses and Junctions The Resting Neuron - Not transmitting an _____________________________ Outside has a net ____________________________ Inside has a net _________________________ Cells are “_____________________” because there is a difference in _______________ _____________________________________________________ Ions that take part in polarization of nerve cell membrane= 1. 2. Nerve cells pumps ______________________________out of cell and __________________ ______________________ into cell by means of _____________________________________ - Sodium-potassium pump= The Nerve Impulse During an impulse (or signal) the inside of the cell becomes ______________________ _______________ and the inside becomes ________________________ (opposite of resting) This reversal takes place in: Results in a flow of ___________________________________________________ This current moves down the length of the neuron and affects the ________________ ______________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________= reversal of polarization moving down cell 1 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ This impulse is like a set of dominos stacked up; once you knock them down, you can knock them down the other way (only moves in 1 direction) ______________________________________________= brief period when the neuron membrane cannot be _____________________________________________________ Lasts a nanosecond Rate of Impulse Conduction - Rate at which the impulses travel depends on 2 factors: 1. ____________________________________________________________________ a. Larger the neuron=_______________________________________________ 2. Whether or not the nerve fiber has a _____________________________________ _____________________ a. Impulse travels faster _______________________________________ b. Carry impulses more quickly b/c _____________________________________ Nerve Cell Thresholds = “All or nothing”= Like firing a gun Transmission at the Synapse - Tiny gap between end of ________________ and the ______________________of another - Axon ends in a ______________________________________________________ - Gap= synaptic gap Transmission across the gap= - Inside the knob there are small sacs called _____________________________________ - When impulse reaches the knob, some of the ________________________________ ________________________________________________ and starts the impulse in the neighboring nerve cell by changing the__________________________ of its membrane 2 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ - NOTE: It is not the impulse that crosses the synapse, only_________________________ ___________________ - Different types of neurons release ___________________________________________ o Example: Acetylcholine (Ach), Norepinephrine (NE), and histamine o Serotonin, epinephrine, glycine Example of this process in action: Impulses pass from __________________________________________ to muscles at special points of contact called neuromuscular junctions Motor end plates contain neurotransmitters called_____________________________ When an impulse reaches the motor end plates, they cause the ______________ ______________________________________ which diffuses across the gap of the axon and reaches the membrane of the adjacent muscle cell Then it combines with ______________________________________ on the muscle cell membrane This combo increases the __________________________________________________ _________________________ to sodium ions This causes impulses to travel along the _______________________________________ _________________________________ 3 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ INTRODUCTION: In this activity, you will set up a model to simulate how a neuron processes information. The model will include such items as peas, beans, and construction paper. You will need to know the following facts. FACT 1: Lentils represent sodium ions. There are more sodium ions outside the nerve cell than inside, so there are more pintos in the “outside” pan. Lima beans represent potassium ions, pinto beans represent chloride ions, and the wads of construction paper represent proteins. In a real cell, there would be millions of ions, but there is not enough room for that many beans on your poster board. Sodium and potassium ions have a positive charge, while chloride ions and proteins carry a negative charge. FACT 2: A positive charge attracts a negative charge, and vice versa. However, positive charges repel each other, and so do negative charges. FACT 3: Electrical charge (resting membrane potential) is the result of excess ions on one side of the cell membrane. FACT 4: One force acting on the ions is for them to move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration. FACT 5: The facts above describe all cells, even plant cells. However, nerve cells are unique. They have specialized proteins in their membranes called channels or gates. Nerve cells have channels for sodium, potassium, chloride, and other ions, that will only recognize one ion. If a sodium channel opens, sodium ions, but no other ions, can pass through. Channels are very narrow and ions must line up one at a time to pass through the channel, no matter which direction they go. Proteins are too big to fit through any of these channels and must stay inside the cell. In a nerve cell without any channels (gates) open, the charge inside the cell relative to the outside is negative (-70mV). 4 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ MATERIALS PER GROUP: 900 mg of the following: Lentils Lima beans Pinto beans metric ruler 2 aluminum pie pans 2 Post-itTM notes posterboard (or a large piece of paper) toothpicks magic marker PROCEDURE: Follow the teacher’s directions as you set up your nerve cell model. You will use your model cell to answer questions. It may help to take the beans (ions) out of the pans and move them around to visualize the answer to your question. The bean mover in your group can move the beans, and the data recorder can record the results. QUESTIONS: 1. Look at the numbers of lentils representing the sodium ions in the pans inside and outside the cell. If the sodium channel were suddenly opened so that sodium ions could move across the cell membrane: a. Which direction would they tend to move based on their concentration: into or out of the cell? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ b. Which direction would they tend to move based on their charge: into or out of the cell? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 2. A sodium channel opens for about one millisecond. Each group’s timekeeper will time the opening of the sodium channel for 10 seconds, representing one millisecond. Before he/she begins timing, decide which direction the sodium ions will move based on your answers to questions 1a and 1b. When the teacher 5 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ gives the signal, the timekeeper will begin timing for 10 seconds. Immediately have the gatekeeper open the sodium channel by moving the toothpick as shown by the teacher. Then the bean mover should take the lentils out of the pan and drag them through the sodium channel one at a time in the direction you think they will go until the timekeeper stops timing. Note: Leave the sodium ions where they are now as you answer questions 3-8, but close the sodium channel. If you used Post-itTM notes to mark “negative” and “positive” remove these notes now. 3. Look at the numbers of sodium ions on each side of the cell membrane now. Compared to the number in each pan at rest, are there: (circle one) a. More sodium ions inside the cell now than there were before, or b. Fewer sodium ions inside the cell now than there were before? 4. Based on your answer to question 3, do you think the internal medium of the cell is: a. More negative than it was before, or b. More positive than it was before? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Look at the numbers of lima beans in the pans, both inside and outside the cell. If the potassium channel was suddenly opened so that potassium ions could move across the cell membrane: a. Which direction would they tend to move based on their concentration: into or out of the cell? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ b. Which direction would they tend to move based on their charge: into or out of the cell? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 6 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ 6. A potassium channel opens for one to three milliseconds. Follow the directions in number 2 above, except now you must open the potassium channel. Remember to decide which direction the potassium will move based on your answers to questions 5a and 5b before the teacher gives the signal for the timing to begin. 7. Look at the numbers of potassium ions on each side of the cell membrane now. Compared to the number in each pan at rest, are there: (circle one) a. More potassium ions inside the cell now than there were before, or b. Fewer potassium ions inside the cell now than there were before? 8. Based on your answer to question 7, do you think the internal medium of the cell is: a. More negative than it was before you had opened the potassium channel (but after you had opened the sodium channel and moved the lentils), or b. More positive than it was before you had opened the potassium channel (but after you had opened the sodium channel and moved the lentils)? Explain. _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 9. In the nerve cell axon, something happens called sodium channel inactivation. This means that after the sodium gates open and close, they cannot open again for a few milliseconds. a. What is this period of time called?________________________________________________________ b. If you were to line up a number of your models to represent a longer stretch of a nerve cell axon, what effect would this have on the action potential? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ c. Does it make a difference if you start at one end of the long line, or in the middle? Explain. ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________ 7 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ After a lot of action potentials have occurred, will enough lentils/beans/ions move to change significantly the concentration gradients you set up initially when your model was at rest? Would the sodium and potassium ions continue to move as they did during the action potential you simulated in this activity? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10. In order to continue functioning properly, the cell must now somehow get back to its resting state. How might the cell do this? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________________ 11. The simulation you have completed is with a model of an unmyelinated neuron. How would a myelinated neuron simulation differ? __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________________ 8 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ Online Field Trip! Navigate to the sites below and answer the following questions/fill in the blanks: http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter45/animations.html# Click on the link titled “Function of the Neuromuscular Junction (699.0K)” Watch the video and take notes IN YOUR OWN WORDS: Click on the last link titled “Action Potential Propagation in an Unmyelinated Axon (366.0K)” 9 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ Now navigate to http://www.miketheheadlesschicken.org/story.php Read the story about Mike the Headless Chicken. 1. How long did Mike live without a head? 2. Why didn’t Mike bleed to death? 3. How did Mike survive the beheading and how was he still able to live without a brain? (Where where is motor impulses sent to?) 4. How did Mike ultimately perish? 10 of 11 Name: ________________________________________________________________ Date: ________ Hour: _________ Now navigate to http://www.scientificamerican.com/article.cfm?id=fact-or-fiction-cockroachcan-live-without-head Read the article and answer the following: Why can cockroaches live so long without a head and humans can’t? Lastly, navigate to http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/words.html Try the experiment. Your results: Word Set 1 Time= Word Set 2 Time= Why does this occur? 11 of 11