* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diapositiva 1
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
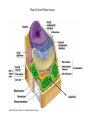
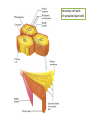
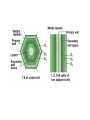
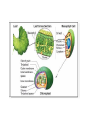
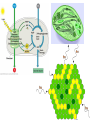
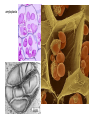
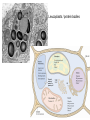
Plant Cell and Plant tissues plastids Cell wall Primary wall composition and architecture Primary walls isolated form higher plant tissues and cells are composed predominantly of polysaccharides together with lesser amounts of structural glycoproteins (hydroxyproline-rich extensins), phenolic esters (ferulic and coumaric acids), ionically and covalently bound minerals (e.g. calcium and boron), and enzymes. In addition walls contain proteins (expansins) that are believed to have a role in regulating wall expansion Cellulose - a polysaccharide composed of 1,4-linked β-D-glucose residues Hemicellulose - branched polysaccharides that are structurally homolgous to cellulose because they have a backbone composed of 1,4-linked β-D-hexosyl residues. The predominant hemicellulose in many primary walls is xyloglucan. Other hemicelluloses found in primary and secondary walls include glucuronoxylan, arabinoxylan, glucomannan, and galactomannan. Pectin - a family of complex polysaccharides that all contain 1,4-linked α-Dgalacturonic acid. To date three classes of pectic polysaccharides have been characterized: Homogalacturonans, rhamnogalacturonans, and substituted galacturonans. Microcrystalline cellulose is embedded in a hydrated matrix consisting of coextensive networks of complex heteropolysaccharides and sometimes glycoproteins. Cell walls also constitute renewable resources and are often present in by-products of industrial production. Genetic engineering of crop plant cell walls can identify biopolymers with novel functional properties, as well as simplify their extraction, thus increasing the value of these "waste-products." Cell walls will become more important in the future, as they are an abundant resource that can contribute to our biofuel needs. Chitin is a polymer of β1–4-linked GlcNAc, which occurs in chains that typically exceed 1000 residues. These chains self-associate to form microfibrils and are deposited primarily at the bud neck of yeast or at septa in filamentous fungi. The cell-wall polysaccharides that have been described so far are composed of polymers of mannose, glucose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, and/or rhamnose, and these include mannans, glucans, chitin, galactomannans, glucomannans, rhamnomannans, and phosphomannans. Secondary cell walls of specialized plant cells sclerenchymatic cell walls tannins Chloroplasts Chromoplasts Plastids amyloplasts Leucoplasts / protein bodies All plant seeds that store triglycerides as future energy sources, eg. safflower, sunflower, canola, cottonseed, etc, sequester these oils in specialized organelles called Oleosomes