* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) - LSU School of Medicine
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
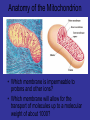
Biochemistry is fun!!! La Bioquímica es divertida!!! Citric Acid Cycle (CAC) “Kreb Cycle” Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle 2/3 of O2 consumption needed for oxidation of Acetyl CoA CO2 • Occurs exclusively in the mitochondrion (matrix) • OAA acts as carrier or acceptor of acetyl CoA units – is regenerated • “Burns” acetyl CoA to CO2 – during this oxidation eˉs from acetyl CoA are trapped in the form of: Pyruvate NADH Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex “links” glycolysis to CAC FADH + 2eˉ + 2eˉ + 2eˉ + 2eˉ GTP ATP (substrate level phosphorylation) The Three Stages of Metabolism (H.A. Krebs) The Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle; The TCA Cycle • Pyruvate (actually the acetyl group) from glycolysis is degraded to CO2 – The acetyl group is formed in stage II of metabolism from carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism • 1GTP (ATP in bacteria) and 1 FADH2 is produced during one turn of the cycle • 3 NADH are produced during one turn of the cycle • NADH and FADH2 energize electron transport and oxidative phosphorylation • Eight reactions make up the Krebs cycle – If you are given the name of the enzyme, you should be able to draw the structure of the reactants and products – You may be given the names of all eight reactions and will be expected to reproduce the whole cycle Overview of the Krebs Cycle: A Mitochondrial Process Anatomy of the Mitochondrion • Which membrane is impermeable to protons and other ions? • Which membrane will allow for the transport of molecules up to a molecular weight of about 1000? Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex Multimolecular aggregate 3 Enzymes Cytoplasm Pyruvate * Pyruvate transporter 5 Coenzymes 5 Reactions CoA contains the vitamin Pantothenic acid Product Inhibition Coenzymes Thiamine Pyrophosphate (TTP) NAD+ FAD+ CoA Lipoic acid * Pyruvate mito matrix Irreversible Links glycolysis to CAC Mitochondrial matrix PDH Deficiency – results in Congenital Lactic Acidosis Pyruvate cannot enter the CAC and results in ↑ Lactic Acid Primarily affects the brain – neonatal death 3 Forms – psychomotor retardation √ Possible treatment is ketogenic diet: Low in CHO CAC High in fats Produces ketone bodies as an alternate form of energy for the brain Arsenic Poisoning – Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Both require lipoic acid as a cofactor – a-Ketoglutarate Dehydrogenase Arsenite – Trivalent form of arsenic I° – Forms a stable complex with the thiol (-SH) group of Lipoic Acid II° – Glyceraldehyde 3-PO4 step forms complex with inorganic Pi thus prevents ATP formation in glycolysis Affects the brain – Death, neurologic problems Skeletal muscle Contraction √ Allosteric Regulation cAMP dependent √ Allosteric Regulation Carrier Aldo condensation The entrance of acetyl CoA does not ↑ or ↓ intermediates in the CAC Fluorocitrate Fluoroacetate Rat poison (¯) Oxidative decarboxylation ADP (+) One of the rate limiting Rxs of the CAC ATP NADH¯ e¯ Irreversible (1) Oxidative decarboxylation Very similar to the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase complex Irreversible (2) ( ¯ ) e¯ From oxidation of odd number FAs ADP ATP. GTP Succinyl CoA NADH GDP ATP Nucleoside Biphosphate Kinase e¯ “Substrate Level Phosphorylation” Irreversible (3) Oxidation reaction Hydration reaction Reversible oxidation reaction e¯ (4) Summary Regulation of the CAC Dependent on the energy state of the cell which is reflected by [ADP] [Pi] [ATP] ratio This ratio determines the rate of oxidative phosphorylation Named “Respiratory Control” of energy production because oxidation and phosphorylation of ADP must occur simultaneously Biochemistry is fun!!! La Bioquímica es divertida!!!