* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
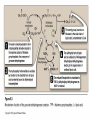
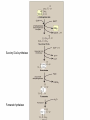
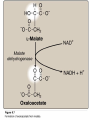
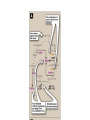
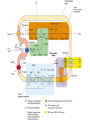
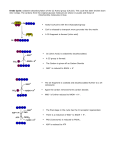
TRICARBOXYLIC ACID CYCLE DENTAL BIOCHEMISTRY 2015 LECTURE 12 Michael Lea LECTURE OUTLINE • The tricarboxylic acid cycle (Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle) is a focal end point for the oxidation of carbohydrate, fat and amino acids via acetyl coenzyme A. • Pyruvate is converted to acetyl coenzyme A by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex. • The reactions of the TCA cycle generate carbon dioxide, reduced NAD, reduced FAD and GTP • There are negative and positive controls for the TCA cycle SUGGESTED READING • Lippincott’s Biochemistry, 6th edition, pages 109-115 Succinyl CoA synthetase Fumarate hydratase COMPETING REACTIONS • Intermediate compounds in glycolysis and the TCA cycle can be used in many metabolic pathways • Diversion of intermediates creates a need for reactions that will maintain the level of oxaloacetate. ANAPLEROSIS (filling up) • One of the most important reactions for the production of oxaloacetate is the reaction catalyzed by pyruvate carboxylase. • High levels of pyruvate carboxylase for gluconeogenesis occur in liver and kidney but other cells have lower activities of pyruvate carboxylase to maintain the concentration of oxaloacetate. REGULATION OF PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE AND THE TCA CYCLE Enzyme Inhibitor PyruvateDH ATP NAD H Acetyl CoA Citrate synthase ATP IsocitrateDH ATP NAD H -Ketoglutarate DH NAD H Succinyl CoA Activator ADP LECTURE OBJECTIVES • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • After studying this lecture material you should be able to Regarding the tricarboxylic acid cycle 1. describe the enzymes and cofactors for each reaction. 2. recognize the regulated reactions and effectors. 3. identify the location of the cycle enzymes in the cell. Regarding the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex 1. distinguish the subunits and cofactors of the complex. 2. recognize the individual reactions catalyzed by the enzyme sub units. 3. recognize the effecters of control of the complex. Regarding the integration of the cycle in cell metabolism 1. recognize the anapleurotic reaction that replenishes the cycle from pyruvate. 2. name the sources of acetyl CoA for the cycle.