* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download B cells and T cells Immunoglobulins
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
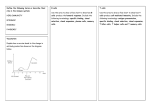
Immune system B cells and T cells - many different types of cells mediate the immune response to destroy bacteria and viruses as well as pre-cancerous cells stem cell myeloid progenitor lymphoid progenitor Y T - all cells in the immune system, as well as all the red blood cells, arise from totipotent stem cells in the bone marrow B Y Y Y r.b.c Y Immunoglobulins (antibodies) B cells and T cells IgA, IgE, IgG Y Memory T cell Effector Y Y Y Plasma B cells T cells Memory T cell Effector T cells Class [IgX]/ml IgG 12 mg IgA 1 mg Y Plasma B cells IgA, IgE, IgG, IgM Y Immunoglobulins Y Y Memory B cell Y Memory B cell Y pre B cell Y Y Y pre T cell Y Y stem cell Y lymphoid progenitors Immunoglobulins structure function K2 2 bind antigens which invade body Class IgM [IgX]/ml structure function 1 mg K2 2 immature Ab IgD 1 mg K2 2 K2 IgE * 0.001 K2 2 2 in tears, saliva, mucus; resp., intestinal tracts * IgE levels are elevated during allergic response unknown -stimulates mast cells to release histamine Immunoglobulins Antibody structure (antibodies) N N N - antibody molecules (Ab) are large globular proteins located on surfaces of B lymphocytes N L L light chain heavy chain - oligo saccharide chains of specific seq. of sugars is attached to some a.a., generally asn, ser and thr residues constant region carbohydrate C Light chains N 1 constant a.a. seq. C Heavy chains N C variable 109 a.a. seq. variable region 214 - variable a.a. sequence is different in each antibody - constant a.a. sequence is same in each antibody Functions of different regions 1. variable region = site of antigen binding - hypervariable segments of both chains are extremely variable in a.a. sequences antigen binding site 1 CHO chains 109 variable a.a. seq. C 446 constant a.a. seq. - variable a.a. sequence is different in each antibody - constant a.a. sequence is same in each antibody Functions of different regions 2. constant regions - recognize cell membrane glycoproteins of host cells recognizes host cell membranes antigen binding site oligosaccharide chains Immunogenetics Healthy adults have about 500,000 different antibody molecules circulating in blood. Does a new antigen (foreign protein) cause a new antibody to be formed specifically against it? - each antibody has a unique H chain and L chain NO! Is there one gene for each unique H protein and L protein in the human body? NO! Heavy chain formation in B cell Different regions of the different V,D,J and C genes in the DNA of B lymphocytes are selected AT RANDOM to form the mRNA. DNA V genes D J genes genes 10 families 12 4 “gene” for antibody DNA RNA polymerase DNA “new gene” for antibody Modifications are made to nascent protein (pre-pro IgG Heavy chain) N 1. N-terminal seq. is removed at membrane immature m RNA removal of intervening sequences 8 genes joining randomly selected V, D, J and C regions This mRNA is modified and translated into an immature antibody protein (Ab). Formation of heavy chain mRNA C genes 2. 2 H chains and 2 L chains associate m RNA V DJ C 3. sugars are added C Clonal selection theory of immune response 1. RANDOM selection of specific V, D, J, and C genes to produce “recombinant gene’ for antibody Clonal selection theory of immune response 3. Mature B cells die unless activated by an antigen binding to V region Y Y Y B cell Y Clonal selection theory of immune response 2. Each mature B lymphocyte produces only ONE specific antibody protein. Clonal selection theory - each Ab protein recognizes a specific chemical grouping on antigen surface - if antigen binds Ab, then B cell divides rapidly producing millions of B cell clones Y - V region of antibody projects out of cell membrane Immune repertoire Many different antibodies are formed against one virus coat or one bacterial cell wall. Antigens such as virus coat proteins and bacterial cell walls may be bound by different antibodies . New viruses and bacteria are usually bound by one or more old antibodies. Y Y Y Y Y Y Y Y B cells B cells Immune system Bone marrow Totipotent stem cells are dividing continuously and the daughter cells are differentiating into red and white blood cells. bone marrow B lymph tissue bone marrow B lymph tissue B T B B B B B virus T B B B B Antigen independent bone marrow Antigen dependent lymph tissue B Antigen independent Antigen dependent Typical pattern of immune dysfunction after HIV infection 1000 B B T AIDS virus kills helper T cells B concen. T cells 250 B 0 B Antigen independent Antigen dependent Nutrition and the Immune system - folate, vitamins C, E, B-6 and B-12 are essential for optimal functioning of immune system - also a moderate to high protein diet increases immune efficiency 12 24 36 48 60 months after infection Deficiencies and decreased immune response • deficiency of vitamin B-6 causes reduced stimulation of lymphocytes by antigens • Cu++ and Zn++ deficiencies lead to decreased number of B lymphocytes • deficiency of vitamins A, C and E result in impaired T-cell mediated immunity Cancer and immune surveillance - pre-cancerous cells arise in all humans every day - most pre-cancerous cells are identified by T cells of the immune system and are destroyed before dividing Cancer risks for Americans Risk factors for cancer Deaths / yr. per million Amer. 1. diet quality (anti-oxidants) 2. tobacco use 3. sexual behavior 4. alcohol 5. pollution 6. industrial waste 7. occupational 8. food additives 714 612 143 82 61 41 < 20 < 20 Cancer risks for Americans Risk factors for cancer alcohol abuse food additives diet quality industrial waste occupational hazards pollution sexual behavior tobacco use Deaths / yr. per million Amer. 714 612 143 82 61 41 < 20 < 20