* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dominant Traits - Stronger Trait Recessive Traits
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
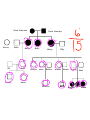
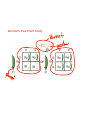
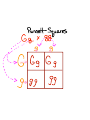
Dominant Traits - Stronger Trait The trait that shows up Shown with a capital letter Example: Brown Eyes (BB) or (Bb) Recessive Traits - Weaker Trait The Hidden trait Shown with a lower case letter Example: Blue Eyes (bbO Principles Of Genetics 1. Traits are passed from parents to offspring 2. Traits are controlled by genes 3. Inherit genes in pairs - One from each parent 4. Some genes are Dominant and others are recessive 5. Dominant genes hide recessive genes 6. Some genes show incomplete dominance Genetics And Probability What are the odds of having blue-eyed children? Great Grandma Bunny Bilbo Betty Bif Babs Buddy Berta Great Grandpa Buffy Bianca Becky Bess Bubba Beatrice Billy Brooke Barnie Basil Bobby Beth Bonnie Blaire Belle Structure of DNA 1. The Thread of Life 2. In each cell that makes up your body information is stored in the form of DNA 3. Genetic Blueprint that contains all the directions that control your body 4. Looks like a twisted ladder 5. Made up of 3 substances connected in a certain pattern a. Phosphate b. Deoxyribose c. 4 bases - That make up the rungs of the ladder DNA One small section of a chromosome is called a GENE. Gregor Mendel is known as the "Father of Genetics". He was the first to study traits and heredity. (He is famous for his Pea Plant Study.) 7. A change or mistake in the DNA is called a mutation 8. The division of the body cells is called Mitosis 9. Meiosis is the division of the sex cells Mendel's Pea Plant Study * Punnett Squares - Show ways that traits can be combined. Upper case letters - show dominant traits lower case letters - show recessive traits Example: Brown eye color is dominant to blue eye color BB - Pure Brown eyes (Purebred) Bb - Brown eyes (Hybrid) bb- Pure blue eyes (Purebred)







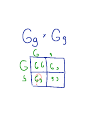










![Heredity Study Guide Chapter 3 [4/27/2015]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009964088_1-f698bb7235ac59e0a498ee34afee979f-150x150.png)


