* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory`s 3 Main Ideas
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
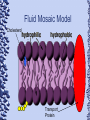
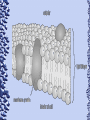
Cell Theory’s 3 Main Ideas 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of organisms 3. All cells come from preexisting cells -a cell divides to form two identical cells Two Basic Types of Cells • Prokaryotes: Cells that lack internal membrane-bound structures – Usually unicellular organisms such as bacteria • Eukaryotes: Contains membrane-bound structures called organelles – Usually multi-cellular organisms such as plants and animals Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Cells Have Boundaries • Both types of cells contain a plasma membrane which creates a boundary between the cell and its environment • The membrane allows only certain materials to enter or leave (Selective Permeability). This helps the cells maintain homeostasis – Kind of like the screen in a window; It lets air in but keeps bugs out Structure of Plasma Membrane • The membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer which contains hydrophobic (water fearing) fatty acid tails and hydrophilic (water loving) phosphate heads – This is known as the fluid mosaic model Fluid Mosaic Model Cholesterol Transport Protein The Bilayer Also Has… • Cholesterol: Helps stabilize the phospholipids by making sure they don’t stick together • Transport Proteins: Span the entire membrane to allow larger molecules to pass through Osmosis • Although the plasma membrane can stop molecules that cannot pass freely through it, it does not stop the movement of water • Diffusion of water across the membrane is called Osmosis