* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Generalities Main amino acid reactions
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
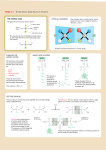
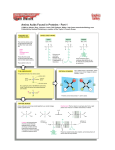
Generalities Proteins are the polypeptides formed by sequences of amino acids General formula of the a-amino acids NH2-CH-COOH R The amino acids occupy a central position in the metabolism of nitrogenous compounds Main amino acid reactions • • • • TRANSAMINATION DEAMINATION DECARBOXYLATION • The degradation of the amino acids occurs in the mitochondria. • By a transamination reaction (1) the amino group is transferred to aketoglutarate to form glutamate in a reversible way. • Glutamate release ammonia through an oxidation reaction • Most amino acids have their specific transaminase, and those that do not have can be transformed into other that has. (1) Transaminations are reactions involved in both, anabolism and catabolism. 1 Transamination reaction COO CHNH2 R COO CO R PLP COO CO CH2 CH2 COO aKG COO CHNH2 CH2 CH2 COO Glu Reaction : transamination (exchange of amine group) Enzyme: transaminase (aminotransferase) in cytosol Coenzyme activateur: Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP) Reversible Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) H HO C NH2 H C H HO CH2 OP O N CH2 OP N CH3 Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) COO CO R PLP Glu CH3 Pyridoxamine phosphate (PMP) Mechanisme COO CHNH2 R Coenzyme associated with numerous enzymes acting on nitrogen compounds - transaminases - isomerase - decarboxylase... PMP a KG Ping–pong reaction: 1 - fixation of the substrate 1 to the active site of the enzyme, then formation of the product which is detached from the active site 2 - fixation of the substrate 2 to the active site of the enzyme 2 Oxidative deamination Elimination of nitrogenous from glutamate H2 N CH COO - NAD+ CH2 CH2 COOH H2 O NADH O C COO CH2 CH2 COOH NH4 + Transformation of glutamate (formed by protein degradation or by AA transamination) in α-ketoglutarate and NH4+ Oxidation coupled to hydrolysis Enzyme: Dehydrogenase (Glutamate dehydrogenase) Amoniac fate Stored as glutamine NH4 + H2 N CH COOH H2 N CH2 CH2 C O ATP ADP + P OH CH COOH CH2 CH2 C O NH2 Glutamine synthétase Coupled reaction: hydrolysis of ATP and condensation of NH4+ on glutamate (double transfer) Elimination by urea cycle 3 Lateral chain degradation In general, N elimination occurs by transamination, then CO2 is liberated by an oxidative decarboxylation : - Formed a-ketoacides are Krebs or glycolysis intermediates : pyruvate, a-ketoglutarate, OAA… Example (LipSS, TPP, FAD) aKG COOH CHNH2 NAD+ Glu (PLP) CH3 COOH CO CH3 Transaminase NADH CH3 COSCoA HSCoA CO2 Déshydrogénase Aminoacids catabolism and anabolism are linked to glycolysis and Krebs intermediates 4