* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 7.1 Guided Notes
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
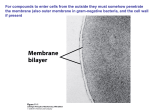
Applied Biology Notes Chapter 7.1: Life Is Cellular WHAT IS A CELL? • • The basic unit of _______________ and _________________ in living things. They carry out life processes: o o o • All organisms are made of cells! They are either ___________________________ (single celled) or _____________________________ (many cells). SCIENTISTS: Match the correct scientist with his discovery/contribution. ______ Leeuwenhoek A. Discovered that all animals are composed of cells ______ Shleiden B. Invented the first electron microscope ______ Schwann C. Discovered that all plants are composed of cells ______ Ruska D. Was the first person to observe living cells under the microscope ______ Hooke E. Discovered that all cells come from existing cells ______ Virchow F. Observed and named “cells” The CELL THEORY states: 1. 2. 3. Key Microscope Terms: • Lens – • Micrograph – • Total Magnification – MICROSCOPE PARTS & FUNCTIONS 3 TYPES OF MICROSCOPES: COMPOUND LIGHT MICROSCOPE TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM) SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (SEM) Utilizes WHAT to view specimen? What does it allow you to see? (what is the micrograph show?) Total Magnification Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes: Two Main kinds of cells 1. ________________ – Cells that enclose their DNA in a nucleus 2. ________________ – Cells that do not have a nucleus. The DNA is not separated from the rest of the cell. Prokaryotes: 1. Smaller and simpler than ______________________. 2. DNA floats freely in the _______________________. 3. Prokaryotes _____________, ____________and ________________to their environment. 4. Some prokaryotes can __________________ along surfaces and ___________________ through liquids. 5. An example of a prokaryote is ___________________. Eukaryotes: 1. Larger and more ____________________ than prokaryotes. 2. Most eukaryotes have dozens of ___________________ and ___________________ inside them. 3. The _________________ separates the DNA from the rest of the ________________. 4. _________________ live as single __________________. 5. Others make up larger __________________ with _________________ cells such as _____________, ___________________, and __________________. Chapter 7.2: Cell Structure Cells are different by: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A cell’s form fits its function Similarities that cells share. All eukaryotic cells (plant & animal cells) have the same general structures: 1. 2. 3. 1. Nucleus = __________ __________ Has 3 main parts: 1. 2. 3. a. Nucleolus b. Nuclear Envelope (membrane around nucleus) • • Allow exchange of _____________ ( into & out of nucleus) Made up of a _________________ bilayer c. Chromatin of nucleus • • DNA (and protein mixed in) Clumps up to form _________________ during cell division. 2. Cytoplasm – Gel-‐filled space that organelles float around in Organelles – Mini “organs” – Perform ____________ ______________in cytoplasm. (Ex: Mitochondria) 3. Cell Membrane – (aka plasma membrane) • Boundary between ____________ and ____________ of cell. • Made up of __________________ bilayer. Organelles: 1. A part/piece inside of a cell that has a _______________ job. 2. Organelle means “_______-‐ _______” 3. There are many ____________ types of organelles in cells. Mitochondria – Location for ______________ ________________ process that makes ________ molecules (useable energy) Ribosomes – Site for ____________ ____________ (Process by which proteins are made) Endoplasmic Reticulum-‐ ________________and ______________ materials. • Rough ER = With Ribosomes • Smooth ER = No Ribosomes Golgi Apparatus (Golgi Body) • Fixes, _____________, and sends _______________ and other chemical products around the cell. Lysosomes – Contain ___________ ____________ that breakdown ____________________ (proteins, nucleic acids, lipids) or __________________ bacteria. Vacuoles – Storage (water, _________, _________) Cell (Plasma) Membrane • Makes up _______________ between ______________ and _______________ of cell. • Makes up phospholipid bilayer. cell membrane Special Structures of Plasma membranes • __________ moves materials across the cell surface • _______________ helps the cell “swim” (pushes it through water like a __________). Plant Parts: Chloroplasts (Found only in plant cells) • • Organelle where _____________________ takes place. Uses _____________(Energy) to make __________________ (food). 1. What is a Chloroplast? • • Chloroplasts are like “_________ ________ packs” Trap light _________________ energy and turn it to _______________ energy for the cell via ___________________________. 2. Cell Wall (Only found in plant cells) • Protects the plant cell and is _____________ to keep the cell’s _________-‐ like shape. • Outer-‐most layer of plant cells. • The cell wall _____________ the plant cell’s insides and gives it _______________. Chapter 7.3: Cell Transport Cell Membranes: Function of Cell Membranes Cell (Plasma) Membranes: 1. Is the boundary between inside and outside the cell. 2. It controls what goes in & out of the cell. Structures of Cell Membranes-‐ Parts include: 1. 2. Phospholipid Bilayer: Made up of ______________________ in 2 layers “bilayer” AND many _________________ are squeezed into the membrane. Protein Functions: The proteins in the phospholipid bilayer carry out many function. 1. ________________ -‐ (catalysts) speed up chemical reactions 2. _____________ _____________ -‐ carry materials into and out of cell. 3. __________________ -‐ with other cells (“cell to cell recognition”) 4. _____ ___________ -‐ as “chemical messengers” Fluid Mosaic Model Sometimes the membrane is referred to as the “________________________________________ model” because the parts move around constantly. Cell Membranes are “Semi-‐Permeable” = allow _________ materials to pass through and restricts/stops others! What characteristics might keep a molecule from being able to pass through a membrane?? TRANSPORT • Cellular membranes control traffic of molecules __________________________________ of the cell. KEY IDEA: Molecules move because of _________________________ differences. High Concentration of Molecules (dots) Low Concentration of Molecules (dots) Passive Transport Type of transport in which it is easy for molecules to move through/across cell membranes • • NO ENERGY IS REQUIRED for the molecules to move because particles naturally move down a concentration gradient! Molecules move from _________ à __________ concentration There are 3 types of Passive Transport: 1. ________________ Diffusion (movement of molecules straight through membranes) 2. ____________________ Diffusion (movement of molecules with help from proteins) 3. __________________ (movement of water molecules) 1. Simple Diffusion: • Movement of the particles of a substance from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated ( molecules move from _________ à ________ concentration) • Doesn’t stop until ________________________ is established Equilibrium Transport protein 2. Facilitated Diffusion: • Is diffusion of molecules through ______________________________. • This occurs because some molecules can’t simply squeeze through the phospholipid bilayer, so they need help. • Molecules move from _____________ à ____________ concentration. 3. Osmosis: • Special type of diffusion where _______________________ move across a semipermeable membrane. • Water molecules move from ________ à ________ concentration. 3 Types of Aqueous Solutions: (use Kool Aid as a way to remember J) 1. Hypertonic – (solution with): – LOWER concentration of water molecules (than the cell)… because there is a lot of solute (NacL) What will happen to the cell? __________________ 2. Hypotonic – HIGHER concentration of water molecules (than the cell) …because there is not much solute. What will happen to the cell? ________________ 3. Isotonic – solution with equal concentration of water & solutes J – What will happen to the cell? _______________ REAL LIFE APPLICATION: What is Plasmolysis? ACTIVE TRANSPORT: KEY CONCEPTà Cells use energy to transport materials that cannot diffuse across a membrane OR need to be pumped against the normal concentration gradient. Let’s compare the 2 types of transport (active and passive)…. Molecules involved Direction of molecule movement Energy required? (yes or no) Examples: Passive Transport Active Transport Active Transport: • • Allows a cell to move a substance against its normal concentration gradient. ….so now molecules are moving _______à________ concentration Requires energy from the cell in the form of _________ molecules. There are 3 types of Active Transport: 1. __________________ (proteins push molecules across membranes ______ à _______ concentration) 2. Exocytosis (“sounds like___________”) – the process of expelling material ______________________. 3. Endocytosis -‐ the process of taking large materials _____________________________. So….Cells can _______________(bring in) & __________________ (move out) large materials or large amounts of materials using Endocytosis and Exocytosis active transport methods Chapter 7.4 Homeostasis and Cells Homeostasis – Relatively ____________ internal physical and chemical conditions. • Single-‐celled organisms 1. 2. 3. 4. Unicellular Organisms • • Prokaryotes are very _______________. They live everywhere (Ex: Bacteria_ Soil, on leaves, in the ocean, in the air and within the human body. Multicellular Organisms • ____________ _________ and other __________________ organisms do not live on their own. • • • They need other cells to _________________. They become _________________ for certain jobs. They _________________ with one another to maintain ___________________. Cell Specialization 1. Some cells are specialized for _________________. 2. Some must ____________ to their environment. 3. Some must take in substances that the organism needs. Ex: air passages have cilia to sweep dust away to keep lungs clean. Levels of Organization • • • Specialized cells are organized into ______________. Tissues are organized into _____________. Organs are organized into _______________ ______________. Cellular Communication 1. Cells in large organisms use _________________ ________________ to communicate. 2. They can __________ ______ or __________ __________ activities of the cells that receive them. 3. Cells have _____________ ______________ to help communicate with other cells. Ex: ________________ to receive communication.