* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria: An Overview
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
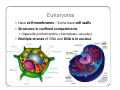
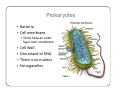
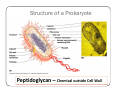
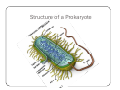
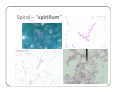
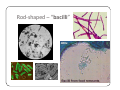
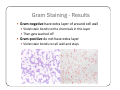
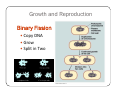
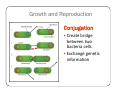
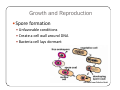
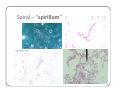
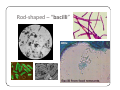
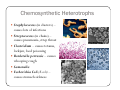
Bacteria: An Overview Eukaryotes y Have cell membranes – Some have cell walls y Structures in confined compartments y Organelles (mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles) y Multiple strands of DNA and DNA is in nucleus Prokaryotes y Bacteria y Cell membrane y Some have an outer layer over membrane y Cell Wall y One strand of DNA y There is no nucleus y No organelles Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote Eukaryote Prokaryote y Plants and Animals y Bacteria y Cell membrane y Cell membrane y Some have cell y Cell Wall walls y DNA is inside the nucleus y Structures are in compartments (organelles) y DNA floats around, no nucleus y No organelles Prokaryotes (aka. Bacteria) Most successful organisms on Earth (~3.5 BILLION years old) Two Types of Prokaryotes Eubacteria Archaebacteria y Cell wall contains y Cell wall peptidoglycan y Most common type lacks peptidoglycan y Can live in very harsh environments (heat, cold, salt ponds, acidic ponds, no oxygen) y DNA is more similar to eukaryotes Hydrothermal Vents Pink, green, and brown‐colored archaebacteria occupy the thermal gradients in the flowing water (60‐100°C). Salt Ponds Arctic Ice Acidic Environments Structure of a Prokaryote Peptidoglycan – Chemical outside Cell Wall Structure of a Prokaryote Three Shapes y Spherical – “cocci” y Greek – berry y Spiral – “spirillum” y Latin – spiral y Rod‐shaped – “bacilli” y Latin – little stick Spherical – “cocci” Spiral – “spirillum” Rod‐shaped – “bacilli” Identify the Bacteria Based on the Name y Staphylococcus (in clusters) – y y y y y causes lots of infections Streptococcus (in chains) – causes pneumonia, strep throat Clostridium – causes tetanus, lockjaw, food poisoning Bordetella pertussis – causes whooping cough Samonella Escherichia Coli (E.coli) – causes stomach sickness Identifying Types of Bacteria y Gram‐staining y Used to identify what type of bacteria y Helps us determine if antibiotics will be effective y Cells that have extra layer cannot be penetrated by antibiotics Gram Staining - Steps 1) Stain it red y Red stain bonds to peptidoglycan in cell membrane y All bacteria cells have peptidoglycan in cell membrane 2) Stain it violet y If bacteria stays violet – gram‐positive (violet stain sticks) y If bacteria washes back to red – gram‐negative (violet stain washes off) Gram Staining - Results y Gram‐negative have extra layer of around cell wall y Violet stain bonds to the chemicals in this layer y Then gets washed off y Gram‐positive do not have extra layer y Violet stain bonds to cell wall and stays Gram Staining - Implications y Gram Negative – Have extra layer outside cell wall y Cannot be penetrated by Antibiotics y Gram Positive – No extra layer outside cell wall y Can be penetrated by Antibiotics Growth and Reproduction Binary Fission y Copy DNA y Grow y Split in Two Conjugation y Create bridge between two bacteria cells y Exchange genetic information Growth and Reproduction Binary Fission Conjugation y Copy DNA y Create bridge y Grow between two bacteria cells y Exchange genetic information y Split in Two Growth and Reproduction y Spore formation y Unfavorable conditions y Create a cell wall around DNA y Bacteria cell lays dormant Colony Growth y Cell division can be rapid y Some can multiply once every 20 minutes y 1Æ2Æ4Æ8Æ16 Æ32 y 64Æ128Æ256Æ512 Æ1024Æ2048 y 4096Æ8196Æ16382Æ32764Æ65528Æ131056 y 262112Æ524224Æ1048448 2 hour 4 hours 6 hours 7 hours y The growth of a colony of bacteria is limited by the nutrients available and by the amount of waste products it produces y http://www.tulane.edu/~dmsander/WWW/Video/pneu mo.html Nutrition Autotroph Hetertroph y Makes its own y Gets food from food another source Autotroph Photosynthetic Autotroph Chemosynthetic Autotroph y Makes food from y Makes food from other sunlight y Cyanobacteria – usually first to recolonize wiped out area y Blue‐green Algae chemicals y Chemical Vents, Soil, Swamps Photosynthetic Autotroph Chemosynthetic Autotroph Heterotroph Chemosynthetic Heterotroph Photosynthetic Heterotroph y Uses other cells for y Uses sun for energy energy y Decomposers y Parasites y Uses other cells for carbon Spherical – “cocci” Spiral – “spirillum” Rod‐shaped – “bacilli” Chemosynthetic Heterotrophs y Staphylococcus (in clusters) – y y y y y causes lots of infections Streptococcus (in chains) – causes pneumonia, strep throat Clostridium – causes tetanus, lockjaw, food poisoning Bordetella pertussis – causes whooping cough Samonella Escherichia Coli (E.coli) – causes stomach sickness Energy Release y Obligate aerobes y Need oxygen to survive y Obligate anaerobes y Destroyed by oxygen y Facultative aerobes y Do not need oxygen, but are not killed by it