* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fact sheet B2.1 Cells and tissues
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
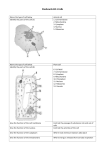
Fact sheet B2.1 Cells and tissues Cells and organelles 1. Name the type of cell below 2. Identify the parts of the cell (5) 3. Name the type of cell below 4. Identify the parts of the cell (8) Animal cell 1. Cell membrane 2. Mitochondria 3. Cytoplasm 4. Nucleus 5. Ribosomes Plant cell 6. Cell Wall 7. Cell membrane 8. Cytoplasm 9. Mitochondria 10. Chloroplast 11. Nucleus 12. Ribosomes 13. Vacuole 5. Give the function of the cell membrane 6. Give the function of the nucleus Controls the passage of substances into and out of cells Controls the activities of the cell 7. Give the function of the cytoplasm Where most chemical reactions take place 8. Give the function of the mitochondria Where energy is released from aerobic respiration 9. Give the function of the ribosomes Where protein synthesis occurs 10. Give the function of the chloroplast Absorb light energy to make food 11. Give the function of the vacuole Filled with cell sap 12. Give the function of the cell wall and say what it’s made of (2) 13. Give the 2 different ways that cells can be specialised (2) Strengthens the cell Made of cellulose Have a structure that other cells don’t (e.g. sperm cell has a tail) They can have LOTS of a particular part (e.g. muscle cells have LOTS of mitochondria) Tissues, organs and organ systems 14. Define ‘tissue’ 15. Define ‘organ’ A group of similar cells, eg muscle. 17. Describe the function of glandular tissue A group of tissues that work together to perform a specific function, eg the stomach. A group of organs which work together to perform a function, eg the digestive system or the reproductive system. Produce substances like hormones and enzymes 18. Describe the function of muscular tissue Contracts for movement 16. Define ‘organ system’ 19. Describe the function of the glandular tissue in the stomach 20. Describe the function of the muscular tissue in the stomach 21. Describe the function of the epithelial tissue in the stomach Stem cells 22. What happens when a cell differentiates? 23. Why do cells differentiate during the development of multicellular organisms? 24. What are human stem cells? 25. Name the 2 places where human stem cells are found 26. What could human stem cells potentially be used for and why? (2) 27. When do most types of animal cells differentiate? 28. When do most types of plant cells differentiate? 29. What is cell division mostly restricted to in mature animals? (2) Bacteria and yeast 30. Name 2 types of single celled organisms 31. Name the type of cell below 32. Identify the parts of the cell (5) Produces digestive juices to digest food Contracts to churn food with digestive juices Covers the outside and the inside of the stomach It becomes specialised/ adapted to carry out a specific function To become specialised so that they can carry out different functions Cells which have the ability to develop into any kind of human cell. Embryos and adult bone marrow To treat conditions such as paralysis As they can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, eg nerve cells At an early stage They retain the ability to differentiate throughout life Repair of tissues Replacement of lost/ dead cells Bacteria and yeast A bacterial cell 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Genes NOT in a distinct nucleus Cell wall Flagellum (not always present) Cytoplasm Membrane 33. Name the type of cell below 34. Identify the parts of the cell (4) Diffusion 35. How do dissolved substances move into and out of cells? 36. Define ‘diffusion’ (2) 37. What would happen if the difference in concentration between 2 areas was increased? 38. Which substance that is needed for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion? Yeast cell 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm 3. Membrane 4. Cell wall Diffusion 1. The net movement of particles in a gas or liquid 2. from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. The rate of diffusion would be faster Oxygen