* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Remember, transcription copies the DNA into mRNA
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
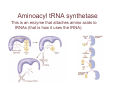
Remember, transcription copies the DNA into mRNA Transcription • • • • DNA gets copied. mRNA is the copy. If: DNA IS: ATGAAAAACAAGGTACACATCTAG, what is the mRNA? • UACUUUUUGUUCCAUGUGUAGAUC Translation • The mRNA gets read… tRNA brings in amino acids… • UACUUUUUGUUCCAUGUGUAGAUC • AUGAAAAACAAGGUACACAUCUAG • Each group of three on the mRNA is called a Codon. Each corresponding group of 3 on the tRNA is called an anticodon. Now, number 2 • ATGAAAAACAATTGCACGTAG = DNA • UACUUUUUGUUAACGUGCAUC =mRNA • AUGAAAAACAAUUGCACGUAG =tRNA Translation Continued! Some antibiotics block translation: Transfer RNA It is a strand of RNA that has a 3 base ‘anticodon’. This anticodon corresponds to a 3 base ‘codon’ on the mRNA. Each tRNA carries an amino acid specific to its anticodon. Aminoacyl tRNA synthetase This is an enzyme that attaches amino acids to tRNAs (that is how it uses the tRNA). Ribosome Made of 2 subunits that sandwich the mRNA The large subunit has a ‘p’ site (polypeptide) and an ‘a’ site (amino acid) Hey! The tRNA comes into the ‘A’ site, connects the amino acid to the polypeptide chain that is located in the ‘P’ site. Reading frame/Codons/Anticodons mRNA is read in groups of 3 (reading frame). Each group of 3 is called a codon. tRNA has an anticodon on the base that lines up with the codon of the mRNA. Codon Practice! AUG! What does it code for? How about AAA? What happens if our genetic information gets changed? It depends on the type of change! Point mutation – a single nucleotide is changed; •Substitution is a point mutation… (bases are ‘swapped’) Frameshift mutation – nucleotides added or deleted from a sequence, and sometimes copied. Insertions –add a base… whole codon sequence changes. Deletion –take out a base Non-sense if it no longer functions at all. Missense if it functions, though likely improperly. Do chromosomes mutate? Translocations occur when two DIFFERENT chromosomes swap pieces. Inversions occur when different parts of the same chromosome trade places. (This is what happened with our fruit flies in the packet!) Causes of Mutations Spontaneous: Pairs break down and change to other nucleotides by losing a H, deaminating, or losing correct base. Induced: Chemical – certain chemicals cause known damages, i.e. hydrocarbons (benzene) and oxygen (free radicals). Radiation – UV (260-280nm), T and C are weak here; Ionizing (i.e., x-rays) Hotspots – Certain parts mutate more often; this happens in bacteria Measure Twice, Cut Once Cells check their work a lot! Ligase puts strands back together, if broken. Polymerases check base pairs consistently throughout replication and translation, through checkpoints. Some cells may be euthanized (apoptosis).