* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biology Notes: Fermentation
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
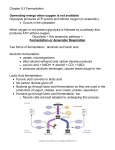
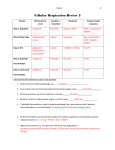
Name: _________________________________________________ Date: _______________ Period: ________ Biology Notes: Fermentation Directions: Fill in as we cover the topic in the PowerPoint. Corresponds to pages 122 – 125 in textbook. Step 1: Glycolysis • Where? In _______________ of __________ (_____________) • What happens? a) ____________________ (___________________)from our food is ______________ down into 2 _____________________________ b) 2 ____________ molecules released for _____________________ processes What’s after Glycolysis? • Glycolysis - Leads to either: 1) Aerobic Respiration (cellular respiration) • With __________ present • _________________________ Cycle • _________________________ transport chain 2) Anaerobic Respiration (fermentation) • _______________ O2 • _________________________ • Allows ___________________ to _______________________/_______________________ Step 2: Fermentation • Two Types of Fermentation (both ________________________): a) Lactic ____________________ fermentation – Performed by animals when ____________________ cells are not receiving oxygen (some bacteria too) – ______________________________ created b) Alcoholic fermentation – Performed by yeast, some plants, some bacteria – ___________________________________________ created Additional Information Lactic Acid vs. Alcoholic Fermentation Lactic Acid • Location: ________________________ • Amount of ATP created: ____________ • The Point? Make molecules to restart ________________________________ • Product: _________________________ Glycolysis (anaerobic) Where? In the cytoplasm What happens? • Glucose is split into 2 Pyruvate • 2 ATP created Review 1) Name the two types of fermentation. Alcoholic • Location: ________________________ • Amount of ATP created: ____________ • The Point? Make molecules to restart ________________________________ • Product: _________________________ Cellular Respiration (aerobic respiration) Where? In the mitochondria Steps? Kreb’s cycle and electron transport chain What happens? 2 Pyruvate converted into 34 ATPs (plus the 2 from glycolysis = 36) Fermentation (anaerobic) Where? In the cytoplasm What happens? • Pyruvate are broken into either lactic acid or alcohol • Molecules to restart/continue glycolysis created (No ATP) a) _____________________________________ b) ____________________________________ 2) How much ATP does glycolysis create? ____________________ 3) How much ATP does fermentation create? _________________ 4) Which molecule is broken down during glycolysis? ______________________________ 5) A buildup of which molecule causes sore muscles? ______________________________ 6) Which molecules are created by alcoholic fermentation? ___________________________________ 7) Which molecules are created by lactic acid fermentation? __________________________________ 8) Circle answer: Fermentation is aerobic or anaerobic a) What does this mean? ___________________________________________________________ 9) Why is aerobic (cellular) respiration preferred vs. fermentation? _______________________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________ 10) What is the purpose of fermentation? _______________________________________________________________________________________