* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Discussion Notes
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
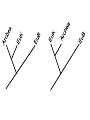
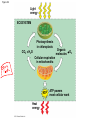
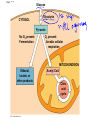
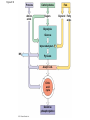
AP Biology Discussion Notes Monday 12/06/2016 Goals for the Day • Begin understanding the process of cellular respiration 12/05 Question of the Day: Does flipping branches at a branch point on a phylogentic tree change the meaning? Explain your answer. Redraw our tree of the 3 domains of life in a different way, that still means the same thing. Make sure to include characteristics! Grab a Partner Send one person up to get a set of Cards. Work together to lay out the cards so that they show the reaction for Photosynthesis Overview: Life Is Work • Living cells require energy from outside sources • Some animals, such as the chimpanzee, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 9.1 • Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat • Photosynthesis generates O2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration • Cells use chemical energy stored in organic molecules to regenerate ATP, which powers work © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 9.2 Light energy ECOSYSTEM Photosynthesis in chloroplasts CO2 H2O Cellular respiration in mitochondria ATP Heat energy Organic O2 molecules ATP powers most cellular work Chemical Equation for Cell Respiration C6H12O6 + O2 CO2 + H2O + ATP • Label the reactants & Products • What organisms do cellular respiration? Why (What is the KEY product)? Cellular respiration • Do ALL organisms need to do this? • Do ALL organisms do it the same way? Figure 9.18 Glucose CYTOSOL Glycolysis Pyruvate No O2 present: Fermentation O2 present: Aerobic cellular respiration MITOCHONDRION Ethanol, lactate, or other products Acetyl CoA Citric acid cycle Figure 9.16 Electron shuttles span membrane 2 NADH Glycolysis 2 Pyruvate Glucose MITOCHONDRION 2 NADH or 2 FADH2 2 NADH Pyruvate oxidation 2 Acetyl CoA Citric acid cycle 2 ATP 2 ATP Maximum per glucose: CYTOSOL 6 NADH About 30 or 32 ATP 2 FADH2 Oxidative phosphorylation: electron transport and chemiosmosis What are our major biomolecules & what are their monomers? Figure 9.19 Proteins Carbohydrates Amino acids Sugars Glycolysis Glucose Glyceraldehyde 3- P NH3 Pyruvate Acetyl CoA Citric acid cycle Oxidative phosphorylation Fats Glycerol Fatty acids Cellular respiration Pre-lab Work Order for Today 1. Cell Respiration Pre-Lab 2. Chapter 26 pg. 536 – Key terms & Main Ideas – 26.1 *This is what we discussed as a class, so just add the noted figure… • 26.5 – 26.2 • 26.8,26.9,26.10,26.11 – 26.3 • 26.4 &26.5 – Not responsible for but might find interesting – 26.6