* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Step 2: Pyruvate Oxidation
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Lactate dehydrogenase wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
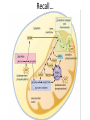
Pyruvate Oxidation & Krebs Cycle STEP 2: PYRUVATE OXIDATION Recall… Recall Step 1 - Glycolysis • Happens in the cytoplasm • Does not require oxygen (anaerobic) • Inefficient (net 2 ATP produced) Glycolysis Summary What went in: • 1 Glucose • 2ATP • 2 NAD+ • 4 ADP • 4 Pi What was produced: • 2 pyruvate • 2 ADP • 2 NADH + H+ • 4 ATP Step 2 – Pyruvate Oxidation Overview The two pyruvate molecules formed in glycolysis are transported through the two mitochondrial membranes into the matrix Within the matrix, enzymes catalyze the following three changes Happens twice for every glucose molecule Three Steps of Pyruvate Oxidation 1. A carboxyl group is removed as CO2 2. The remaining two-carbon molecule is oxidized by NAD+. This is a redox reaction – pyruvate is oxidized, and NAD+ is reduced 3. Coenzyme A (CoA) is attached to the carbon compound, forming acetyl-CoA 2 pyruvate + 2 NAD+ + 2 CoA 2 acetyl-CoA + 2 NADH + 2 CO2 Overall The two molecules of acetyl-CoA enter the Krebs cycle The two molecules of NADH proceed to step 4 to participate in oxidative phosphorylation The two CO2 molecules diffuse out of the cell as waste The two H+ molecules remain dissolved in the matrix No ATP is directly produced in this step STEP 3: KREBS CYCLE Overview • also called the Citric Acid Cycle • named after the Nobel Prize winner who discovered it • Occurs in the mitochondrial matrix • 8 step process • Remember that the Krebs Cycle happens TWICE for every one molecule of glucose. Overall The Krebs cycle will produce the following products for every glucose molecule broken down • • • • 6 NADH 2 FADH2 2 ATP 4 CO2