* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The lifelong impact of child abuse
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in learning and memory wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetic clock wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of diabetes Type 2 wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of depression wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
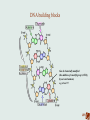
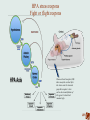
Early life stress changes the way our genes function Pervasive and enduring effects of early life stress • • • • • • • • • Obesity (ANNA) Neurodevelopmental delays HPA axis dysfunction (stress) Metabolic disorder Cardiovascular disease Immune system dysfunction Major depressive disorder Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Cancer Child Abuse and Neglect ACE study Vincent Fellitti Scientific Gaps “Nature” versus “Nurture” (Genetics versus environment) Jean-Baptiste de Lamarck DNA building blocks Can be chemically modified (the addition of a methyl group (-CH3)) by our environment, e.g. stress!!!! Epigenetics (environment determines activity of genes) ACTIVE GENE INACTIVE GENE e.g. a gene that reduces stress Filling in the scientific gaps -Studies on animal behavior (maternal care) -Studies of CAN victims (epigenome) Moshe Szyf Patrick McGowan Michael Meaney Epigenetic interference by maternal care •Behaviour of pup determined by care of mother. •This is reflected in the pup’s activity of genes. •Altering the epigenome (DNA-methylation) alters behaviour. HPA stress respons Fight or flight respons GR Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) takes away the cortisol after the stress event. In stressed pups this receptor is less active due to methylation of this gene. Cortisol level remains high. What about CAN victims? • Chronic childhood stress alters the stress response by epigenetic changes (lifetime changes). • Many other genes are altered in the same way especially genes involved in the immune system, brain development, heart disease, cancer, psychiatric and substance abuse disorders. A high risk for Tom, Rita and Anna. • Epigenetic changes due to stress can be transmitted to the next generation. Good news! • Some children are resilient for the effect of CAN (genetic, epigenetic). • Epigenetic changes are reversible in theory (Interference throught medication or cognitive therapy). Writers, readers, erasers Take home message • Gene function is altered by childabuse and neglect. • This causes frequent major health problems throughout life.