* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MP2 QUARTERLY EXAM STUDY GUIDE
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
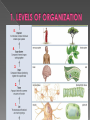
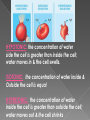
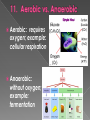
5. 4. 3. 2. 1. Unicellular organisms are made up of one cell. Multicellular organisms are two or more cells and the cells are arranged in the levels of organization (tissues, organs, organ systems). Cell membrane Diffusion – the movement of particles from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated; examples: sugar, O2, salt Osmosis – the diffusion of water Particles are in constant motion and they want to move from high to low. Particles are constantly moving to create an equal concentration of the solute on both sides of the cell membrane. Active transport: the movement of molecules with energy from low concentration to high concentration. Cells need active transport to keep a concentration gradient and to move large molecules. Molecular transport: small molecules & ions are carried across membranes by proteins; example: Na+/K+ Pump Endocytosis: taking materials into the cell by infoldings or pockets in the cell membrane; example: phagocytosis & pinocytosis Exocytosis: the release of large amounts of material from the cell HYPOTONIC: the concentration of water side the cell is greater than inside the cell; water moves in & the cell swells. ISOTONIC: the concentration of water inside & Outside the cell is equal HYPERTONIC: the concentration of water inside the cell is greater than outside the cell; water moves out & the cell shrinks Autotroph: organisms capable of producing their own food; example: plants Heterotroph: organisms that can not produce their own food; example: humans Aerobic: requires oxygen; example: cellular respiration Anaerobic: without oxygen; example: fermentation Photosynthesis Cell Respiration Organelle: chloroplast Occurs: plant cells only Chemical & Word formulas: Organelle: mitochondrion Occurs: all eukaryotic cells Chemical & Word formulas: ATP is adenosine triphosphate, it is the energy molecule. Cells use it for things like active transport. X Plants: convert light energy from the sun into chemical energy. Plants use both photosynthesis and cellular respiration to create and use energy. Humans: eat plants & other animals and convert the energy in nutrients they receive into energy (ATP). Humans (and animals) eat their food and use cellular respiration to release the energy in food.