* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ATP
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
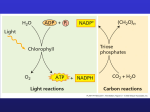
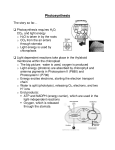
Match structure and function Double membrane chloroplast envelope As much light as possible can be absorbed Thylakoids have large surface area Needed for the lightindependent reaction to take place ATP synthase molecules in thylakoid membrane Reactants kept close to reaction sites Stroma contains enzymes, sugars and organic acids Produce ATP in the lightdependent reaction Learning Objectives • Outline how the products of the LDS are used in the LIS • Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the LIS • State what TP is used to make • State that TP is recycled to make RuBP Photosynthesis Photophosphorylation: ‘The making of ATP energy using the energy from light’ May involve cyclic or non-cyclic phosphorylation Cyclic – PSI – intergranal lamellae Non – cyclic PSI & PSII – granal lamellae Non-cyclic • Light excites electrons of Mg in PSII & PSI • Electrons passed along electron carriers • Energy released drives H+ proton pumps • H+ accumulates in thylakoid space – gradient forms • H+ flow down gradient through ATP synthase • ATP used in light independent stage • Photolysis of H20 and generation of NADPH Cyclic • Only uses PSI • Excited electrons are passed back to Mg in PSI • No photolysis or generation of NADPH • Small amounts of ATP made Used in light independent or to open stomata 1.3.4 Light independent stage • Occurs in the stroma – also called the Calvin Cycle • Uses ATP made in the light dependent stage • CO2 becomes fixed into complex organic compounds • C & O used for structure and energy store Three phases 1. Carboxylation Carbon dioxide fixation with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) 2. Reduction Reduction of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GALP) 3. Regeneration Re-formation of the CO2 acceptor molecules Rubisco Regeneration of RuBP TP RUBISCO 1.3.4 Light Independent • CO2 diffuses into the stroma • Combines with a 5C acceptor RuBP – uses enzyme • RuBP has become carboxylated – carboxyl group • Produces 2 x 3C molecule – glycerate 3-phosphate • GP is reduced & phosphorylated to TP • TP recycled by phosphorylation to RuBP 1.3.4 Light Independent stage Products of the Calvin Cycle • • • • • • GP used to make amino acids & fatty acids TP combines to form 6C glucose Some glucose isomerised to Fructose Fructose & glucose combine = disaccharide Some sugars polymerised – cellulose TP converted to glycerol – makes lipids The light-independent reaction Triose phosphates (TPs) are used to form glucose. 3C (TP) + 3C (TP) 1C (x6) Hexose (6C) 5C Regenerate RuBP 6C ATP •`6 cycles are required to form 1 molecule of glucose • RuBP is then joined with carbon dioxide to re-start the cycle. 1C (6 cycles) 5C RuBP) + 1C (CO2) 6C 2 x 3C (TP) Hexose 6C 5C Regenerate RuBP The Maths • 2 molecules of GALP are made each turn • 5 out of 6 molecules of GALP are used to regenerate RuBP • 2 molecules of GALP are needed to make a hexose sugar • How many turns are needed to make 1 molecule of hexose sugar? • How many molecules of ATP and reduced NADP are needed? Products of the Calvin cycle Products of the light-independent reaction that pass back into the light-dependent reaction: NADP ADP inorganic phosphate Products of the light-independent reaction that are used in other processes: triose phosphate – used to build complex carbohydrates, amino acids and lipids. How much can you remember? Summary of photosynthesis light light- dependent reactions light- independent reactions carbohydrates, other complex molecules Photosynthesis: true or false? Outline how light energy is converted to chemical energy (ATP and reduced NADP) in the light-dependent stage (reference should be made to cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation) Explain the role of water in the light-dependent stage. Outline how the products of the light-dependent stage are used in the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle) to produce triose phosphate (TP) (reference should be made to ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (rubisco) and glycerate 3-phosphate (GP)). Explain the role of carbon dioxide in the light-independent stage (Calvin cycle). Carbon Fixation – Light Independent Stage (Calvin Cycle) • The carbon fixation stage occurs in the stroma and results in the production of glucose. • It is a result of an enzyme controlled sequence of reactions requiring ATP and hydrogens (from reduced NADP) from the light stage, and carbon dioxide (“fixed” from the air). • It involves the reduction of carbon dioxide, that is the addition of hydrogen (from reduced NADP), to form carbohydrate. • CO2 is accepted by the 5C compound ribulose 1,5-biphosphate (RuBP) to form an unstable 6C compound. • The 6C compound formed immediately splits into two molecules of a 3C compound called glycerate 3-phosphate (GP). • ATP and reduced NADP is used to convert the two GP molecules into two molecules of triose phosphate (TP), a 3 carbon compound. • TP’s are used in the formation of carbohydrate (glucose) and to regenerate RuBP • ATP is required to regenerate RuBP Examination Questions – Model Answers 1 ATP Reduced NADP / NADPH / NADPH2 / NADPH + H+ Regenerates / produces, ribulose bisphosphate / RuBP So cycle can continue / for (further) CO 2 fixation / to combine with CO2 Formation of , sugar / glucose / hexose / sucrose / starch / cellulose Formation of fat / triglyceride / lipid fatty acids / glycerol / amino acids / protein / nucleic acids / nucleotides Most triose phosphate used to produce RuBP and the rest for production of hexose Oxygen used and CO2 produced / excreted Light energy required Uses Rubisco Involves calvin cycle Reduces rate of photosynthesis / increases rate of photorespiration Less Rubisco available for CO 2 / more oxygen competing with CO2 for Rubisco More O2 binding to Rubisco O2 outcompetes CO2 for Rubisco Less CO2 fixation / for Calvin cycle CO2 given off Less GP / TP, produced Less RuBP, regenerated O2, not a substrate for / cannot bind to / will not compete for. PEP carboxylase PEP carboxylase, is only specific to CO 2 2 (i) A (ii)D (iii)A Flattened membrane bound sacs Termed thylakoids Arranged as stacks / grana Contain pigment / chlorophyll arranged in photosystems / quantosomes, in membrane (62.4 / 162) x 100 Answer 38.5 % Different lighting has little effect Variation in percentage less than 3 Probably not significant Yield is less for low pressure sodium lamps The best yield is metal halide Crops can be grown out of season /all year round Plants photosynthesize 24 hours a day Less physical damage from weather /animals Pest control easier Other factors can be controlled – e.g. Temperature, CO2, water supply, humidity