* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 3 - kehsscience.org
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrial DNA wikipedia , lookup
DNA damage theory of aging wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Frameshift mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
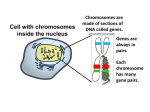
Unit 3 Name _________________________ Our Cells at Work DNA , Chromosomes, & Genes DNA is a molecule made of base pairs attached to two strands of sugars and phosphates (the “backbone”). The base pairs in DNA are: ____ pairs with ____ ____ pairs with ____ The order of the base pairs in DNA determine the order that the amino acids are linked together when proteins get built. Proteins are what living things are made up of; your traits (characteristics) are proteins…. which means, your DNA is the instructions to make you! You got these instructions from your biological parents. When a sperm fertilizes an egg, the nuclei combine….so ½ your DNA came from your biological mother, and ½ came from your biological father. Because we have so much DNA, it is organized into chromosomes (as shown in the diagram), which are protected in the nucleus of the cell. Humans have a total of ______ chromosomes in the nucleus of every body cell….which means, ½ of that, or ____ chromosomes came from your biological mother’s egg (gamete) , and _____ chromosomes came from your biological father’s sperm (gamete). A segment (piece) of DNA is a gene. Each gene carries the instructions to build just one protein. Your genome has about 25,000 genes, so there are many genes on each chromosome. Each chromosome you got from your mother “matches” up with a chromosome that you got from your father…..so it is the “combination of instructions” that you received in those 23 pairs of chromosomes that makes you unique. Protein Synthesis (building proteins from the instructions in DNA) Protein Synthesis is the process that causes traits to be expressed…..the process that created your eye color pigments, your skin tissue and color, your muscle, your digestive enzymes, etc. The “instructions” (DNA) are stored and protected in the cell’s nucleus…..but proteins get built outside of the nucleus (at ribosomes). To get the instructions out of the nucleus, another nucleic acid – RNA – is needed….. A gene is transcribed by mRNA (messenger RNA). It does this by “paring up with” the genetic code on DNA – the only difference is there are no “Ts” in RNA, so, when there is an “A” in DNA, RNA will pair that with a “U”. C’s still pair with G’s. Once transcribing is complete, the instructions to build that protein are carried by mRNA out of the nucleus to a ribosome. When mRNA arrives at the ribosome, tRNA (transfer RNA) arrives carrying an amino acid. When tRNA locates the “drop off point” by reading the code on mRNA, it lets go of the amino acid so it can be linked to the others. A chain of amino acids is a protein. If this were a skin cell, the protein made might be the pigment melanin that gives your skin color. If the cell is a muscle cell, the protein made might be “myosin or actin” which are the proteins that muscle tissue is made of. If the cell was in your mouth, the protein made might be an enzyme in your saliva that helps break down food. Review: 6. Protein Synthesis Every organism that reproduces sexually has an even number of chromosomes in the nucleus of each of their body cells…..this is because ½ of them came from the mother’s ______ and ½ came from the father’s ___________. For example, humans have a total of ______ chromosomes in every body cell -- ____ came from the sperm, and ____ came from the egg. Chromosomes neatly package all of the DNA of that organism, and DNA is the instructions to make all of the proteins that make up that organism and allow that organism to function. What is the relationship between DNA , genes , and chromosomes? What is the relationship between proteins, genes, and traits (characteristics)? Name the process that causes traits to be expressed in offspring: __________________ This is how it works: 1. A gene (segment of DNA) = GTC ATT GCA 2. …..is transcribed by mRNA = __________________ ; this takes place in the _______________ of the cell. 3. ….mRNA caries the copy out of the nucleus to a _________________ 4. ….at the ribosome, tRNA arrives carrying an ____________ ____________ that will be linked together to make a ___________________ 5. Proteins are your traits/characteristics. What is a characteristic of DNA that determines what protein is made? So, describe how a rabbit ends up with pink eyes. ____ COE: “It’s in the Genes #1” Mutations Mutations are changes in _____ Mutations are fairly common in DNA, and, luckily most are harmless. Mutations can occur in several ways: Random errors during DNA replication – these are fairly common and occur when a nucleotide is substituted, inserted, or deleted from a gene. Since mRNA will copy the error, an incorrect amino acid will be inserted when the protein is being built. Exposure to certain chemicals and radiation can also cause DNA mutations. If a mutation occurs in a body cell of an organism…..like a skin cell, liver cell, muscle cell, bone cell, etc., it can cause “bad proteins” to be built and cause a defect in those cells and tissues. A body cell mutation will only impact the individual with the mutation….they _____ ______ be passed on to the offspring!!! If a mutation occurs in a gamete, or sex cell (sperm or egg) then it will not affect the “parent organism”, but the mutation ___________ cause a defect in an offspring – again, because “bad proteins” could be made from the error in the “instructions” (DNA). Sometimes mutations can benefit an individual. So, if the gamete mutation resulted in a new trait that made that individual more likely to survive and reproduce, then that mutated gene would most likely be passed on to the next generation. …….and the next generation…….and the next….. If that gene gets passed on to enough individuals (through several generations), over time, most of the population will express this beneficial gene mutation --- so the population would have “changed”…..or evolved. Review: 7. Mutations Mutations are changes in ___________ Original DNA strand: ATC GGC AAC *compare all mutations to the original DNA Mutated DNA: ATC GTC AAC Type of mutation: ___________________ Mutated DNA: ATC GGA CAA C Type of mutation: ___________________ Mutated DNA: ATG GCA AC Type of mutation: ___________________ Original DNA Strand: CGT AAT CTG Show what a substitution might look like: __________________________ Show what a deletion might look like: _____________________________ Show what a deletion might look like: _____________________________ An original DNA strand and the same strand after a mutation are shown below. Describe the type of mutation that has occurred in the strand. DNA: Mutated DNA: TAC GGT CCA TAC GTC CA In your description, be sure to: Identify the type of mutation Describe one way this mutation can occur Type of Mutation: One way this mutation can occur: A local pond has been receiving fertilizer run-off from a new farm nearby; the pond is now surrounded year around with green, lush vegetation. A mutation occurred in a duck egg resulting in offspring with a darker, greener coloration. Describe how this trait could allow the offspring to survive and reproduce in its pond ecosystem. Imagine that there is a new mutation in a skin cell (body cell) of a frog. What effect could this mutation have on this organism (the frog)? If the same frog has a mutated sperm (gamete) what effect could this mutation have on this organism (the frog)? Effect of body cell mutation on the organism: Effect of sperm mutation on the organism: Imagine that there is a new mutation in a skin cell (body cell) of a frog. What effect could this have on the organism’s offspring (the baby frogs)? Imagine that there is a mutation in a sperm (gamete/sex cell) of the frog. What effect could this have on the organism’s offspring (the baby frogs)? Effect of body cell mutation on the offspring: Effect of gamete mutation on the offspring: Now let’s imagine that this frog’s sperm mutation gives the offspring the ability to produce a new skin protein that tastes really nasty. How can this mutation help the baby frogs survive and reproduce in their environment? How can that one mutation eventually benefit the entire population of frogs in this particular pond ecosystem? ____ COE: “It’s in the Genes #2” How New Cells are Formed Before a cell can divide, it must make another copy of its DNA – so that the new cell has all of the DNA, too! This process is called DNA Replication… After replication, chromosomes look like this; the copy stays “attached” until it is time to for the cell to divide…then one copy goes to each cell. Mitosis Mitosis is the way you get more body cells for growth, development, repair of damaged tissues, replacing dead cells, etc. DNA replication occurs before a cell divides because there needs to be two copies of each chromosome --enough for each new cell to get a “full set” So, during mitosis, a cell that starts with 4 chromosomes will divide one time to create two cells, each with 4 chromosomes. ….so an identical cell is created. From the time an egg is fertilized, the organism grows and develops by creating new cells – and the process that makes new cells is mitosis. Mitosis is an organized way to divide the chromosomes into two separate nuclei….when this is done, the cell can divide. Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes in their body cells: Meiosis Meiosis only takes place in specialized cells located in reproductive structures of organisms. After DNA replication, the cell divides twice to create four cells, each with ½ the original chromosome number. So, meiosis is the organized way to reduce chromosome number so that each gamete only has one copy of each chromosome. This produces the gametes (sperm & egg). So, our organism with 4 chromosomes in every body cell, will produce gametes containing 2 chromosomes. Then, when the sperm fertilizes the egg, a new organism with 4 chromosomes will be produced. There are three events that take place during meiosis that lead to unique combinations of genes in the gametes: 1. Independent Assortment – the way that the chromosomes line up to start meiosis is completely random…..and then when they separate into the gametes, it is random as to which chromosome goes to which gamete. So it’s kind of like “shuffling a deck of cards and dealing out half the deck”……each gamete gets a different combination of genes. 2. Crossing Over – This occurs when the chromosome pairs first line up next to each other at the start of meiosis……some of the chromosomes “swap parts”, creating new combinations of genes 3. Mutations – it is possible for random mutations to occur during DNA replication that precedes meiosis; these “mistakes” can then end up in the egg or sperm and passed on to the offspring. 8. Mitosis Describe mitosis in a goldfish cell; or how a goldfish makes new body cells: 1. Each gold fish cell starts with ______ chromosomes in each body cell 2. DNA _______________________ has to occur first so there are ____ copies of each chromosome before the cell divides. 3. The cell makes sure that the chromosomes get separated correctly then divides _______ time 4. After mitosis, there are _____ cells, and each one has _____ chromosomes in the nucleus. 9. Meiosis Meiosis is the type of cell division that produces gametes, or ___________ and ________. This only takes place in very specialized cells in the organism’s body, and it reduces the total chromosome number by ½. How many chromosomes would be in the sperm or eggs of each of the following organisms? ____ dog ____ mosquito ____ cat ____ human ____ cabbage Describe meiosis in a goldfish; or how a goldfish makes gametes: 1. Each gold fish cell starts with ______ chromosomes in each body cell, and in the specialized cells that produce sperm and egg. 2. DNA _______________________ has to occur first so there are ____ copies of each chromosome before the cell divides. 3. The cell divides __________ 4. After meiosis, there are _____ cells, and, in a goldfish, each one has _____ chromosomes in the nucleus – which is ____ the original chromosome number. Describe one event that takes place during meiosis that results in “unique” sperm or eggs. Genes are pieces of DNA that code for specific proteins. You have your eye color because you inherited certain genes from your parents. We often describe genes with letters, and alleles are different forms of the same gene. You may have inherited a dominant brown eye allele (B) from one parent, and a recessive blue eye allele (b) from the other parent, so the combination of genes you inherited (your genotype) is Bb. Mom and Dad both have brown eyes (BB or Bb); two of their kids have brown eyes (BB or Bb), and two of their kids have blue eyes (bb). What is one event that occurs during the formation of egg or sperm (meiosis) that makes it possible for these two brown-eyed parents to have kids with brown eyes and kids with blue eyes? Fertilization – Creating unique new organisms through sexual reproduction _____________________ occurs when the male gamete (___________) combines its genetic material (chromosomes) with the female gamete (_______) to create a fertilized egg, called a zygote. Each gamete only has ____ set of chromosomes, so when they unite, they restore the original chromosome number, in the case of humans, that number is _____ (or ____ pairs) In the case of a dog…… Review: 10. Fertilization Punnett Squares are used to show the probability of outcomes if fertilization were to occur. Brown eyes (B) are dominant over blue eyes (b). Mom and Dad both have brown eyes; 2 of their kids have brown eyes, and two of their kids have blue eyes. What is one event that occurs during fertilization that makes it possible for these two brown-eyed parents to have kids with brown eyes and kids with blue eyes? Explain your answer. ____ COE: “Bear Crossing #3” (Review 8, 9, & 10 before starting) Genetics The genes you inherit from your parents can come in different forms, or ___________. You only inherit one allele from each parent, so the combination you inherit will determine which proteins are made…..these are your traits. Some alleles are completely dominant, which means, that if it is present, it will be expressed; we use a _______________ letter to represent the dominant allele. Some alleles are recessive, which means that the trait will not be expressed if a dominant allele was also inherited. The only way that a recessive trait would be expressed is if a recessive allele was inherited from both biological parents. We use a lower-case letter to represent recessive alleles. The combination of alleles that an organism inherits is its genotype. So a dominant genotype for a given trait could be _____ or _____; a recessive genotype would be ______. If the two alleles in the genotype are the same, it is called homozygous; so _____ is a homozygous dominant genotype. An example of a homozygous recessive genotype would be ______. If the two alleles are different, the genotype is heterozygous…..he may have inherited a brown eyed allele (B) and a blue eyed allele (b), but his eyes will be brown because brown is dominant (Bb). Phenotype is what trait is expressed…or “what it looks like” because of the genes it inherited. So “blue eyes”, “long fur”, “spotted wings”, “yellow petals”, etc. are all phenotypes. Practice: Let’s say that in a certain butterfly, blue wings (B) are dominant over red wings (b). Use a Punnett Square to show the possible outcomes (genotypes and phenotypes) of cross between a homozygous blue winged bug and a red winged bug. Genotypes: Phenotypes: The offspring produced in this example are called ____________, or “offspring of different parents”. Now, cross two of the hybrids and describe the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Genotypes: Phenotypes: In a certain breed of llama, black spots (S) are completely dominant over fur with no spots (s), and long floppy ears (E) are completely dominant over short, pointy ears (e). Cross a spotted, long floppy eared male llama (homozygous for both traits) with a female llama that has no spots and short, pointy ears. Describe the possible genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring. Genotype of male: ________ Genotype of female: ________ Genotypes of offspring: _______ Phenotypes of offspring: __________________ The offspring have grown into adult llamas. One llama, Lolla, is ready to reproduce. What are the possible allele combinations that could be found in Lolla’s eggs after the process of meiosis? Lolla’s genotype: _______ Lolla’s eggs: Review: 11. Genetic Crosses A dihybrid cross means we are looking two traits, and the probability of outcomes if fertilization were to occur. In guinea pigs, brown fur (B) is dominant over white fur (b) and Pink eyes (P) are dominant over blue eyes (p). A male guinea pig is homozygous dominant for both traits --- he has brown fur and pink eyes. He is being bred with a female that is homozygous recessive for both traits – she has white fur and blue eyes. Male’s genotype: ____________ Female’s genotype: __________ When sperm and egg are formed, each will only have one copy of each “allele” (gene), but each has to have a “fur color gene” and an “eye color gene”….. Genes in every sperm: _________ Genes in every egg: __________ What will the genotype of the offspring be when the sperm fertilizes the egg? __________ What will the phenotype of the offspring be? _________________________________ Now let’s imagine that the offspring are old enough to mate. We will take one female from this litter, and mate it with a male that has white fur and blue eyes. What are the parent genotypes? Male’s genotype: _______________ Female’s genotype: ___________ Genes in every sperm: ___________ Possible gene combinations in eggs: ____ ____ ____ ____ Determine the possible genotypes and describe the odds of each phenotype for their offspring: Sperm: Eggs: Brown w/ pink eyes: _______ Brown w/ blue eyes: _______ White w/ pink eyes: _______ White w/ blue eyes: _______ In the next pair to breed, the male is homozygous dominant for fur color and heterozygous for eye color. The female is white with blue eyes. Male’s genotype: _______________ Female’s genotype: ___________ Possible gene combinations in sperm: Genes in every egg: ___________ ____ ____ ____ ____ Determine the possible genotypes and describe the odds of each phenotype for their offspring: Sperm: Eggs: Brown w/ pink eyes: _______ Brown w/ blue eyes: _______ White w/ pink eyes: _______ White w/ blue eyes: _______ Children inherit traits from their biological parents, because traits are encoded in the DNA that they receive from the sperm and egg. Describe the process that will cause these traits to be expressed in the newborn baby. Humans, like other animals, eat food to acquire energy, attain the required molecules to build and repair tissues, etc. Describe how you transform the energy from the salad you ate for lunch into a form of energy that your cells can use for life functions such as growth and development. Identify the process that transforms the energy in plants into energy that you can use for life functions Identify the molecule that contains energy in plants and the molecule that contains the energy that you can use Many plant products can be used to make biofuels, like ethanol, that are added to gasoline (a fossil fuel). Describe two similarities and differences between cellular respiration in humans and the burning of fossil fuels, like gasoline. ____ COE: “Planning a School Garden #4” ____ COE: “Columbia White Tailed Deer #3”