* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mutations Notes - Mr. Coleman`s Biology
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
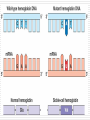
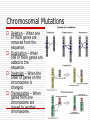
Mutations Notes Mutation A change in a nucleotide. Usually has a negative affect on an organism, but occasionally can have a positive effect, leading to the organism being better suited to its environment (adaptation). Mutation (cont.) Mutations can happen in somatic (body) cells or in gametes (sex cells). Only mutations in gametes can be inherited. Mutagen Factors that cause mutations. Mutagens can be chemical, radiation, high temperature, X-Rays, or UV light. 3 Types of Mutation Point Mutation: A change in a single nucleotide. Frameshift Mutation: The addition or deletion of a nucleotide or group of nucleotides. Chromosomal Mutation: A change in an entire gene or section of a chromosome. Point Mutations There are 3 types of point mutations, Missense, Nonsense and Silent. Missense mutations are mutations that cause a change in one amino acid. Nonsense mutations cause a premature stop codon to appear in the DNA sequence. Silent mutations have a change in the DNA sequence but no change in the amino acid sequence. Frameshift Mutations Insertion – when one or more nucleotides are added to the sequence, this changes all of the amino acids following the mutation Frameshift Mutation (cont.) Deletion - when one or more nucleotides are removed from the sequence, this changes all of the amino acids following the mutation Chromosomal Mutations Deletion – When one or more genes are removed from the sequence. Duplication – When one or more genes are added to the sequence. Inversion – When the order of genes on the chromosome is changed. Translocation – When genes from one chromosome are moved to another chromosome.