* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download membranes
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
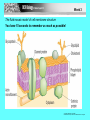
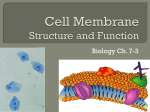
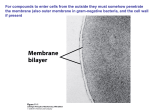
Week 3 • State that plasma (cell surface) membranes are partially permeable barriers. • Outline the roles of membranes within cells and at the surface of cells. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original What are the functions of cell membranes? What are the functions of cell membranes? • Separate cell contents from the external environment • Separating cell components from cytoplasm • Cell recognition and signalling • Holding the components of some metabolic pathways in place • Regulating the transport of materials in and out of cells Cell membranes are made of phospholipids. What is a phospholipid?! • Phospholipids are made from triglycerides or fats • Remember back to GCSE: • Fats are digested to fatty acids and glycerol, therefore that is what they must be made from. Structure of Glycerol and Triglyceride • Fatty acid chains are joined to glycerol by “Condensation Reactions” • These result in the formation of “Ester Bonds” • We will cover this later in the course! • Don’t panic Phospholipids • In a phospholipid one of the three fatty acids in a triglyceride is replaced by a phosphate group • See page 16 in your text book In a phospholipid molecule the phosphate head is attracted to water molecules (Hydrophilic) The fatty acid tail is repelled by water molecules (Hydrophobic) • If phospholipid molecules are put into water they interact with the water molecules to produce a single layer orientated as in the diagram Week 3 A phospholipid bilayer produced by mixing phospholipid into water Hydrophilic Heads attracted to the water molecules Hydrophobic Tails repelled by water molecules, so tucked inside © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 3 • Describe the fluid mosaic model of membrane structure. • Describe the roles of the components of the cell membrane, including phospholipids, cholesterol, glycolipids, proteins and glycoproteins. • Outline the effects of changing temperature on membrane structure and permeability. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Week 3 The fluid mosaic model of cell membrane structure You have 15 seconds to remember as much as possible! © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original Homework! • Find animations of cell membrane structure and function on the internet to help you to understand and remember the components of the cell membrane! Week 3 • Explain the term ‘cell signalling’. • Explain the role of membrane-bound receptors as sites where hormones and drugs can bind. © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 This document may have been altered from the original